* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
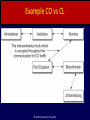
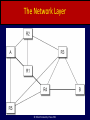
Computer Networks Bhushan Trivedi, Director, MCA Programme, at the GLS Institute of Computer Technology, Ahmadabad © Oxford University Press 2011 Chapter 1 Introduction to computer networks © Oxford University Press 2011 Questions to be answered • How is a file downloaded • How do emails reach their intended recipients? • How does a wired and a wireless connection work the same? • How is receipt of new data (for example a new antivirus update), handled and by whom? © Oxford University Press 2011 Layering Example © Oxford University Press 2011 Advantages of layers • • • • • Reducing the complexity Division of Work Standard Interfacing between Components Replacing a component is easy Independence in Protocol design © Oxford University Press 2011 Disadvantages of layers • Reduced Speed and Performance • Increased Memory usage • Sensor Networks Node © Oxford University Press 2011 Layers for OSI and TCP/IP © Oxford University Press 2011 Connection Oriented vs Connectionless • • • • • • • Connection establishment Complete line occupied or not Multiplexing Robustness of the connection Cost of the connection Quality of service Order of delivery © Oxford University Press 2011 Example CO vs CL © Oxford University Press 2011 OSI and TCP IP difference • OSI has seven layers, TCP/IP has five layers. • The OSI was connection-oriented, TCP/IP model was connectionless • The TCP/IP provided a choice (TCP or UDP) to the customers. • TCP/IP describes an existing set of protocols The OSI model was more general © Oxford University Press 2011 OSI and TCP IP difference • OSI model distinguishes between an interface and a protocol TCP IP does not • The OSI model clearly mentions the physical and data link layers. • The Internet provides both, connection oriented service over connectionless transfer and connectionless service over connectionless transfers, © Oxford University Press 2011 The Physical Layer © Oxford University Press 2011 The Data Link Layer © Oxford University Press 2011 The Network Layer © Oxford University Press 2011 Network Layer Functioning © Oxford University Press 2011 Routing at Network Layer © Oxford University Press 2011 Extracting Prefix © Oxford University Press 2011 Routing between different networks © Oxford University Press 2011 Transport layer and reliability by retransmitting © Oxford University Press 2011 Application Layer © Oxford University Press 2011 Other • Distributed Systems – WWW • Peer to peer networks • Client server networks © Oxford University Press 2011 X.25 © Oxford University Press 2011 DTE routing © Oxford University Press 2011