* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download variation/spread
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
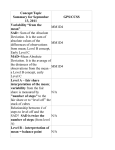
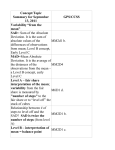
Some Measures of the Spread (Variability) of a Data Set The range of a data set is equal to the difference between the largest measurement and the smallest measurement in the set. The sample variance for a sample containing n measurements is equal to the sum of the squared distances from the mean divided by (n – 1). In symbols, s2 represents the sample variance. s 2 "(x ! x ) = 2 n !1 The sample standard deviation, s, is the positive square root of the sample variance, s2. s = s2 The population variance is denoted by σ2. The calculation is similar to that of the sample variance except we divide by N, the number of measurements in the population. ! 2 "(X ! µ ) = 2 N The population standard deviation is denoted by σ. It is the positive square root of the population variance. ! = !2 The mean absolute deviation (MAD) offers another way to describe the variation in data. The MAD is the mean absolute distance each value is from the mean. To calculate the MAD, determine the absolute (non-negative) difference of each data value compared to the mean of the data set. Determine the sum of these absolute differences. Divide the sum by the number of data values. " x!x MAD = n Interpretations of Variability • Measures of variability indicate whether the values in a distribution cluster closely about the center or spread out in one or both directions from the center. • A measure of variability that is relatively small in terms of the unit of measurement for the data set indicates that the data cluster more closely about the mean; a larger value for the variability indicates that the data are more spread out. • The standard deviation can be thought of as representing the average (mean) distance the data value deviate from the mean of the data. This can be seen in the calculation formula. Sources of Variability • • • • • Measurement Variability stems from the fact that repeated measurements of the same individual vary. Natural Variability describes the variability inherent in nature. Induced Variability describes variation that is intentionally introduced, such as for an experiment in which there is a treatment group and a control group. The intent of an experiment is often to induce variability in one characteristic hold other variation in check. Sampling Variability refers to variability that is to be expected from sample to sample. Chance Variability is the variability resulting from the randomization used to generate a data set.