* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download There are two types of tics—motor and vocal
Sluggish cognitive tempo wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Parent management training wikipedia , lookup
Fragile X syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Autism and working memory wikipedia , lookup
Autism therapies wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Externalizing disorders wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral theories of depression wikipedia , lookup
Autism spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Counterproductive work behavior wikipedia , lookup
Diagnosis of Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
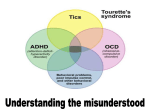
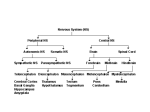
1.2.1 Neurodevelopmental Disorders 1. Autistic Spectrum Disorders Signs and Symptoms Parents or doctors may first identify ASD behaviors in infants and toddlers. School staff may recognize these behaviors in older children. Not all people with ASD will show all of these behaviors, but most will show several. There are two main types of behaviors: “restricted / repetitive behaviors” and “social communication / interaction behaviors.” Restrictive / repetitive behaviors may include: Repeating certain behaviors or having unusual behaviors Having overly focused interests, such as with moving objects or parts of objects Having a lasting, intense interest in certain topics, such as numbers, details, or facts. Social communication / interaction behaviors may include: Getting upset by a slight change in a routine or being placed in a new or overly stimulating setting Making little or inconsistent eye contact Having a tendency to look at and listen to other people less often Rarely sharing enjoyment of objects or activities by pointing or showing things to others Responding unusually when others show anger, distress, or affection Failing to, or being slow to, respond to someone calling their name or other verbal attempts to gain attention Having difficulties with the back and forth of conversations Often talking at length about a favorite subject without noticing that others are not interested or without giving others a chance to respond Repeating words or phrases that they hear, a behavior called echolalia Using words that seem odd, out of place, or have a special meaning known only to those familiar with that person’s way of communicating Having facial expressions, movements, and gestures that do not match what is being said Having an unusual tone of voice that may sound sing-song or flat and robot-like Having trouble understanding another person’s point of view or being unable to predict or understand other people’s actions. People with ASD may have other difficulties, such as being very sensitive to light, noise, clothing, or temperature. They may also experience sleep problems, digestion problems, and irritability. ASD is unique in that it is common for people with ASD to have many strengths and abilities in addition to challenges. Strengths and abilities may include: Having above-average intelligence – the CDC reports 46% of ASD children have above average intelligence Being able to learn things in detail and remember information for long periods of time Being strong visual and auditory learners Exceling in math, science, music, or art. 2. What is Tourette Syndrome? For a person to be diagnosed with TS pursuant to DSM-5 criteria he or she must: have both multiple motor tics (for example, blinking or shrugging the shoulders) and vocal tics (for example, humming, clearing the throat, or yelling out a word or phrase), although they might not always happen at the same time. have had tics for at least a year. The tics can occur many times a day (usually in bouts) nearly every day, or off and on. have tics that begin before he or she is 18 years of age. have symptoms that are not due to taking medicine or other drugs or due to having another medical condition Tourette Syndrome is a condition of the nervous system. It causes people to have “tics”. Tics are sudden twitches, movements, or sounds that people do repeatedly. Sometimes people can stop themselves from doing a certain tic for awhile, but it’s hard. Eventually the person has to do the tic. Types of Tics There are two types of tics—motor and vocal: Motor Tics: are movements of the body. Examples of motor tics include the following: 1. Blinking 2. shrugging the shoulders 3. jerking an arm. 4. grimacing and smacking lips 5. repeating movements of others 6. copropraxia (obscene gestures). Vocal Tics: may occur with the movements, and can include the following: 7. grunting 8. throat clearing 9. shouting and barking. Vocal tics may also be expressed as 10. coprolalia (the involuntary use of obscene words or socially inappropriate words and phrases) or copropraxia (obscene gestures).. 11. Echo phenomena (echo speech or echolalia) are also reported, although less frequently. These may include repeating word of others (echolalia), repeating ones own words (palilalia), 3. Attention Deficit Disorder - Based on the presenting symptom ADHD can be divided into three subtypes—predominantly inattentive, predominantly hyperactiveimpulsive, or combined if criteria for both types are met.[24]:p.4 An individual with inattentive concentration may have some or all of the following symptoms:[26] Be easily distracted, miss details, forget things, and frequently switch from one activity to another Have difficulty maintaining focus on one task Become bored with a task after only a few minutes, unless doing something enjoyable Have difficulty focusing attention on organizing and completing a task or learning something new Have trouble completing or turning in homework assignments, often losing things (e.g., pencils, toys, assignments) needed to complete tasks or activities Not seem to listen when spoken to Daydream, become easily confused, and move slowly Have difficulty processing information as quickly and accurately as others Struggle to follow instructions An individual with hyperactivity-impulsivity may have some or all of the following symptoms:[26] Fidget and squirm in their seats Talk nonstop Dash around, touching or playing with anything and everything in sight Have trouble sitting still during dinner, school, doing homework, and story time Be constantly in motion Have difficulty doing quiet tasks or activities Be very impatient Blurt out inappropriate comments, show their emotions without restraint, and act without regard for consequences Have difficulty waiting for things they want or waiting their turns in games Often interrupts conversations or others' activities People with ADHD more often have difficulties with social skills, such as social interaction and forming and maintaining friendships. They also may drift off during conversations and miss social cues.[32]