* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Uterine Myoma
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
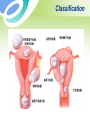
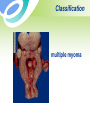
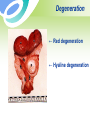
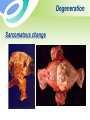
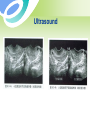
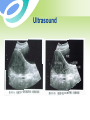
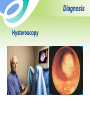
Uterine Myoma Women’s Hospital, School of Medicine Zhejiang University Prof. Lin Jun Introduction Most common benign tumor of female reproductive system Benign neoplasm composed primarily of smooth muscle and connectives tissue Common in women 30-50y Usually asymptomatic Etiology Not detectable before puberty and after menopause Probably relates to female hormones Estrogen and ER ↑ Progestin may promote mitosis of myoma Classification According to the location: Uterine body myoma Cervical myoma 10% 90% Classification According to the relationship between myoma and uterine myometrium : intramural myoma 60%-70% subserous myoma 20% submucous myoma 10%-15% Classification Classification multiple myoma Pathology Gross Appearance: round, smooth, and usually firm false capsular covering ——pseudocapsule can be clearly demarcated from the surrounding myometrium Pathology Gross Appearance: Transverse section : light gray a whorl-like arrangement or an intertwining pattern Pathology Microscopic examination: composed of smooth muscle cells and varying amounts of connectives tissue Individual cells are quite uniform in size, spindle shaped, have elongated nuclei. Nonstriated muscle fibers are arranged in interlacing bundles of varying size running in different directions. Degeneration Hyaline degeneration Cystic degeneration Red degeneration Sarcomatous change Degeneration with calcification Degeneration Red degeneration most common during pregnancy and puerperium venous thrombosis and congestion with interstitial hemorrhage Degeneration ← Red degeneration ← Hyaline degeneration Degeneration Sarcomatous change malignant rare, 0.4-0.8% old women enlarge rapidly with irregular vaginal bleeding Degeneration Sarcomatous change Symptoms Usually no symptoms Associate with location, and degenerations Not associate with the size and the number Symptoms 1. menorrhagia and prolonged menses large intramural myoma submucous myoma 2. abdominal mass 3. leukorrhagia Symptoms 4. pressure effects pressure bladder or rectum → urinary frequency, constipation intraligamentous myoma and large cervical myoma → obstruct ureter 5.others infertility spontaneous abortion abdominal pain Sign associated with: size location number degeneration large myoma→ palpable abdominal mass Pelvic examination: uterus —— enlarged,irregular and hard Diagnosis Typical symptoms and signs Ultrasound Hysteroscopy Laparoscopy Ultrasound Ultrasound Diagnosis Hysteroscopy Diagnosis Laparoscopy Differential diagnosis Pregnancy Ovarian neoplasms Adenomyosis Malignant tumors of uterus uterine sarcoma endometrial carcinoma cervical cancer Treatment According to : age desire for childbearing symptoms location , size and amount of myoma Treatment Observation and Follow Up Small,asymptomatic,especially near menopause Interval:3~6 months Medical measure Indications: smaller than 2 months in size slight symptoms near menopause Medical measure 1.Androgenic agents: testosterone propionate 2.Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist, (GnRH-a) GnRH-a LH、FSH↓ E2↓ shrinkage of myoma leuprorilin goserelin Medical measure 2.GnRH-a Side effects: Hypoestrogenic side effects Osteoporosis 3.Mifepristone Surgical measures Indications: greater than 10 weeks in size menorrhagia→ anemia pressure effects grows rapidly failure in medical treatment infertility or recurrent abortion Surgical measures Approaches: laparotomy hystereoscopy laparoscopy Surgical measures 1. Myomectomy preserve fertility, <35 years old 2. Hysterectomy Large myoma Numerous tumors Obviously symptomatic patient No wish of preserving fertility Suspected to malignant transformation Myomas during pregnancy Impact on pregnancy and delivery : abortion preterm labor fetal malpresentation placenta previa birth canal obstruction postpartum hemorrhage Myomas during pregnancy Red degeneration Clinical finding: rapid growth of myoma pain, fever, WBC↑ Conservative treatment