* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download International Flow of Financial Resources
Survey
Document related concepts
Transition economy wikipedia , lookup
Balance of payments wikipedia , lookup
Global financial system wikipedia , lookup
Economic growth wikipedia , lookup
Transformation in economics wikipedia , lookup
Post–World War II economic expansion wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
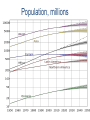
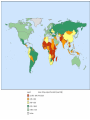
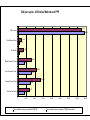
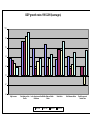
MIBE The economics of emerging economies The role of Finance in economic development and the emerging economies Gianni Vaggi University of Pavia April, 2014 MIBE The economics of emerging economies The role of Finance in economic development and the emerging economies Finance 1-1 Different financial flows and the Balance of Payments Introduction: The rich and the poor Countries with more than 100 million people, 2011 (World Development Indicators 2013) China 1.344 India 1.241 United States Indonesia Brazil Pakistan Nigeria Bangladesh 311 242 196 176 162 150 Russian Federation 143 Japan 127 Mexico 114 Population Density Population, millions World Bank income groups GNI per capita 2012, WDI 2014 Low $ 1,035 or less Lower middle $ 1,026 – 4,085 Upper middle $ 4,085 – 12,616 High $ 12,616 or more GNI per capita 2010 Atlas Method and PPP 37,317 High Income 38,910 2,148 Sub-Saharan Africa 1,176 3,124 South Asia 1,176 8,068 Middle East & N. Africa 3,874 10,926 Latin America & Carib. 7,733 13,396 Europe & Central Asia 7,272 6,657 East Asia & Pacific 3,696 0 5,000 10,000 Gross National Income per capita 2010 [$] PPP 15,000 20,000 25,000 30,000 Gross national income per capita 2010 [$] Atlas method 35,000 40,000 Part 1 Economic growth and capital accumulation GDP growth rates 1965-2010(averages) 10 8 6 4 2 0 -2 -4 High Income East Asia and the Pacific Latin America and the Middle East and North Caribbean Africa 1965-1980 1980-1990 1990-2000 South Asia 2000-2010 Sub-Saharan Africa East Europe and Central Asia -10 -20 -30 2011 2009 2007 2005 2003 2001 1999 1997 1995 1993 1991 1989 1987 1985 1983 1981 1979 1977 1975 1973 1971 1969 1967 1965 1963 1961 GDP Growth rates 30 20 China 10 Korea, Rep. Mexico 0 Brazil South Africa Vietnam Malaysia Gross fixed capital formation (% of GDP) 50 45 BRA 40 35 RUS 30 IND 25 CHN 20 15 SAF 10 EAS 5 0 1960 1965 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 BRICS Capital accumulation The engine for growth-1 The role of the governments: – Policies ensuring macroeconomic stability – Government and financial markets – Policies promoting equality(education, land reform) The engine for growth-2 •The profit-saving-investment nexus •Industrial policies (promoting accumulation of physical and human capital) •activities (altering the allocation of resources) Export promotion-SEZ Part 2 What if a country does not have its own capital to accumulate? Financing Development Private Public-ODA •FDIs •Bilateral •Workers’ remittances •Portfolio Investment Non debt •Multilateral •Stocks •Bonds •Loans •NGOs •Technical assistance Debt •Concessional loans •Grants •Debt cancellation Total net resource flows to developing countries, by type of flow, 1990-2016f (Billions of Dollars) Short Memo about: 1. AID THROUGH NGOS 2. OFFICIAL DEVELOPMENT ASSISTANCE 3. PORTFOLIO INVESTMENTS 4. FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTEMENTS 5. REMITTANCES 1-NGOs Represent specific local and international interest groups concerning • Emergency relief • Child health • Women’s rights • Alleviating poverty • Increasing food production NGOs; PROs and Cons PROs • Less constrained by political imperatives • Strength at local levels Cons • Small projects • Short-medium term projects 2-Foreign Aid, ODA DEF. Any flow of capital to LDCs • Its objective should be non commercial from the point of view of the donor • It should be characterized by concessional terms (i.e. i and repayment period for borrowed capital less stringent then commercial terms) Aid can be tied • By SOURCE (loans or grants have to be spent on the purchase of donor-country goods and service) • By PROJECT funds can only be used for a specific project Aid Allocation Rarely determined by relative needs of DCs. Most bilateral aid seems unrelated to development priorities and are based largely on POLITICAL or ECONOMICALLY RATIONAL considerations. 3-Portfolio Investments • Foreign Portfolio Investment stocks bonds in emerging credit or equity market • 1/3 of overall net resource flows to DCs • INVESTOR: investing in emerging countries permits to – Increase returns – Diversify risk • RECIPIENT: portfolio flows as vehicle for raising capital for domestic firms LARGE but VOLATILE … May represent a destabilizing force for • Financial markets • Overall economy (i.e. Mexico crisis, hot money)