* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download m5zn_ca35989fc269b62
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
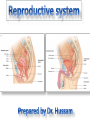
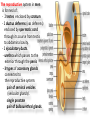
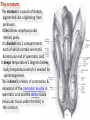
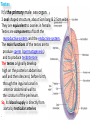
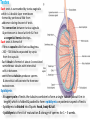
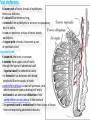
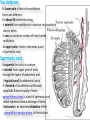
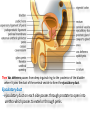
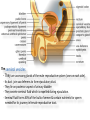
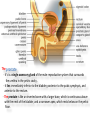
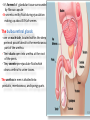
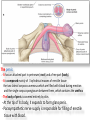
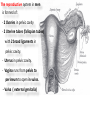
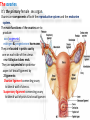
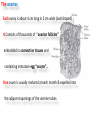
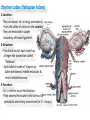
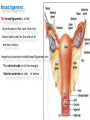
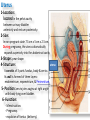
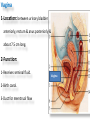
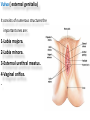
The reproductive system in men is formed of: - 2 testes enclosed by scrotum - 2 ductus deferens (vas deferens) enclosed by spermatic cord through its course from testis to abdominal cavity. - 2 ejaculatory ducts. - urethra which passes to the exterior through the penis - 3 types of accessory glands connected to the reproductive system: pair of seminal vesicles (vesicular glands). single prostate pair of bulbourethral glands. The scrotum: The scrotum is a pouch of deeply pigmented skin originating from perineum. It lies below symphysis pubis behind penis. It’s divided into 2 compartments each of which contain one testis & testicular end of spermatic cord. It keeps temperature 2 degrees below body temperature which is needed for spermatogenesis. This is done by means of contraction & relaxation of the cremaster muscle in spermatic cord and the dartos fascia (muscular tissue under the skin) in the scrotum, Testes It’s the primary male sex organ. 2 oval shaped structure, about 5cm long & 2.5cm wide. They are equivalent to ovaries in female. Testes are components of both the reproductive system and the endocrine system. The main functions of the testes are to produce sperm (spermatogenesis) and to produce testosterone The testes originally develop high on the posterior abdominal wall and then descend, before birth, through the inguinal canal in anterior abdominal wall to the scrotum of the perineum. So, its blood supply is directly from aorta by testicular arteries . Testes Each testis is surrounded by tunica vaginalis which is A double layer membrane formed by peritoneal fold from abdomen during descent of testis The connection between tunica vaginalis & peritoneum is closed at birth & if not a congenital hernia develops. . Each testis is formed of - Fibrous capsule called tunica albuginea. - 200 – 300 lobules separated by septa from the capsule. - Each lobule is formed of about 4 convoluted seminiferous tubules with interstitial cells in between. - seminiferous tubules produces sperms & interstitial cells secrete the hormone testosterone. Epididymis - At upper pole of testis the tubules combine to form a single tubule (about 6 m in length) which is folded & packed to form epididymis on posterior aspect of testis - Epididymis is divided into 3 parts head, body & tail. - Epididymis is the sit of maturation & storage of sperms for 1 – 3 weeks. Vas deferens - At lower pole of testis the tail of epididymis forms vas deferens. - It’s about 45 centimeters long. - it extends from epididymis in scrotum to ejaculatory duct in pelvis. - It runs on posterior surface of testis beside epididymis. - At upper pole of testis it becomes a part of spermatic cord. Spermatic cord - It suspends the testis in scrotum - it extends from upper pole of testis through the layers of abdominal wall ( inguinal canal) to abdominal cavity. - It’s formed of vas deferens with blood, lymphatic & nerve supply of testis - pampiniform plexus is a part of spermatic cord which represent venous drainage of testis. - Varicocele is an abnormal dilatation of the pampiniform venous plexus in the scrotum -The spermatic cord is ensheathed in three layers of tissue: from corresponding abdominal muscles. Vas deferens - At lower pole of testis the epididymis forms vas deferens. - It’s about 45 centimeters long. - it extends from epididymis in scrotum to ejaculatory duct in pelvis. - It runs on posterior surface of testis beside epididymis. - At upper pole of testis it becomes a part of spermatic cord. Spermatic cord - It suspends the testis in scrotum - it extends from upper pole of testis through the layers of abdominal wall ( inguinal canal) to abdominal cavity. - It’s formed of vas deferens with blood, lymphatic & nerve supply of testis - pampiniform plexus is a part of spermatic cord which represent venous drainage of testis. - Varicocele is an abnormal dilatation of the pampiniform venous plexus in the scrotum Then Vas deferens passes from deep inguinal ring to the posterior of the bladder where It joins the duct of the seminal vesicle to form the ejaculatory duct. Ejaculatory duct - ejaculatory duct on each side passes through prostate to open into urethra which passes to exterior through penis. The seminal vesicles - They are accessory glands of the male reproductive system (one on each side). - Its duct join vas deferens to form ejaculatory duct. - They lie on posterior aspect of urinary bladder - They secrete seminal fluid which is expelled during ejaculation. - Seminal fluid forms 60% of the bulk of semen & contain nutrients for sperm needed for its journey in female reproductive tract. The prostate - It’s is a single accessory gland of the male reproductive system that surrounds the urethra in the pelvic cavity . - It lies immediately inferior to the bladder, posterior to the pubic symphysis, and anterior to the rectum. - The prostate is like an inverted cone with a larger base, which is continuous above with the neck of the bladder, and a narrower apex, which rests below on the pelvic floor. - It’s formed of glandular tissue surrounded by fibrous capsule - It secrets a milky fluid during ejaculation making up about 30% of semen. The bulbourethral glands - one on each side, located within the deep perineal pouch lateral to the membranous part of the urethra. - Their ducts open into urethra at the root of the penis. - They secrete pre-ejaculate fluid which clears urethra fro urine traces. The urethra in men is divided into: prostatic, membranous, and spongy parts The penis . - It has an attached part in perineum (root) and a free part (body). - It is composed mainly of 3 cylindrical masses of erectile tissue the two lateral corpora cavernosa which are filled with blood during erection and the single corpus spongiosum between them, which contains the urethra. - The body of penis is covered entirely by skin. - At the tip of its body, it expands to form glans penis. - Parasympathetic nerve supply is responsible for filling of erectile tissue with blood. The reproductive system in men is formed of: - 2 Ovaries in pelvic cavity - 2 Uterine tubes (fallopian tubes) with 2 broad ligaments in pelvic cavity. - Uterus in pelvic cavity. - Vagina runs from pelvis to perineum to open in vulva. - Vulva ( external genitalia) The ovaries It’s the primary female sex organ. Ovaries are components of both the reproductive system and the endocrine system. The main functions of the ovaries are to produce: ova (oogenesis) estrogen & progesterone hormones They are located in pelvic cavity one on each side of the uterus near fallopian tubes ends. They are suspended on posterior aspect of broad ligament by 2 ligaments: Ovarian ligament connecting ovary to lateral wall of uterus. Suspensory ligament connecting ovary to lateral wall of pelvis & to broad ligament The ovaries Each ovary is about 4 cm long in 2 cm wide (oval shaped) It Consists of thousands of “ovarian follicles” embedded in connective tissues and containing immature egg “oocyte”.. One ovum is usually matured at each month & expelled into the adjacent openings of the uterine tubes. Uterine tubes (fallopian tubes) 1-Location: - They are about 10 cm long, and extend, from the sides of uterus to the ovaries - They are enclosed in upper boundary of broad ligament. 2-Structure: - The distal end of each tube has a finger like projection called “fimbriae”. - Each tube is made of 3 layers an outer peritoneal, middle muscular & inner ciliated mucosa. 3-Function: - It’s a site for ovum fertilization. - They convey the ovum to the uterus by peristalsis and ciliary movement (in 3 – 4 days). . Broad ligament The broad ligament is a fold of peritoneum that runs from the lateral pelvic wall to the uterus to enclose uterus. Important structure inside broad ligament are: The uterine tube in its free margin. Uterine arteries on side of uterus Uterus 1-Location: located In the pelvis cavity between urinary bladder anteriorly and rectum posteriorly. 2-Size: In non pregnant state 7.5 cm x 5 cm x 2.5 cm. During pregnancy, the uterus dramatically expands superiorly into the abdominal cavity. 3-Shape: pear shape. 4-Structure: uterus It consists of 3 parts fundus, body & cervix. Its wall is formed of three layers: endometrium, myometrium, & Perimetrium. 5- Position: cervix joins vagina at right angle with body lying over bladder. 6- Function: - Menstruation. - Pregnancy. - expulsion of foetus (delivery). Vagina 1-Location: between urinary bladder anteriorly, rectum & anus posteriorly & about 7.5 cm long. 2-Function: 1-Receives seminal fluid. 2-Birth canal. 3-Duct for menstrual flow Vagina Vulva ( external genitalia) It consists of numerous structures the important ones are: 1-Labia majora. 2-Labia minora. 3-External urethral meatus. 4-Vaginal orifice. . Vagina