* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lab 4: Planetary Motions
Observations and explorations of Venus wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Earth's rotation wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
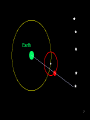
Astronomy 101 Planetarium Lab Instructor: Brian Pohl ConOps: Craig Zdanowicz www.physics.unc.edu/~bpohl/ YOU MAY SIT WHERE YOU WISH Planetary Motions • How long does Mars take to orbit the Sun? • How about Venus? • Why do the planets appear to move backwards … sometimes?? 2 3 The Original Planets! The Sun The Moon Mercury Venus Mars Jupiter Saturn NO EARTH!! 4 5 6 7 8 Periodic Orbital Motion Synodic period - the period as seen from earth •Tied to the motion of the Earth Sidereal period - the true period as seen from “outside”, relative to the background stars •Independent of the motion of the Earth 10 Lab Instructions • Find synodic periods - synodic period is complete when planet appears at same place in sky with respect to the sun • We will measure the angle between the sun, us, and the planet. – Mark position of sun and planet on ecliptic – Use the ecliptic as a ruler so that the date is a measurement. The current date is the number that the sun is on. – Measure the difference between the two positions (the units will be days, later convert to angles) – This gives you the angle. • When the angle repeats, one period has been completed. – Write down how many days elapsed between period – Hint: Use difference in DOY for sun (col. 2). 11 Oct-15,2007 – Dec-15, 2008 Things to watch out for! Write this Down!! • Add 365 days to DOY after each year has passed • The period for Mars will be is in between the measurements, so you might not see the exact angle repeat. Need to interpolate! – Guess the DOY of Sun where period would repeat Use fractions or graph it • Keep track of negative angles: -225 degrees = 135 degrees 135-360 = -225 +135 deg -225 deg 12 Calculations • Find synodic period using your measurements – Show any relevant calculations (e.g. interpolation) • Convert this to sidereal period using equation • Calculate theoretical sidereal period using Kepler’s law • Find % error for: sidereal of Venus and Mars from measurements compared to value you look up & sidereal of Venus and Mars from measurements compared to those you calculate from Kepler’s law (4 total). 13 Lab Write Up • Separate page for calculations • Include sample calculation for: each calculation in the table, sidereal, Kepler’s, & % error. Include equation for each. • Explain how you found the synodic period – Include your interpolation method (if any) • Two sources of error: questions to consider: – Is this a ‘significant’ source of error? – What does it mean to make a ‘good’ measurement? 14 All Power Points are on my website: http://www.physics.unc.edu/~bpohl Visit office hours or email me if you have questions! [email protected] Morehead room 404 Mondays (week-after-lab) 3:00 pm – 5:00 pm Tuesdays (week-after-lab) 5:00 pm - 7:00 pm