* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 10 Monday February 9
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Nanogenerator wikipedia , lookup
Electric battery wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Rechargeable battery wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
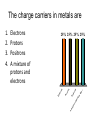
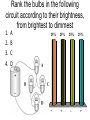
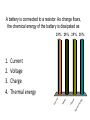
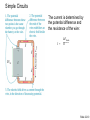
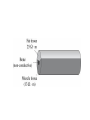
Lecture 9: Currents Friday—February 6 Batteries and EMF Lecture 10 Monday February 9 Properties of a Current Slide 22-5 Reading Quiz 1. The charge carriers in metals are A. electrons B. positrons C. protons D. a mix of protons and electrons Slide 22-2 The charge carriers in metals are A m ix t ur eo ... nd sa fp ro to n Po sit ro n Pr ot on s s 25% 25% 25% 25% s Electrons Protons Positrons A mixture of protons and electrons El ec tr on 1. 2. 3. 4. Rank the bulbs in the following circuit according to their brightness, from brightest to dimmest 25% 25% D 25% C 25% B A B C D A 1. 2. 3. 4. Problems due Monday • • • • • Problems: 22: CQ6, 1, 2, 6, 11 CQ6: ranking currents using sum in = sum out 1: I =ΔQ/Δt in coulombs and electrons 6: I =ΔQ/Δt lightning strike 11: sum in = sum out QUIZ #4 • In a typical lightning stroke, 2.5 C flows from a cloud to ground in 0.20 ms. What is the current in the strike? Circuits • Current needs a complete circuit to flow. • What makes the current flow around the circuit? We know energy is being lost, for example as heat and light in a light bulb. • What is flowing? – Electrons in metals – Average velocity very low because so many – Collisions with ions cause energy loss so velocity on the average is constant even though E field is always accelerating the electrons. A battery is connected to a resistor. As charge flows, the chemical energy of the battery is dissipated as 25% 25% 25% 25% en er gy ge er m al Th C ha r e ol ta g V ur re nt Current Voltage Charge Thermal energy C 1. 2. 3. 4. Batteries The potential difference between the terminals of a battery, often called the terminal voltage, is the battery’s emf. ∆Vbat = W chem ____ q= Slide 22-9 Simple Circuits The current is determined by the potential difference and the resistance of the wire: I = ∆Vchem _____ R Slide 22-10 Resistivity The resistance of a wire depends on its dimensions and the resistivity of its material: Slide 22-11 Measuring Body Fat The resistivity of the body is a good measure of its overall composition. A measure of the resistance of the upper arm is a good way to estimate the percent fat in a person’s body. Let’s model a person’s upper arm as a cylinder of diameter 8.0 cm and length 20 cm. We can model the composition of the arm by assuming that the muscle, far, and nonconductive portions (the bone) form simple regions. This simple model actually works quite well. For a typical adult, the bone has a cross-sectional area of 1.0 cm2; to a good approximation, the balance of the arm is fatty tissue or muscle. A. Assume that the arm has 30% fat and 70% muscle. What is the resistance of the arm? B. Now, assume that the arm has only 10% muscle. What is the resistance now? The measurement of the resistance of the arm is made by applying a voltage and measuring a current. Too much current can be uncomfortable and, as we will see, can be dangerous. Suppose we wish to limit the current to 1.0 mA. For each of the above cases, what is the maximum voltage that could be employed? Slide 22-14 Wednesday • 22: 5-6 Ohm’s Law and Power Wednesday’s Homework • 22: 13, 14, 16, 17, 18, 19, 21, 27, 40, 41, WB 22: 5-7