* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download conventions
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Agglutination wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lojban grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Word-sense disambiguation wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Classical compound wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Symbol grounding problem wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Comparison (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Untranslatability wikipedia , lookup
Morphology (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
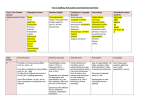
F & P Writing skills continuum – Conventions for Grades 1 - 4 Source: The Continuum of Literacy Learning Grades Pre-K-8, Second edition This document contains a summary of conventions skills by grade level. New skills that are introduced are shown in red. CONVENTIONS ____________________________________________________________________________________ TEXT LAYOUT Grade 1 Understand that the print and pictures can be placed in a variety of places on the page within a book Place words in lines, starting left to right, top to bottom Place titles and headings in the appropriate place on the page Understand that layout of print and illustrations are important in conveying the meaning of a text Use underlining and bold print to convey meaning Use spaces between words. Grade 2 Arrange print on the page to support the text’s meaning and to help the reader notice important information Understand that layout of print and illustrations are important in conveying the meaning of a text Understand how to use layout, spacing, and size of print to create titles, headings, and subheadings. Grade 3 Arrange print on the page to support the text’s meaning and to help the reader notice important information Use layout of print and illustrations to convey the meaning of a text Use the size of print to convey meaning in a printed text Use layout, spacing and size of print to create titles, headings and subheadings Use underlining, italics, and bold print to convey a specific meaning Use underlining in words in titles Grade 4 Use layout, spacing and size of print to create titles, headings and subheadings Use underlining, italics, and bold print to convey a specific meaning Arrange print on the page to support the text’s meaning and to help the reader notice important information Use and understand the layout of print and illustrations are important to conveying the meaning of a text Use and Understand that size of text conveys meaning in printed text Use indentations or spacing to set off paragraphs GRAMMAR Sentence Structure Grade 1 Use conventional sentence structure (noun + verb) Grade 2 Write complete sentences Use a range of complete sentences (declarative, interrogative, exclamatory) Grade 3 Use a range of complete sentences (declarative, interrogative, exclamatory) Write some sentences with embedded clauses (complex) and dialogue Use conventional sentence structure for both simple and compound sentences Write uninterrupted dialogue in conventional structure Grade 4 Write dialogue in conventional structures Use conventional sentence structure for compound sentences with embedded clauses Use a range of sentence types (declarative, interrogative, exclamatory Write complete sentences with noun and verb Place clauses in sentences Place phrases in sentences Write simple and compound sentences Sometimes vary sentence structure and length for reasons of craft Write sentences in past, present, future, present perfect, and past perfect tenses Parts of Speech Grade 1 Use noun and verb agreement (I can) Use prepositional phrases (to the bus, on the bus) Use modifiers (red dress; ran fast) Grade 2 Use subject and verb agreement in simple sentences (we were) Use nouns and pronouns that are in agreement (Mike / he) Use prepositional phrases, adjectives and adverbs correctly Grade 3 Use subject and verb agreement (we were) Use nouns and pronouns that are in agreement (Mike / he) Use prepositional phrases, adjectives and adverbs correctly Use nouns and adjectives correctly Grade 4 Use nouns and pronouns that are in agreement (Mike / he) Use prepositions and prepositional phrases, adjectives and adverbs correctly Use nouns and adjectives and adverbs correctly Use objective and nominative case pronouns correctly (me, him, her, I, he, she) Use indefinite and relative pronouns correctly (everyone, both, who, whom) Use verbs that are often misused (lie, lay, rise, raise) Use verb and objects that are often misused ([verb] to her and me, she and I) Tense Grade 1 Write in past tense (I went home yesterday.) Write in future tense (I’m going to go…) Grade 2 Write in past tense (I went home yesterday.) Write in future tense (I’m going to go…) Write in present tense (Owls love to…) Grade 3 Write in past tense (I went home yesterday.) Write in present tense (Owls love to…) Write in future tense (I’m going to go…) Grade 4 Write sentences in past, present, future, present perfect and past perfect tenses Maintain consistency of tense PARAGRAPHING Grade 4 Understand and use paragraph structure (indented or block) to organize sentences that focus on one idea Create transitions between paragraphs to show the progression of ideas Understand and use paragraphing to show speaker change in dialogues CAPITALIZATION Grade 1 Demonstrate knowledge of the use of upper and lowercase letters of the alphabet Show awareness of the first place position of capital letters in words Use uppercase letters in titles Use a capital letter for the first word of a sentence Use capital letters in the beginning position in a few familiar, known proper nouns Grade 2 Use a capital letter for the first word of a sentence Use capital letters appropriately to capitalize days, months, provinces Use capital letters for names of people and places Use all capital letters for a head or for emphasis Use capitals to start the first word, last word and most other words in titles. Grade 3 Use a capital letter for the first word of a sentence Use capital letters appropriately to capitalize days, months, and specific places Use capital letters for names of people and places Use all capital letters for a head or for emphasis Use capitals to start the first word, last word and most other words in titles. Use capitals for the first word in a greeting or a letter. Use capital letters correctly in uninterrupted dialogue Grade 4 Use a capital letter for the first word of a sentence Use capital letters appropriately to capitalize days, months, places, holidays, city names and titles of books Use capital letters correctly in dialogue Use capitalization for specialized functions (emphasis, key information, voice) Use more complex capitalization with accuracy, such as abbreviations and quotation marks in split dialogue PUNCTUATION Grade 1 Notice the use of punctuation marks in books and try them out in own writing Read one’s writing aloud and think where punctuation would go. Grade 2 Use periods, exclamation points, and question marks as ending marks Understand and use ellipses to show pause or anticipation, usually before something surprising Use dashes and ellipses for emphasis or to slow down the text for readers Use quotation marks around the speaker’s exact words Use periods after abbreviations Notice the use of punctuation marks in books and try them out in own writing Use apostrophes in contractions and possessives Use commas to identify a series Grade 3 Use periods, exclamation points, and question marks as ending marks Use commas to identify a series Understand and use ellipses to show pause or anticipation, usually before something surprising Notice the use of punctuation marks in books and try them out in own writing Use apostrophes in contractions and possessives Understand and use quotation marks to indicate simple dialogue Break words at the syllables at the end of a line using a hyphen Use correct punctuation in uninterrupted dialogue Grade 4 Use commas to identify a series Use apostrophes in contractions and possessives Break words at the syllables at the end of a line using a hyphen Consistently use periods, exclamation points, and question marks as ending marks Learn about the possibility of using punctuation and its effect on readers by studying mentor texts Notice effective or unusual use of punctuation marks by authors Try out new ways of using punctuation Use dashes to indicate a longer pause or slow down the reading to emphasize particular information Use commas and quotation marks correctly in writing interrupted and uninterrupted dialogue Use brackets to set aside a different idea or kind of information Use colours to indicate something is explained or described Use commas and parentheses to set off parenthetical information Use hyphens to divide words Use indentations to identify paragraphs SPELLING Grade 1 Use conventional symbols to write words Spell one hundred or more high-frequency words conventionally Say words to break them into syllables to spell them Use some phonogram patterns to generate words Attempt unknown words through sound analysis Say words slowly to hear a sound and write a letter that represents it Write some words with consonant letters appropriate for sounds in words (beginning and ending) Write a letter for easy to hear vowel sounds Represent several sounds, including beginning and ending Use some inflectional endings such as -s and -ing Represent many short and long vowel sounds in words Spell words with regular consonant sound relationships and with regular short vowel patterns correctly Represent many consonant sounds or vowel sounds with letters Attempt unknown words using known word parts Construct phonetic spelling that are readable Include a vowel in each word Represent consonant blends and digraphs with letter clusters in words Use simple resources to check spelling (word walls, personal word lists) Grade 2 Correctly spell familiar high frequency words (200+) words with regular letter-sound relationships (including consonant blends and digraphs and some vowel patterns) and commonly used endings Take apart multisyllable words to spell the parts accurately or close to accurately Use knowledge of phonogram patterns to generate multisyllable words Spell simple and some complex plurals Use simple rules for adding inflectional endings in words (drop e, double letter) Spell simple possessives Spell most contractions Spell words that have been studied (spelling words) Write easy compound words accurately Spell many one-syllable words that have vowel and r correctly Grade 3 Correctly spell a large core of high frequency words (300+) words with regular lettersound relationships (including consonant blends and digraphs and some vowel patterns) and commonly used endings Take apart multisyllable words to spell the parts accurately or close to accurately Use knowledge of phonogr500+am patterns to generate multisyllable words Spell simple and some complex plurals Use simple rules for adding inflectional endings in words (drop e, double letter) Spell most possessives Spell most contractions Spell words that have been studied (spelling words) Write many compound words accurately Spell many one-syllable and two-syllable words that have vowel and r correctly Grade 4 Correctly spell words that have been studied (spelling words) Correctly spell a large number of high frequency words (500+) words with a wide range of plurals, and base words with inflectional endings Use a range of spelling strategies to take apart and spell multisyllable words (word parts, connections to known words, complex sound to letter cluster relationships) Spell complex plurals correctly (knife, knives; woman, women, sheep, sheep) Be aware of the spelling of common suffixes (ion, ment) Spell a full range of contractions, plurals and possessives, and compound words Spell two or three syllable words Use difficult homophones (their, there) correctly HANDWRITING / WORD PROCESSING Grade 1 Leave appropriate space between words Hold pencil or pen with satisfactory grip Return to the left margin to start a new line Use a preferred hand consistently for writing Write left to right in lines Write letters and words that can be easily read Write letters in groups to form words Form upper and lowercase letters efficiently in manuscript print Form upper and lowercase letters proportionately in manuscript print Access and use simple programs on the computer (easy word-processing games) Locate letter keys on a computer keyboard to type simple messages. Grade 2 Form upper and lowercase letters efficiently and proportionately in manuscript print Begin to develop efficient keyboarding skills Use word processor to plan, draft, revise, edit and publish Make changes on the screen to revise and edit, and publish documents Grade 3 Use word processor to plan, draft, revise, edit and publish Make changes on the screen to revise and edit, and publish documents Use efficient keyboarding skills Write fluently in both manuscript and cursive handwriting with appropriate spacing Grade 4 Write fluently and legibly in cursive handwriting with appropriate spacing Use word processing with understanding of how to produce and vary text (layout, font, special techniques) Use word processor to get ideas down revise, edit and publish Use efficient keyboarding skills to create drafts, revise, edit and publish Show familiarity with computer and word-processing terminology Create website entries and articles with appropriate text layout, graphics and access to information through searching Make wide use of computer skills in presenting text.