* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Final Exam Review Ch. 5
Survey
Document related concepts
Algebraic K-theory wikipedia , lookup
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Group action wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Atiyah–Singer index theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Riemann–Roch theorem wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
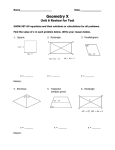
FINAL EXAM REVIEW Chapter 5 Key Concepts Chapter 5 Vocabulary parallelogram ► opposite sides ► opposite angles ► diagonals rectangle rhombus square trapezoid Defn. of a Parallelogram A quadrilateral with both pairs of opposite sides parallel A B In D C ABCD, AB DC and AD BC Theorem Opposite sides of a parallelogram are congruent. Theorem Opposite angles of a parallelogram are congruent. Theorem Diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other. Theorem One pair of opp. sides both // and ~= Parallelogram The Five Ways to Show a Quadrilateral is a Parallelogram 1) Defn. of 2) Both pairs of opp. sides =~ 3) One pair of opp. sides both // and ~= 7 4) Both pairs of opp. ~ ‘s = 5) Diagonals bisect each other Theorem If 2 lines are parallel, then all points on one line are equidistant from the other line. A B l m C D AC = BD Theorem If 3 parallel lines cut off congruent segments on one transversal, then they cut off congruent segments on every transversal. A B C If X AB = BC then XY = YZ Y Z Theorem A line that contains the midpoint of one side of a triangle and is parallel to another side passes through the midpoint of the third side. X M Y If M is the midpoint of XY then N is the midpoint of XZ N Z Theorem A segment that joins the midpoints of 2 sides of a triangle; 1. is parallel to the third side. 2. is half as long as the third side. X M Y 1.MN YZ 2.MN = ½YZ N Z Theorem: The diagonals of a rectangle are congruent Theorem: The diagonals of a rhombus are perpendicular. Theorem: Each diagonal of a rhombus bisects two angles of the rhombus. Theorem: The midpoint of the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equidistant from all three vertices. . Theorem: If an angle of a parallelogram is a right angle, then the parallelogram is a rectangle. Theorem: If two consecutive sides of a parallelogram are congruent, then the parallelogram is a rhombus. Trapezoid (Defn.) A quadrilateral with exactly one pair of parallel sides. leg base base leg IsoscelesTrapezoid (Defn.) A trapezoid with congruent legs. Theorem Base angles of an isosceles trapezoid are congruent. Theorem The median of a trapezoid: 1. is parallel to the bases. 2. has a length equal to the average of the base lengths. A XY = ½(AB + CD) X C B median Y D Homework ► Chapter 5 Review WS