* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plates Move
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
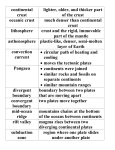
Plates Move Good Morning! Take out your homework, have it on your desk so we can come around and check it in. Get all your materials then, put bags in the back. Pick up a green sheet of paper off the front table. Work on the Day 5 activity. You are rating your learning and answering three questions. If you were absent yesterday, come in during Ac. Lab for an alternative assignment. Question 1 Did both trials result in the movement of water? Why or why not? Only trial 1, in which the warm water was placed in the vial, resulted in the movement of water (the warm water rose upward and outward). There was no movement of water in Trial 2. This is because warm water rises and cold water sinks. In Trial 2, the warm water was already on top and the cold water was at the bottom. Question 2 What do you think is necessary for a convection current to form? It is necessary for warm water to be at the bottom (heated from below) and the cooler water to be sitting above it. It is the rising of warm water and its resulting displacement of the cool water that results in the formation of a convection current. Question 3 Compare the results of your two trials. When warm water and cold water are mixed, what happens to: A. The warm water? It rises to the top B. The cold water? It sinks to the bottom. Question 5 Imagine the hotter magma is lying beneath an area of cooler magma deep in the mantle. What do you predict will happen? Why do you think this? The hotter magma would rise and the cooler magma would sink. This would results in a current. In this activity, water was used to model magma, so what happened to the water, would happen to the magma. What do scientists believe causes plates to move? Convection currents within the earth’s mantle caused by differences in temperatures of magma within the mantle. Schedule Plate Movement Notes 15-20 minutes ABCD Card Review 10 Minutes Comic Strip Activity 30-40 Minutes Exit ticket 5-10 Minutes Plates move Plates are what move They move what is on top of them Crust is on top of the plates Continental Crust- The crust that makes up continents/land Oceanic Crust- The crust that makes up the oceans Divergent Boundary Plates move apart Most are found in the ocean Mid-ocean ridges are found where this happens In the ocean they move apart and riff valleys form This is how continents split apart New crust is formed Process 1. Hot material rises from the mantle 2. The heat causes the crust to bulge upward 3. The crust cracks, and a riff valley is formed 4. Magma rises, the continent splits apart Transform Boundaries Plates move past each other in opposite directions Crust is not formed or destroyed Occur mostly at the sea floor but can form on land too San Andreas Fault Convergent Boundary Plates push together 3 different types Continental-continental collision Oceanic-oceanic collision Oceanic- continental collision Crust is destroyed or folded Continental- Continental Collisions Two continental plates collide Each plate is the same density No plates can sink, so it has to collide Mountains are made when the two plates run into one another EX: Rocky Mts. Oceanic- Continental Collision An piece of oceanic crust runs into a piece of continental crust Oceanic crust sinks Deep-ocean trenches Costal mountains EX: Andes Mts. Oceanic-Oceanic Collision 2 plates run into one another The older plate will sink under the newer plate Subduction- When one plate sinks beneath another The plate moves into earth, and melts Forms Deep ocean trenches- deep canyons on the ocean floor Island arcs- volcanic islands EX: Hawaii Hot Spot Heated rock rise in plumes, are thin columns from the mantle The magma eventually hardens The magma could have risen so high that it peaks out of the water More islands will form in an arc, this shows how the plate is moving EX: Hawaii Schedule Plate Movement Notes 15-20 minutes ABCD Card Review 10 Minutes Comic Strip Activity 30-40 Minutes Exit ticket 5-10 Minutes Review In what direction do plates move in convergent boundaries? A. Towards each other B. Away from each other C. Depends on stress D. Past each other Review In what direction do plates move in transform boundaries A. Towards each other B. Away from each other C. Depends on stress D. Past each other Review In what direction do plates move in divergent boundaries A. Towards each other B. Away from each other C. Depends on stress D. Past each other Review What feature occurs at a divergent boundry A. Island arc B. Riff valley C. Mountains D. surface fault Review The Andes Mountains in South America occur at what type of boundary? A. Continent-continent convergent boundary B. Continent-oceanic convergent boundary C. Divergent boundary D. Transform boundary Schedule Plate Movement Notes 15-20 minutes ABCD Card Review 10 Minutes Comic Strip Activity 30-40 Minutes Exit ticket 5-10 Minutes Schedule Plate Movement Notes 15-20 minutes ABCD Card Review 10 Minutes Comic Strip Activity 30-40 Minutes Exit ticket 5-10 Minutes