* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cold War
Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Iron Curtain wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of the Winter War wikipedia , lookup
Ursula Kuczynski wikipedia , lookup
Propaganda in the Soviet Union wikipedia , lookup
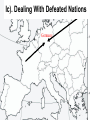
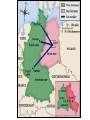
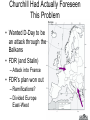
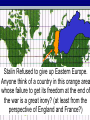
Basic Themes of Chapter 30 • The Cold War (1945 to 1991) – Polarization of the world into American and Soviet ‘camps’ – Nuclear weapons gave the struggle for world dominance a new element • Decolonization – Underdeveloped countries throw of old European masters – Struggle to gain independence – These countries get caught in the middle of the Cold War struggle Basic Themes of Chapter 30 (continued) • For Western Europe, the Cold War has Two Phases – 1st Phase 1950s and early 1960s • a great economic recovery and remarkable political stability in Western Europe – 2nd Phase late 1960s and early 1970s • Economic progress stagnates damaging social and political unity • Cold War turns to its hottest phase I. Picking Up the Pieces After WWII 1a) Nuremberg War Tribunal •Interesting International Question Here…. •Why was this city chosen? 1b) Zionism • What is the greatest asset of the Zionists in 1946? • What is their greatest obstacle? Ic). Dealing With Defeated Nations Germany • Germany and Japan were occupied – Specific breakup of Germany – Japan flag issue Berlin 1d) The United Nations General Assembly (all members…1 vote each) Security Council (Veto Power) China, France, England, USSR, U.S. II. U.S. versus the Soviet Union I don’t trust this commie bastard! ! How did the Two New Super Powers Feel About Each Other??? “Howdy, Ruski!” Elbe River Давай оторвёмся , Yankee! Следи за базаро м! Why didn’t the U.S. and the U.S.S.R. get along? 1. Superpowers (+ atomic bomb) 2. Race for ‘spheres of influence’ in the world a. What does that mean? b. Immediate hotspot- Eastern Europe c. Why were so many countries up for grabs? 3. Anger over WWIIa. Why was Stalin angry? b. Why were the Americans angry? 4. Historical animosity (the U.S. had tried to put down the Russian Revolution) 5. Different Political Systems Race for ‘Spheres of Influence’ outside of Europe Why had the allies allowed the Soviets to develop such a strong position? • Teheran (1943) , Yalta (early 1945), and Potsdam (mid 1945) … America and Britain were not in a position of power when negotiating with Stalin • – – – Didn’t want a separate German-Soviet peace Western Allies got to Germany later The Soviets were making the central sacrifice against Hitler Stalin ended up in possession of Eastern Europe – • • “No General ever gave up at the conference table that which his men has won be blood on the battlefield” American eagerness to ‘bring the boys home’ at the end of the war. Justification for doing so the atom bomb. Churchill Had Actually Foreseen This Problem • Wanted D-Day to be an attack through the Balkans • FDR (and Stalin) – Attack into France • FDR’s plan won out – Ramifications? – Divided Europe East-West III. Increasing Tension Stalin Refused to give up Eastern Europe. Anyone think of a country in this orange area whose failure to get its freedom at the end of the war is a great irony? (at least from the perspective of England and France?) Stalin’s Attempts to Institute Friendly Regimes in Eastern Europe Were Particularly Brutal in One Country • Can you guess? • Czechoslovakia – Why so brutal there? ? The Iron Curtain From Stettin in the Balkans, to Trieste in the Adriatic, an iron curtain has descended across the Continent. Behind that line lies the ancient capitals of Central and Eastern Europe. - Sir Winston Churchill, 1946 American Anti-Isolationism • Britain has abandoned its role as global policeman • U.S. steps in • U.S. will increasingly become an imperialist-type power – Example • directly after WWII, U.S. argues that France should give up Vietnam since their influence hasn’t brought any gains to the Vietnamese people • A mere ten Years Later, when France agrees to leave Vietnam, U.S. policy has shifted so greatly that the U.S. enters Vietnam to prevent a communist ‘takeover’ of the country Were American fears justified? • Yes… – There were growing communist parties in western Europe • Soviet Union had a shiny glow for many after defeating Hitler – Communism advocates worldwide revolution – Communism seeks to take away private property • Wealthy in Europe and the U.S. threatened – The Soviet Union is a surviving Totalitarian state, which means • Censorship, propaganda, secret police, etc. • Soviets get the A-Bomb in 1949 • After Yugoslavia bucked being a Stalinist puppet, Stalin cracked down and forced a very strict doctrine on other Communist govs • No… – Soviets had been CRUSHED in WWII – Economy is MUCH weaker than the United States’ – Much of the ‘aggressive’ action of the Soviet Union can be traced to their paranoia after having been invaded time and again by other nations IV. First Clashes The Truman Doctrine • Containment of Communism!!! • A Response to Stalin’s Efforts to Pull Turkey, Iran, and Greece into the Soviet ‘orbit’ The Marshall Plan Why give $$$ to Europe? • Lessons learned after Treaty of Versailles • Convince countries to join America’s ‘Sphere of Influence’ – “Democratic Capitalism is the way to go!” Stalin saw ‘Containment’ as ‘Encirclement’ Damn you, Truman. You are really pissing me off!!! Hee, hee, hee, hee, hee, hee, hee, hee… Berlin Blockade & Airlift (1948-49) •Stalin Figured ‘if you are going to contain me, I’ll contain you!’ •closed the roads into West Berlin •Another reason for the Berlin blockade •West Berlin presented a problem for Totalitarian style gov. in Eastern Europe •Do you see why? • The ‘Berlin Airlift’ Broke Stalin’s Blockade • As tensions rose, NATO was formed. The Warsaw Pact was formed in response. • 1 plane per minute, 24 hours a day, for 9 months… • In the end, Stalin removed his blockade… the Western Allies could fly to Berlin… – To understand why Stalin gave in, keep in mind that there is a battle in progress for the hearts and minds of the decolonizing nations – Any bad press hurts – Trying to blockade and having these efforts fail is humiliating • Berlin will remain a flashpoint Western Bloc= NATO Eastern Bloc= Warsaw Pact So why is it called a “Cold War?” • Brinksmanship – Moving towards war between the U.S. and Soviet War (without going across the ‘brink’) in an attempt to make the other guy ‘blink’ – Berlin Airlift – Cuban Missile Crisis • Proxy Wars – Indirect fights between the superpowers through third countries – Korea – Vietnam – Afghanistan – Many, many other smaller ones • Arms Race – Flex your muscles/weapons without having to use them – ICBMs • Spies, etc. – Keep one step ahead of the enemy Slightly More Formal Definition of the Cold War An attempt by the Soviet Union and the United States to spread their respective economic, political, and social models to the rest of the globe without resorting to direct nuclear conflict. The Importance of 1949 • Soviets conducted a successful test of the atom bomb – Rosenbergs • China ‘falls’ to Communism – Mao Zedong – Failure of the Truman Doctrine – America becomes determined to put ‘teeth’ into its defenses • Red Scare Hansen Name ____________________ AP Euro Period _________ Intro to the Cold War (Note-Taking Guide) ► Basic Themes of Chapter 30 • The Cold War (1945 to 1991) – Polarization of the world into _________________ ‘camps’ – _______________gave the struggle for world dominance a new element • Decolonization – ______________________ threw of old European masters – Struggle to gain independence – These countries get ________________________ of the Cold War struggle • For Western Europe, the Cold War has Two Phases – 1st Phase 1950s and early 1960s • a _____________________ and remarkable _______________ in Western Europe – 2nd Phase late 1960s and early 1970s • ________________________________ damaging social and political unity • Cold War turns to its ______________ ► Picking Up the Pieces After WWI • Nuremberg War Tribunal • Zionism • Dealing with Defeated Nations • The United Nations – Security Council – General Assembly ► U.S. Versus the Soviet Union • Why didn’t the U.S. and the U.S.S.R. get along? • __________________ (+ atomic bomb) • Race for ‘_________________________’ in the world • What does that mean? _______________________ _________________________________________ • Immediate hotspot- _____________________ • Why were so many countries up for grabs? _______ __________________________________________ • Anger over WWII• Why was Stalin angry? _______________________ • Why were the Americans angry? _______________ • Historical animosity (the U.S. had tried to put down the _____________________) • Different ____________________________ • Why had the allies allowed the Soviets to develop such a strong position? • Teheran (1943) , Yalta (early 1945), and Potsdam (mid 1945) … • America and Britain were ____________________________ when negotiating with Stalin • Didn’t want a separate ___________ peace • Western Allies ___________________________ • The Soviets were making the _______________ against Hitler • Stalin ended up _______________ Eastern Europe • Stalin- “No General ever gave up _____________________ that which his men hav won ________________________” • American eagerness to ‘____________________’ at the end of the war. Justification for doing so ___ ____________________. • Churchill Had Actually Foreseen This Problem • Wanted D-Day to be an attack ___________________________ • FDR (and Stalin) Wanted __________________ • FDR’s plan won out • Ramifications? ► III. Increasing Tension • Stalin Refused to give up _______________. Anyone think of a country in this orange area whose failure to get its freedom at the end of the war is a great irony? (at least from the perspective of _______________________________-?) – • • • – – – • _____________________________ Stalin’s Attempts to Institute Friendly Regimes in Eastern Europe Were Particularly Brutal in One Country – Can you guess? – _______________________________ • Why so brutal there? _______________________ _________________________________________ The Iron Curtain- ___________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ American Anti-Isolationism Britain has abandoned its role as global policeman ______________________ U.S. will increasingly become an ________________ power • Example – directly after WWII, U.S. argued that France should ____________________ since their influence hasn’t brought any gains to the Vietnamese people – A mere ___________________, when France agreed to leave Vietnam, U.S. policy has shifted so greatly that the U.S. _________________________________ _________________________________ ► IV. First Clashes • The Truman Doctrine • ___________________ of Communism!!! • A Response to Stalin’s Efforts to Pull _________________ ___________________________ into the Soviet ‘orbit’ • The Marshal Plan- __________________________________ ________________________________________________ • • Were American Fears Justified? – Yes… • • • • • – No… • • • There __________________________ in western Europe Soviet Union had ______________________ for many after defeating Hitler Communism advocates ____________________ Communism seeks to take away private property – _________________________ threatened The Soviet Union is a surviving Totalitarian state, which means – Censorship, _________, secret police, etc. – Soviets ________________in 1949 – After ____________ bucked being a Stalinist puppet, Stalin ______________ ________________________ on other Communist govs Soviets had been __________________________ Economy is _______________than the United States’ Much of the ‘aggressive’ action of the Soviet Union can be ________________________________ after having been invaded time and again by other nations • Why Give $ to Europe? • Lessons learned after ____________ ______________________ • Convince countries to join America’s ‘Sphere of Influence’ • “___________________ is the way to go!” • Stalin saw ‘Containment’ as ‘_________________’ Berlin Blockade and Airlift __________ • Stalin Figured ‘if you are going to contain me, ____________!’ • closed the roads ____________________ • Another reason for the Berlin blockade • West Berlin presented a problem for _____________ _______________. in Eastern Europe • Do you see why? - ____________________________ ___________________________________________ • The ‘Berlin Airlift’ Broke Stalin’s Blockade • As tensions rose, _____________________. The ________________ was formed in response. • 1 plane per minute, 24 hours a day, for 9 months… • In the end, Stalin removed his blockade… the Western Allies could fly to Berlin… • To understand why Stalin gave in, keep in mind that there is a battle in progress for the ______________ __________________________________________ • Any bad press hurts • Trying to blockade and having these efforts _______ is __________________ • Berlin will remain a flashpoint Western Bloc= NATO Eastern Bloc = Warsaw Pact • • • So why is it called a ‘Cold War’? – Brinksmanship • Moving towards war between the U.S. and Soviet War (without going across the ‘brink’) in an attempt to __________________________________ • __________________________ • ________________Missile Crisis – Proxy Wars • ____________________ between the superpowers through _____________________ • Korea • _______________ • _______________ • Many, many other smaller ones – Arms Race • Flex your muscles/weapons without having to use them • _____________ – Spies, etc. • Keep one step ahead of the enemy Slightly More Formal Definition of the Cold War – An attempt by the Soviet Union and the United States to spread their respective _________________________ ______________________ to the rest of the globe without resorting to direct nuclear conflict. The Importance of 1949 – – • Soviets conducted a successful test of the atom bomb • __________________ China ‘falls’ to Communism • _____________________ • ________________________ Truman Doctrine • America becomes determined _____________________ defenses ____________________