* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download theory of central bank
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
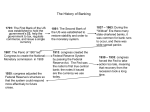
CENTRAL BANK Lecturer: Prof. Insukindro, Ph.D THEORY OF CENTRAL BANK CONCEPT OF CENTRAL BANK - Hegemonic system - Non profit institution Case 1: Transmission Role A C B D m n II I X CB THEORY OF CENTRAL BANK Case 2: Intermediation Role A (+ ) C (+ ) B (-) D (-) FI 1 FI 2 II I CFI THEORY OF CENTRAL BANK FUNCTIONS OF CENTRAL BANK Micro approach: - Club theory, Banker’s bank or lender of last resort - To maintain stability in the banking system. A C B D CoB1 CoB2 II I CB THEORY OF CENTRAL BANK MACRO APPROACH ~ Monetary Authority - Domestics Internal balance: g, π, μ - to preserve the value of the currency - to formulate & implement monetary policy The relationship between Central Bank and government and other financial institutions. - International External balance: BOP = 0 Exchange rate International Financial Institutions Central Bank’s role in the flow of funds Financial System Returns Funds Households Firms Government Financial Market Government / Central Bank Involvement Returns Funds Households Savers Firms Government Borrowers Funds Returns Financial Intermediaries Funds Returns Infrastructure and Environtment Source: PPSK BI, 2006, Insukindro (2007) and Hubbard (2008: 39), modified, 6 7 Key Services Provided by the Financial System Financial System Risk Sharing Returns Funds Households Firms Government Savers / Suppliers Funds Financial Market Government / Central Bank/ Financial Authority Involvement Financial Intermediaries Liquidity Returns Funds Households Firms Government Borrowers / Demanders Funds Returns Returns Infrastructure and Environment Information Source: PPSK BI (2006); Insukindro (2007) and Hubbard (2008:39, 41), modified INTER-RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN ECONOMIC SECTORS Real Sectors Consumption Investment Export Import External Sectors Current Account Export Import Transfer Income Capital and Financial Transactions Direct Investment Financial Flows – Government Sectors – Private Sectors International Reserves Government Sectors Government Budget Government Revenue Government Expenditure Equilibrium (overall) Sources of Funds – Domestic – Foreign Monetary Sectors Monetary Authority Reserve Money Net Foreign Assets Net Domestic Assets Net Claim on Government Commercial Bank Source: PPSK BI, 2006 Net Foreign Assets Net Domestic Assets Money in Circulation VARIOUS TASKS OF CENTRAL BANKS 1. 2. 3. 4. As bank-of the banks and insurer (lender of last resort). As a publicly owned or publicly controlled corporation. As a monopoly provider of public goods (a stable currency and well-functioning payment system). As a regulator that produces & enforces secondary regulation & guideline relating to bank solvency, entry and competition. BALANCE SHEET OF CENTRAL BANK Reserve Money Consolidated Balance Sheet of Central Bank December 31, 2008 Sources of Reserve Money Uses of Reserve Money 1. External Source: 1. Money outside bank International Reserve a. Currency held by the public 2. Internal Sources: b. Private sector demand deposits a. Net Claims on Public Sectors: 2. Banks reserve - Central Bank a. Currency held by the banks - Claims on Official Entities & Public Enterprises b. Banker’s Deposits b. Claims on Deposits Money 3. Other Uses Banks c. Other sources Total Sources Total Uses CENTRAL BANK IN SOME COUNTRIES (Warjiyo, 2004: 23) Country Monet. Authority Bank Regulator Payment System Hongkong Yes No No England Yes No No Australia Yes No Yes Japan Yes Partly Yes USA Yes Partly Partly France Yes Partly Partly Netherlands Yes Partly Yes Italy Yes Partly Yes Germany Yes Partly Yes South Africa Yes Yes No Brasil Yes Yes Partly India Yes Yes Partly Singapore Yes Yes Partly Indonesia Yes Yes Yes Malaysia Yes Yes Yes Frisell et al (2004) Frisell et al (2004) Frisell et al (2004) Frisell et al (2004) Financial Independence (Out of 26 cases) Laws set upon the bank that rules on the allocation of profits to reserves and government, by specifying a decision making process and/or fixed shares or amounts 88% No laws regarding profit 8% Other 4% Frisell et al (2004) The Governor is Appointed by (Out of 41 cases) Frisell et al (2004) Number of Institutions Involved in the Appointment Process (out of 41 cases) A more multi-faceted appointment process takes place 5% Only one institution is involved 27% Frisell et al (2004) One institution appoints and another advises or recommends 36% One institution appoints and another agrees 32% Frisell et al (2004) Frisell et al (2004) STRUCTURE OF CENTRAL BANK 1. Federal Reserve System 2. Bank of China 3. Bank of Indonesia or Bank Indonesia 4. Bank of England 5. Bank of Japan 6. European Central Bank 7. Bank of Canada, etc Mishkin (2003: Ch. 14), Warjiyo (2003). The Formal Structure and Policy of the Federal Reserve System Source: Ritter at al. (2009: 331) The Federal Reserve System Source: Ritter at al. (2009: 332) The Realities of Power Within the Federal Reserve System Source: Ritter at al. (2009:333) Currency Flow Before the Reform in China Source: Gang ,1994: 25 Bank Transfer Money Flow After the Reforms in China Source: Gang ,1994: 26 Financial Institutions in China Source: Gang ,1994: 37 REFERENCES Frisell, L., K. Roszbach and G. Spagnolo (2008), Governing the Governors: A Clinical Study of Central Banks, Sveriges Riksbank Working Paper Series, No. 221, May. Gang ,Yi. 1994. Money, Banking & Financial Markets in China. Westview Press Hubbard, R.G. (2008), Money, the Financial System, and the Economy, Pearson Education, Inc Insukindro (2007), Penilaian Kekayaan Negara dan Daerah: Pendekatan Triangulasi, Makalah Seminar Nasional Penilaian, Kerjasama DJKN Depkeu dan MEP FE UGM, Yogyakarta, 9 Juni. Mishkin, F.S. (2003), The Economics of Money, Banking and Financial Markets, Addison Wesley PPSK BI (2006), Modul Kebanksentralan. Ritter, L.S., W.L. Silber and G.F. Udell (2009), Principles of Money, Banking & Financial Markets, Pearson Education, Inc. Warjiyo, P. (eds) (2004), Bank Indonesia Bank Sentral Republik Indonesia: Sebuah Pengantar, PPSK Bank Indonesia