* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geometry - 6.5 - Parallel Postulate and Triangle Sum Theorem
Projective plane wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Riemann–Roch theorem wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
Brouwer fixed-point theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
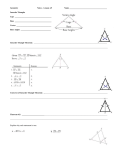
Geometry 6.5 Parallel Postulate and Triangle Sum Theorem January 06, 2017 • Ch 5 Review Problems pp. 206209 #1550 due FRIDAY 01/06 • TEST #2 Wednesday 01/11 • Ch 6 Review Problems pp. 250254 #919, 3353 Theorem 17: Equal corresponding angles mean that lines are parallel. Corollary 1: Equal alternate interior angles mean that lines are parallel. Corollary 2: Supplementary interior angles on the same side of a transversal mean that lines are parallel. Corollary 3: In a plane, two lines perpendicular to a third line are parallel. The Parallel Postulate – Through a point not on a line, there is exactly one line parallel to the given line. Theorem 18: In a plane, two lines parallel to a third line are parallel to each other. 1 Geometry 6.5 Parallel Postulate and Triangle Sum Theorem January 06, 2017 6.4 – Parallel Lines and Angles Theorem 19: Parallel lines form equal corresponding angles. 1 3 2 4 6 5 7 8 Corollary 1: Parallel lines form equal alternate interior angles. Corollary 2: Parallel lines form supplementary interior angles on the same side of a transversal. Corollary 3: In a plane, a line perpendicular to one of two parallel lines is also perpendicular to the other. 2 Geometry 6.5 Parallel Postulate and Triangle Sum Theorem January 06, 2017 3 Geometry 6.5 Parallel Postulate and Triangle Sum Theorem January 06, 2017 SAT Problem Given: a||b 45. Write an equation relating the measures of the two indicated angles. 46. Find the measure of the acute angle. 47. Find the measure of the obtuse angle. 6.5 – The Angles of a Triangle Theorem 20: The Angle Sum Theorem – The sum of the angles of a triangle is 180°. E Given: ∆ABC Prove: A+ B+ C=180° Proof: Statements B D 1 2 3 C Reasons A 1. ∆ABC 2. Through point B, draw line DE||AC 3. 1= A and 3= C 4. 1+ 2= DBC 5. DBC and 3 are supplementary 6. DBC+ 3=180° 7. 1+ 2+ 3=180° 8. A+ B+ C=180° E B D 1 2 3 C A 4 Geometry 6.5 Parallel Postulate and Triangle Sum Theorem January 06, 2017 In nonEuclidean geometries, the angles in a triangle do not necessarily sum to 180! Crocheted hyperbolic planes violating the Parallel Postulate http://theiff.org/oexhibits/oe1e.html Theorem 17: Equal corresponding angles mean that lines are parallel. Corollary 1: Equal alternate interior angles mean that lines are parallel. Corollary 2: Supplementary interior angles on the same side of a transversal mean that lines are parallel. Corollary 3: In a plane, two lines perpendicular to a third line are parallel. The Parallel Postulate – Through a point not on a line, there is exactly one line parallel to the given line. Theorem 18: In a plane, two lines parallel to a third line are parallel to each other. Theorem 19: Parallel lines form equal corresponding angles. Corollary 1: Parallel lines form equal alternate interior angles. Corollary 2: Parallel lines form supplementary interior angles on the same side of a transversal. Corollary 3: In a plane, a line perpendicular to one of two parallel lines is also perpendicular to the other. Theorem 20: The Angle Sum Theorem – The sum of the angles of a triangle is 180°. 5