* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Coronary Artery Bypass Graft
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
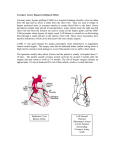
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft MODERATOR: Dr. HARISH NAIR Dr. RAKESH M.G. Prior to 1930’s, heart surgery seen as impossible, with high morbidity and mortality 1937: Dr. John Gibbon designs heart-lung machine, which enables cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) 1955: Vineburg and Buller implant internal mammary artery into myocardium to treat cardiac ischemia and angina 1958: Longmire, Cannon and Kattus at UCLA perform first open coronary artery endarterectomy without CPB During 1960’s and 1970’s, CPB and cardioplegic arrest are adopted, allowing Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) to emerge as a viable surgical treatment CABG Dr. Vasil Kolesov in 1964 Pioneer Dr. Rene Favaloro Dr. Greene did the 1st LIMA ANATOMY Chronic angina Unstable angina Acute myocardial infarction Acute failure of percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) Severe coronary artery disease Investigations Routine Blood investigations RFT, LFT, Coagulation profile Serum electrolytes 12 lead ECG Chest X ray Stress test Echocardiogram Angiogram CORONARY ANGIOGRAM TYPES OF CABG Off pump CABG (OPCAB) On pump CABG –(1)Cardioplegia (2)Fibrillating heart Mid CABG Robotic surgery Anaesthesia preparation ECG leads Peripheral line Arterial line CVP and PA pressure line Intubation Trans-esophageal endoscopy. Most common arteries bypassed: Right coronary artery Left anterior descending coronary artery Circumflex coronary artery Saphenous vein used for bypassing right coronary artery and circumflex coronary artery Internal mammary artery (IMA) used for bypassing left anterior descending coronary artery Patency rate over 90% after 10 years If more veins are needed, alternative sites such as upper extremity veins can be used Patency rate as low as 47% after 10 years Radial/ right gastro-epiploic artery. (also used) Conduit removed Median sternotomy Sternum divided using electric saw Cold potassium cardioplegia Cardiopulmonary bypass Cannulation of: Ascending aorta Femoral artery Right atrium Heparin administered to minimize clotting Grafting Pacing wire Closure Bypass of arteries: Incision in target artery: Anastamosis of graft with artery: Positive: Relief of angina in 90% of patients 80% angina free after 5 years Survival about 95% after 1 year Low chance of restenosis Negative: 2-3 days in ICU, 7-10 day total hospital stay 3-6 month full recovery time 5-10% have post-op complications High cost Long time on CPB Depression of the patient's immune system Postoperative bleeding from inactivation of the blood clotting system Hypotension Minimally invasive surgery does not use CPB Smaller incision Emerging as a replacement for conventional CABG Starting in 1990’s, MIDCAB has gained popularity Usually conducted for LIMA to LDA grafts Thoracotomy incision (~10 cm) Small incisions for video-assisted LIMA harvest LAD exposed Anastamosis preformed with assistance of mechanical stabilizer Completed graft Small portion of front of 4th rib removed LIMA clipped and dissected MIDCAB retractor and LIMA stabilizer facilitates grafting Uses CPB Balloon catheter system for aortic occlusion and cardioplegic arrest 5-8 cm left anterior thoracotomy incision No sternotomy!!! LIMA harvested using specialized retractor Aorta drawn into operating field Aorta clamped, anastamosis performed Benefits: Bloodless field Heart arrested allows more accurate anastomoses than MIDCAB Smaller incision than CABG No sternotomy Drawbacks Uses CPB Technically very difficult Currently, stenting is recommended over surgery for one-vessel disease In the future, drug-eluting stents will probably be used Minimally invasive surgeries could be used in place of stents in diabetic, and other high-risk patients For more than one-vessel disease, surgery is substantially better at preventing restenosis and so will likely continue to be used in the future Minimally invasive surgeries will expand and replace most conventional CABG procedures THANK YOU