* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulatory System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
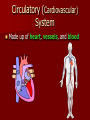
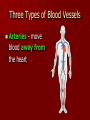
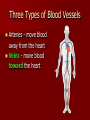
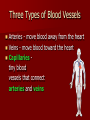
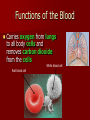
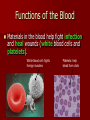
Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System Cardio = “heart” Vascular = “vessels” Circulatory (Cardiovascular) System Made up of heart, vessels, and blood Three Types of Blood Vessels Arteries - move blood away from the heart Three Types of Blood Vessels Arteries - move blood away from the heart Veins - move blood toward the heart Three Types of Blood Vessels Arteries - move blood away from the heart Veins - move blood toward the heart Capillaries tiny blood vessels that connect arteries and veins Functions of the Blood Carries oxygen from lungs to all body cells and removes carbon dioxide from the cells Red blood cell White blood cell Functions of the Blood Red blood cells – contain hemoglobin which combines with oxygen. These cells deliver oxygen to the body. Their disc shape helps them squeeze through vessels. They wear out and are replaced every four months. New red blood cells are produced in the bone marrow. Red blood cell Functions of the Blood Carries waste products of cell activity to the kidneys to be removed from the body Functions of the Blood Transports nutrients from the digestive system to body cells Functions of the Blood Materials in the blood help fight infection and heal wounds (white blood cells and platelets). White blood cell: fights foreign invaders Platelets: help blood form clots Functions of the Blood White blood cells – are generally larger than red blood cells. They can move out of your blood through the capillary walls into tissue fluid and lymph. They then travel around fighting disease. The white blood cells last 13–20 days, after which they are destroyed by the lymphatic system. White blood cell: fights foreign invaders Functions of the Blood Platelets – are irregularly-shaped, colorless bodies that wear out within 5–10 days Their sticky surface lets them, along with calcium, vitamin K, and fibrinogen, form clots to stop bleeding. Platelets: help blood form clots Which two substances does the blood transport away from body cells? 1. 2. 3. 4. Oxygen & carbon dioxide Carbon dioxide & waste Nutrients & waste Oxygen & nutrients What parts of the blood help fight off disease and heal injuries? 1. 2. 3. 4. White blood cells & platelets Red blood cells & platelets White blood cells & red blood cells White blood cells & plasma Which is not a function of the circulatory system? 1. 2. 3. 4. Carry nutrients & oxygen to body cells Carry carbon dioxide & waste away from body cells Attack disease-causing bacteria Produce chemicals that control body processes