* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY School of Microelectronics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
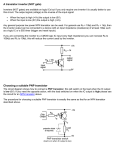
SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY School of Microelectronics Fall 2012, Dr. Guoxing Wang Homework 2 Due date: 2012/10/09 Use A4 paper to write/print your answer. Your name and student ID on the cover page. Language: English. Staple the pages. Q1: Referring to the library file (log018.l), calculate CGS and CGD of nch.1 and pch.1 in three different regions (cutoff region, linear region and saturation region) respectively, choose W/L=9u/0.18u. Q2: The circuits are shown in Fig2.1 and Fig2.2 respectively. Vx changes from 0 to 3.3V. (Hints: The Drain and Source of the transistor are exchangeable depending on the applied voltages.) Draw rough IX-VX curves of Fig2.1 and Fig2.2 respectively. Draw rough gm-VX curves of Fig2.1 and Fig2.2 respectively. Use cadence to verify the curves you drew. IX + VX M1 +1.9V + +1V Fig2.1 - IX +1.5V M2 +1.9V + + +1V - VX - Fig2.2 Q3: The circuit shown in Fig.3 is widely used as a NMOS inverter before the CMOS process came into being. Please point out the differences between the NMOS inverter and the CMOS inverter and give your explanations why the NMOS inverter is now almost completely replaced by the CMOS inverter. Designate the sizes of M1 and M2 at your will and simulate Fig.2 by Hspice. Draw the transfer characteristic curve (Vout versus Vin) of the circuit, use the curve to calculate VIH ,VOH,VOL,VIL and the noise margin of the inverter. Your simulating codes need to be attached. Calculate the rise time tr and the fall time tf of the inverter if ID is a constant . Adjust the sizes of the two transistors to get tr=tf . 3.3V M1 Vout Vin M2 50fF Fig3 Q4: As we all know, a MOSFET can work in three regions: sub-threshold region, linear region and saturation region. Calculate the transconductance (gm) of the transistor in sub-threshold region, linear region and saturation region respectively. Calculate the ratio of the transconductance (gm) and the Drain current (IDS) of the transistor in sub-threshold region, linear region and saturation region respectively and draw a rough curve to show the trend (gm/IDS versus IDS). In analog circuit design, we usually choose VGS-VTH (the overdrive voltage Vov) to be approximately 0.2V, please note what you think the reasons are. (bonus) Try your best to make sure your answers contain detailed deduction and precise explanations!!!