* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Guidelines(Draft) - Liverpool Gastroenterology
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
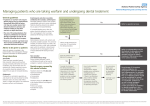
Anticoagulant policy: Endoscopy Unit 2009 RLUH Endoscopy Unit: guidance for patients on anticoagulants or anti-platelet agents who require an Endoscopic procedure. This guidance and process is based on guidelines published in 2008 by the British Society of Gastroenterology [http://www.bsg.org.uk/clinicalguidelines/endoscopy/anticoagulant-antiplatelet-therapy.html] and further information is available from the American Society of Gastroenterology [http://www.asge.org/WorkArea/showcontent.aspx?id=3014]. The guidance was agreed within the Division of Medicine in association with the Anticoagulant Nurse Practitioners. There are two essential components to this guidance: 1. Consider the risk of the procedure in causing haemorrhage for patients on anticoagulation. 2. Consider the risk to the patient of not having anti-coagulation in order for the procedure to take place. The following is a summary of the guidance: 1. Aspirin: omit on morning of procedure only, otherwise continue as normal 2. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (eg brufen, narpoxed etc): omit on morning of procedure only, otherwise continue as normal 3. Pentoxyfilene: omit on morning of procedure only, otherwise continue as normal 4. Clopidogrel: see specific advice 5. Warfarin: see specific advice 6 Heparin: omit on morning of procedure only, otherwise continue as normal 1 Anticoagulant policy: Endoscopy Unit 2009 Clopidogrel: Continue if the patient is having any of the following: Diagnostic Gastroscopy Gastroscopy for assessment or treatment of varices Diagnostic Enteroscopy Diagnostic Colonoscopy (ie surveillance or for colitis: not if known polyp or EMR), Diagnostic EUS (unless staging oesophageal tumour), ERCP with stent insertion or stent change only Stop for 7 days if patient is having any of the following: PEG or PEJ ERCP planned with sphincterotomy EUS-FNA Gastroscopy or Colonoscopy with planned EMR Planned dilatation of strictures DO NOT STOP if patient has had a coronary artery stent within the last 12 months – call a cardiologist!. 2 Anticoagulant policy: Endoscopy Unit 2009 Warfarin: Continue if the patient is having any of the following: Diagnostic Gastroscopy Gastroscopy for assessment or treatment of varices Diagnostic Enteroscopy Diagnostic Colonoscopy (ie surveillance or for colitis: not if known polyp or EMR), Diagnostic EUS (unless staging oesophageal tumour), ERCP with stent insertion or stent change only INR to be checked within the 7 days before the test (patients usually arrange this themselves with anticoagulation monitoring service): level should be <2.5 and patient can continue taking their regular dose. They will have a ‘Coag-u-Check’ in the endoscopy unit on the day of the procedure. Change process if patient is having any of the following: PEG or PEJ ERCP planned with sphincterotomy EUS-FNA Gastroscopy or Colonsocopy with planned EMR Planned dilatation of strictures Convert to Heparin in these circumstances. Book the procedure as normal but inform the Anticoagulant nurse practitioner (Ext 4347 or Bleep 4929 or via ICE) that patient needs a low target INR. The anticoagulant Nurse Practitioner will arrange to see the patient and stop the warfarin 5 days prior to planned procedure and start on LMWHeparin 2 days later – this should be omitted on the morning of the planned procedure. Warfarin can be restarted on the evening of the procedure or on the following morning unless bleeding continues after the procedure. NB: take extra care if patients also require antibiotics as this can cause warfarin displacement and increase the INR. 3 Anticoagulant policy: Endoscopy Unit 2009 Figure 1: Guidelines for the management of patients on warfarin or clopidogrel undergoing endoscopic procedures High Risk Procedure Low Risk Procedure Polypectomy ERCP with sphincterotomy EMR Dilation of strictures Therapy of varices PEG EUS with FNA or Cyst puncture Diagnostic procedures +/biopsy Biliary or pancreatic stenting Diagnostic EUS Warfarin Continue Warfarin Check INR 1 week before endoscopy If INR within therapeutic range continue usual daily dose If INR above therapeutic range but <5 reduce daily dose until INR returns to therapeutic range Clopidogrel Continue clopidogrel Clopidogrel Warfarin Low Risk Condition High Risk Condition Prosthetic metal heart valve in aortic position Xenograft heart valve AF without valvular disease >3months after VTE Prosthetic metal heart valve in mitral position Prosthetic heart valve and AF AF and mitral stenosis <3months after VTE Thrombophilia syndromes Low Risk Condition Ischaemic heart disease without coronary stent Cerbrovascular disease Peripheral vascular disease Stop warfarin 5 days before endoscopy Stop warfarin 5 days before endoscopy Stop clopidogrel 7 days before endoscopy Check INR prior to procedure to ensure INR<1.5 Restart warfarin evening of procedure with usual daily dose Check INR 1 week later to ensure adequate anticoagulation Start LMWH 2 days after stopping warfarin Omit LMWH on day of procedure Restart warfarin evening of procedure with usual daily dose Continue LMWH until INR adequate Continue aspirin if already prescribed If not on aspirin, then consider aspirin therapy while clopidogrel discontinued High Risk Condition Coronary artery stents Liaise with cardiologist Consider stopping clopidogrel 7 days before endoscopy if: >12 months after insertion of drug-eluting coronary stent >1 month after insertion of bare metal coronary stent R (EUS: endoscopic ultrasound, ERCP: endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, EMR: endoscopic mucosal resection, PEG: percutaneous endoscopic gastroenterostomy, FNA: fine needle aspiration, INR: international normalised ratio, AF: atrial fibrillation, VTE: venous thromboembolism, LMWH: low molecular weight heparin) 4