* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download perio int
Special needs dentistry wikipedia , lookup
Dental implant wikipedia , lookup
Endodontic therapy wikipedia , lookup
Crown (dentistry) wikipedia , lookup
Focal infection theory wikipedia , lookup
Remineralisation of teeth wikipedia , lookup
Calculus (dental) wikipedia , lookup
Tooth whitening wikipedia , lookup
Impacted wisdom teeth wikipedia , lookup
Dental anatomy wikipedia , lookup
Dental avulsion wikipedia , lookup
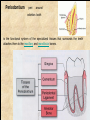
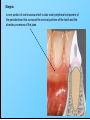
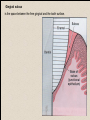
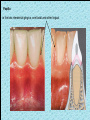
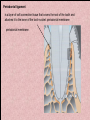
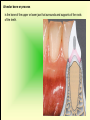
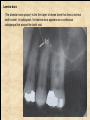
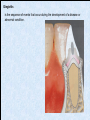
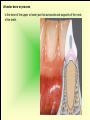
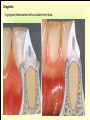
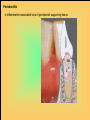
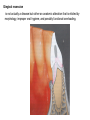
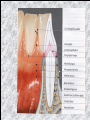
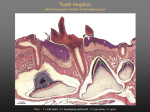
The historical background of periodontology Hippocrates of Cos (Greek 460-377 BC) discussed the function and eruption of teeth and the etiology of periodontal diseases. He believed that inflammation of the gingival could be caused by accumulations of calculus. Abu'l-QAsim Arabic science (936-1013) discussed the function and eruption of teeth and the etiology of periodontal diseases. He believed that inflammation of the gingival could be caused by accumulations of calculus. Anton van Leeuwenhoek (Holland, 1632-1723) first described oral bacterial flora, and his drawings offered a reasonably good presentation of oral spirochetes, and bacilli. Pierre Fauchard described in detail his periodontal instruments and the scaling technique. Levi Spear Parmly (New Orleans dentist 1790-1859) who is considered the fathe of oral hygiene and inventor of dental floss. Salomon Robicsek (Hungary 1845-1928) developed a surgical technique of a scalloped, continuous gingivactomy excision, exposing the marginal bone for subsequent curettage and remodeling. Periodontium peri around odontos tooth is the functional system of the specialized tissues that surrounds the teeth attaches them to the maxillary and mandibular bones. Periodontology is the science to study the tooth-supporting tissues in health and disease condition. Periodontics is the branch of dentistry that deals with the disease and treatment of periodontium. Periodontist A dental specialist who limits his/her practivities to periodontics. Gingiva is one portion of oral mucosa which is also most peripheral component of the periodontium that surround the cervical portions of the tooth and the alveolar processes of the jaws. Gingival sulcus is the space between the free gingival and the tooth surface. Interdental gingiva is the portion of the gingiva that fills the area between two adjacent teeth apical to the contact area. Papilla is the two interdental gingiva, one facial and other lingual. Cementum is a thin layer of hard, mineralized tissue that covers the surface of the root. It is a specialized tissue of ectomesenchymal origin. Periodontal ligament is a layer of soft connective tissue that covers the root of the tooth and attaches it to the bone of the tooth socket. periodontal membrane periodontal membrane Alveolar bone or process is the bone of the upper or lower jaw that surrounds and supports of the roots of the teeth. Lamina dura (The alveolar bone proper) is the thin layer of dense bone that lines a normal tooth socket. In radiograph, the lamina dura appears as a continuous radiopaque line around the tooth root. Pathogenesis is the sequence of events that occur during the development of a disease or abnormal condition. Periodontal disease Those pathogenesis that affect the periodontium. There are numerous diseases that affect the periodontium, most often plaque-associated gingivitis, and periodontitis. Gingivitis is the sequence of events that occur during the development of a disease or abnormal condition. Alveolar bone or process is the bone of the upper or lower jaw that surrounds and supports of the roots of the teeth. Gingivitis is gingival inflammation without attachment loss. Periodontitis is inflammation-associated loss of periodontal supporting tissue. Gingival recession is not actually a disease but rather an anatomic alteration that is elicited by morphology, improper oral hygiene, and possibly functional overloading.