* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Polymorphic II Kick-off meeting
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
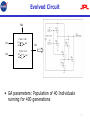
Taking evolutionary circuit design from experimentation to implementation: some useful techniques and a silicon demonstration Adrian Stoica Ricardo S. Zebulum Xin Guo* Didier Keymeulen M. I. Ferguson Vu Duong Outline • Multi-function NAND/NOR circuit controlled by the power supply voltage (Vdd); – Programmable Logic Cells. • New methods to ensure that circuits produced by evolution can be fabricated; • The circuit was fabricated in a 0.5-micron CMOS technology and silicon tests showed good correspondence with the simulations. 2 Methods used in evolutionary designfor-fabrication • Need for comprehensive testing to ensure that evolved solutions cover the intended operational space; • Opposing to conventional design, no assumptions on the circuits’ performance outside the points tested during evolution can be reliably made. 3 Methods used in evolutionary design-forfabrication • Candidate logic circuits were tested in transient analysis for all possible transitions of combinations of input levels; • For example, a circuit may respond well as an AND gate to input combinations of levels 0-0, 0-1, 1-0, 1-1. However, it may have a long switching time when inputs 1-1 following 0-0 - and not 1-0 as above, which is not tested in the simple scheme; • Increased transient analysis: seven input configuration cases opposed to four. 4 Methods used in evolutionary design-forfabrication • • • Loading problem: preliminary experiments showed that evolved circuits were not able to drive similar circuits; Problem: Input/Output impedance of circuit to be evolved is not known in advance; Use of domain knowledge may help: in the case of logic gates we constrain the circuit inputs to connect only to transistor gate terminals, opposed to source or drain: increase input resistive impedance. 5 Methods used in evolutionary design-forfabrication • Timescale Problem: preliminary evolved logic gates changed their behavior over a "frequency range“, i.e. different responses when tested with slow/DC signals and faster input changing signals; • Testing in micro-seconds timescale → Transient solutions; • Testing in seconds timescale → Slow gates; • Solution: extend the transient analysis duration to avoid transient solutions while keeping the transient analysis step small enough to assess the gate speed. 6 Evolved Circuit Vdd In1 If Vdd = 1.8V In1 Out In2 In2 If Vdd = 3.3V In1 Out In2 Out • GA parameters: Population of 40 Individuals running for 400 generations 7 Circuit Layout Layout of the multi-functional logic gate. Chip was manufactured using HP 0.5u technology. 8 Circuit Response NAND function (VDD = 3.3V) Test Configuration In2(V) In2 Out(V) Out 2 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 30 2.7 2.4 2.1 1.8 1.5 1.2 0.9 0.6 0.3 0 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 Output(V) Out 0 0 Time(s) In2 CLoad 1 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2 Time(s) 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 3 2.7 2.4 2.1 1.8 1.5 1.2 0.9 0.6 0.3 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 2 0 1 Out 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2 Time(s) 2 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 20 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 0 2 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 0 In2 CLoad = 40p NOR function (VDD = 1.8V) 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 In1 Test Configuration 2 Time(s) In2 CLoad 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 1 1 0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 1 1 0 0 2 Time(s) 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 0 In2 CLoad= 40p 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 In1 Inverted Output(V) In1(V) In2(V) In2 In1 1 2 Time(s) In1 1 In1 0 Inverted Output(V) In1(V) In1 2 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 2 2 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 1 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 Out 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 Time(s) 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2 1 0 0 0 Time(s) Simulation Silicon 9 Remarks • Stable for 10% variations of Vdd and for temperatures –20oC and 200oC; • Evolution obtained a creative novel topology more compact than what has been achieved by multiplexing a NAND and a NOR gate (conventional solution using a standard digital library with external voltage control). • No conventional design is available with the logic function controlled by Vdd; • Design a 6-transistor NAND/NOR gate controlled by Vdd is a complex task for a human designer; • To be published in the IEE computing/digital techniques journal on evolvable hardware. To be published in 2004. Andy Tyrrell (editor), London, England. 10