* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download UPPER LIMB
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
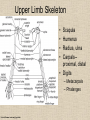
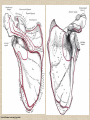
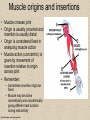
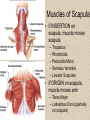
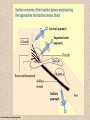
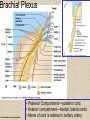
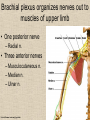
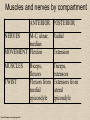
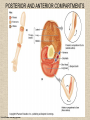
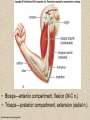
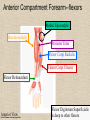
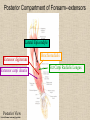
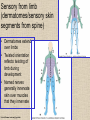
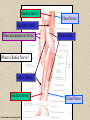
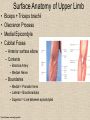
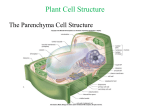
UPPER LIMB • • • • • • • • What is a limb? Skeleton Joints Shoulder/Scapula muscles Brachial plexus— getting spinal nerves out onto limb Muscles—anterior and posterior compartments Sensory innervation Surface anatomy Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb From Royal Collection da Vinci drawings What is a limb? • Ventral somatic outgrowth of outer tube – Bones (made of bony tissue, cartilage, and other tissues) – Joints – Muscles – Nerves (with motor neurons to muscles, sensory neurons to skin, proprioceptors) • No viscera--all innervation is somatic (motor or sensory) from ventral ramus of spinal nerve (except autonomics to blood vessels) Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb Upper Limb Skeleton • • • • Scapula Humerus Radius, ulna Carpals-proximal, distal • Digits – Metacarpals – Phalanges Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb Joints JOINT BETWEEN MOVEMENT TYPE Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb Muscle origins and insertions • Muscle crosses joint • Origin is usually proximal and insertion is usually distal • Origin is considered fixed in analyzing muscle action • Muscle action (concentric) is given by movement of insertion relative to origin across joint • Remember: – Sometimes insertion might be fixed – Muscle may be active isometrically and concentrically giving different real function during real activity Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb Muscles of Scapula • If INSERTION on scapula, muscle moves scapula – – – – – Trapezius Rhomboids Pectoralis Minor Serratus Ventralis Levator Scapulae • If ORIGIN on scapula, muscle moves arm – Teres Major – Latissimus Dorsi (partially on scapula) Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb Rotator Cuff • • • • • Muscles originate on fossae of scapula • Help support “open socket” of shoulder joint • Insert around ball of femur • Medial and lateral rotation of upper limb • Typical baseball pitcher injury Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres minor Subscapularis Axilla = Armpit • Region between arm and chest • Boundaries – Ventral - pectoral muscles – Dorsal = latissimus dorsi, teres major subscapularis – Medial = serratus ventralis – Lateral = bicipital groove of humerus • Contents – Axillary nerves and blood vessels – Axillary lymph nodes – And….the……Brachial plexus Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb Brachial Plexus Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb • Posterior Compartment—posterior cord • Anterior compartment—medial, lateral cords • Name of cord is relative to axillary artery Brachial plexus organizes nerves out to muscles of upper limb • One posterior nerve – Radial n. • Three anterior nerves – Musculocutaneous n. – Median n. – Ulnar n. Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb Muscles and nerves by compartment ANTERIOR POSTERIOR NERVES M-C, ulnar, median MOVEMENT Flexion Radial MUSCLES Triceps, extensors Extensors from lateral epicondyle TWIST Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb Biceps, flexors Flexors from medial epicondyle Extension POSTERIOR AND ANTERIOR COMPARTMENTS Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb • Biceps—anterior compartment, flexion (M-C n.) • Triceps—posterior compartment, extension (radial n.) Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb Anterior Compartment Forearm--flexors Medial Epicondyle Brachioradialis Pronator Teres Flexor Carpi Radialis Flexor Carpi Ulnaris Flexor Retinaculum Anterior View Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb Flexor Digitorum Superficialis is deep to other flexors Posterior Compartment of Forearm--extensors Lateral Epicondyle Extensor digitorum Extensor carpi ulnaris Posterior View Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb Brachioradialis Ext Carpi Radialis Longus ANTERIOR MUSCLES • M-C nerve – Biceps – brachialis • Median nerve – Forearm flexors – Thumb intrinsics (1M$ nerve) • Ulnar nerve – Flexor carpi ulnaris – Hand intrinsics Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb POSTERIOR MUSCLES • Muscles (radial nerve) – – – – Triceps Anconeus Brachioradialis Carpal, digit extensors Sensory from limb (dermatomes/sensory skin segments from spine) • Dermatomes extend over limbs • Twisted orientation reflects twisting of limb during development • Named nerves generally innervate skin over muscles that they innervate Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb Sensory territory of nerves REMEMBER: Brachial plexus re-directs spinal routes into named nerves covering certain territory Cutaneous branches of medial cord/ulnar nerve Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb Routes of nerves (in human) • M-C: between biceps brachii and brachialis • Median: medial/posterior to biceps, branches into forearm flexors at elbow then to hand through carpal tunnel – Recurrent median (1M$) superficial at wrist to thumb over thenar emminence) deficit - ape’s hand • Ulnar: medial in arm, posterior to medial epicondle of humerus (funny bone) down medial forearm medial to carpal tunnel into palm • Radial: deep posterior arm around lateral epicondyle of humerus to forearm (deep and superficial branches) Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb Median Nerve Ulnar Nerve Brachial Artery Musculocutaneous Nerve UlnarArtery Where’s Radial Nerve? Radial Artery Median Nerve Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb Ulnar Nerve Surface Anatomy of Upper Limb • • • • Biceps + Triceps brachii Olecranon Process Medial Epicondyle Cubital Fossa – Anterior surface elbow – Contents • Brachial Artery • Median Nerve – Boundaries • Medial = Pronator teres • Lateral = Brachioradialis • Superior = Line between epicondyles Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb Surface Anatomy of Upper Limb • Carpal Tunnel – Carpals concave anteriorly – Carpal ligament covers it – Contains: long tendons, Median nerve – Inflammation of tendons = compression of Median nerve • Anatomical Snuffbox Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb – Lateral = E.pollicis brevis – Medial = E. pollicis longus – Floor = scaphoid, styloid of radius – Contains Radial Artery (pulse) Suggestion: a muscle table organized by Joint crossed? Nerve innervating? Action? Compartments? All of the above? MUSCLE ACTION ORIGIN INSERTION INNERVATION (cord to nerve) Biceps Radial tuberosity Flex, sup. Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb Humerus, glenoid Medial cord—M-C. Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb