* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Delirium prevention care plan
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
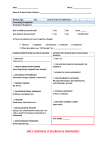
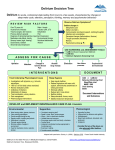
Delirium prevention care plan: template Delirium: diagnosis, prevention and management 2010 NICE clinical guideline 103 1 This delirium prevention care plan accompanies the clinical guideline: ‘Delirium: diagnosis, prevention and management’ (available online at www.nice.org.uk/guidance/CG103). Issue date: 2010 This is a support tool to help people implement NICE guidance on the diagnosis, prevention and management of delirium. It should be read together with NICE clinical guideline 103. It is not NICE guidance. Implementation of the guidance is the responsibility of local commissioners and/or providers. Commissioners and providers are reminded that it is their responsibility to implement the guidance, in their local context, in light of their duties to avoid unlawful discrimination and to have regard to promoting equality of opportunity. Nothing in the guidance should be interpreted in a way that would be inconsistent with compliance with those duties. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence MidCity Place, 71 High Holborn, London WC1V 6NA; www.nice.org.uk © National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence, 2010. All rights reserved. This material may be freely reproduced for educational and not-for-profit purposes. No reproduction by or for commercial organisations, or for commercial purposes, is allowed without the express written permission of NICE. NICE clinical guideline 103: Delirium prevention care plan template 2 Delirium prevention care plan: template care plan Use this care plan template to help develop a local resource to aid care planning for people identified as at risk of delirium, with no indicators of delirium. This template could be incorporated into your existing care planning documents to ensure that all aspects of delirium prevention are considered. Assess patients’ risk of delirium with the NICE ‘Delirium admission assessment’ tool (available from www.nice.org.uk/guidance/CG103). Attach the completed admission assessment form to this document. If the patient becomes at risk of delirium during their stay, attach the local assessment documentation to this document. This tailored multicomponent intervention package consists of assessment for clinical factors that may precipitate delirium along with interventions to address each of these factors. The package should be delivered by a multidisciplinary team trained and competent in delirium prevention. The care plan should be reviewed and updated daily. Make sure that the date and time that the care plan was created and the care plan number are recorded. Intervention – this is what the NICE guideline recommends in order to prevent delirium. If the intervention in sections 1.2 and 2.1 is not applicable, because the patient does not have the identified clinical factor, write ‘not applicable’ in the action taken box. Expected outcome (EO)* – this is what you wanted to achieve from delivering the intervention to the patient – for example, the patient does not become disorientated, or does not show any signs of infection. The outcome should be objective. Action taken* – these are the details of the action you have taken to ensure the patient receives the intervention. Extra lines have been created for when the action needs to be undertaken more than once in the day or where multiple actions are needed. Completed: signed and dated* – this represents when the actions needed to deliver the intervention have been completed. Expected outcome achieved* – this section ensures that the patient’s progress is reviewed regularly. If the patient’s condition deteriorates or the action taken does not produce the expected outcome, this should be escalated according to local protocols and documented in the patient’s notes. The * headings represent columns that should be completed locally in accordance with the patient’s needs. This document may need modifying if multiple actions are needed to deliver an intervention Using this template for care planning could help support the implementation of ‘Essence of Care: Benchmarks for the care environment’ (Department of Health, 2007). NICE clinical guideline 103: Delirium prevention care plan template 3 Date and time care plan written....................................... Care plan review date and time.........................................Care plan number........... 1.1 General interventions for prevention of delirium Intervention Expected outcome (EO) Action taken Completed: sign and date Ensure that patients at risk of delirium are cared for by a team of healthcare professionals who are familiar to the person at risk Avoid moving patients within and between wards or rooms unless absolutely necessary Observe for recent changes or fluctuations in usual behaviour at least daily Assess for all 10 clinical factors that may precipitate delirium (see 1.2.1 to 1.2.10 below) If clinical factor is present, implement recommended intervention and document in ‘action taken’ box. If clinical factor is not present, write ‘not applicable’ in action taken box NICE clinical guideline 103: Delirium prevention care plan template 4 EO achieved? 1.2 Tailored/specific interventions to address clinical factors identified for this person 1.2.1 Person has cognitive impairment and/or disorientation Expected outcome (EO) Action taken Completed: EO achieved? sign and date Person is dehydrated and/or Expected outcome constipated (EO) Action taken Completed: EO achieved? sign and date Provide appropriate lighting and clear signage. A clock and calendar should be easily visible. Consider providing a 24-hour clock in critical care Talk to the person to reorientate them. Explain where they are, who they are and what your role is Introduce cognitively stimulating activities (for example, reminiscence) Facilitate regular visits from friends and family 1.2.2 Ensure adequate fluid intake – encourage the person to drink. Consider subcutaneous or intravenous fluids if necessary Take advice if necessary when managing fluid balance in patients with comorbidities (for example, heart failure or chronic kidney disease) NICE clinical guideline 103: Delirium prevention care plan template 5 1.2.3 Person is hypoxic Expected outcome (EO) Action taken Completed: EO achieved? sign and date Expected outcome (EO) Action taken Completed: EO achieved? sign and date Expected outcome (EO) Action taken Completed: EO achieved? sign and date Assess for hypoxia and optimise oxygen saturation if necessary, as clinically appropriate 1.2.4 Person has an infection Look for and treat infection Avoid unnecessary catheterisation Implement infection control procedures in line with ‘Infection control’ (NICE clinical guideline 2) 1.2.5 Person has immobility or limited mobility Encourage patients to mobilise soon after surgery Encourage patients to walk (provide walking aids if needed – these should be accessible at all times) Encourage all patients, including those unable to walk, to carry out active rangeof-motion exercises NICE clinical guideline 103: Delirium prevention care plan template 6 1.2.6 Person is receiving multiple Expected outcome (EO) Action taken medications Completed: EO achieved? sign and date Review medications taking into account both the type and number of medications 1.2.7 Person is in pain Expected outcome (EO) Action taken Completed: EO achieved? sign and date Expected outcome (EO) Action taken Completed: EO achieved? sign and date Assess for pain Look for non-verbal signs of pain, particularly in people with difficultly communicating (for example, people with learning difficulties or dementia, and people on a ventilator or who have a tracheostomy) Start and review appropriate pain management for anyone in whom pain is identified or suspected 1.2.8 Person is poorly nourished Follow advice given on nutrition in ‘Nutrition support in adults’ (NICE clinical guideline 32) If patients have dentures, ensure they have their own dentures with them and that they fit properly NICE clinical guideline 103: Delirium prevention care plan template 7 1.2.9 Person has sensory impairment Expected outcome (EO) Action taken Completed: EO achieved? sign and date Expected outcome (EO) Action taken Completed: EO achieved? sign and date Resolve any reversible cause of the impairment, such as impacted ear wax Ensure hearing and visual aids are available to, and used by, patients who need them and that they are in good working order 1.2.10 Person has sleep disturbance1 Avoid nursing and medical procedures during sleeping hours Reduce noise to a minimum during sleep periods 1 For more information on good sleep hygiene, see ‘Parkinson’s disease’ (NICE clinical guideline 35). NICE clinical guideline 103: Delirium prevention care plan template 8 2.1 Person has developed indicators of delirium Note: Observe for recent changes or fluctuations in usual behaviour at least daily Intervention Action taken Completed: sign and date Arrange for a healthcare professional trained and competent in the diagnosis of delirium to do a clinical assessment to confirm diagnosis using the: o Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV) criteria or short Confusion Assessment Method (short CAM) o CAM–ICU for people in critical care or in the recovery room after surgery If diagnosis of delirium is confirmed, treat according to ‘Delirium’ (NICE clinical guideline 103) If distinguishing between the diagnoses of delirium, dementia or delirium superimposed on dementia is difficult, treat for delirium first (see ‘Dementia: supporting people with dementia and their carers in health and social care’ NICE clinical guideline 42) NICE clinical guideline 103: Delirium prevention care plan template 9 Other resources to support learning The following versions of NICE clinical guideline 103 are available from www.nice.org.uk/guidance/CG103: The NICE guideline – all the recommendations. A quick reference guide – a summary of the recommendations for healthcare professionals and patient pathway algorithms. ‘Understanding NICE guidance’ – information for patients and carers. The full guideline – all the recommendations, details of how they were developed, and reviews of the evidence they were based on. For printed copies of the quick reference guide or ‘Understanding NICE guidance’, phone NICE publications on 0845 003 7783 or email [email protected] and quote reference numbers N2224 (quick reference guide) and/or N2225 (‘Understanding NICE guidance’). Implementation tools NICE has developed tools to help organisations implement this guideline, available from www.nice.org.uk/guidance/CG103 Implementation advice – this provides practical suggestions for action to help those responsible for planning and implementing the guideline. In particular it details the ‘whole system’ approach which is required in order to prevent delirium. Standard slide set – highlights the key messages from the guideline. Costing tools – a costing statement giving an indication of the savings and costs associated with implementation, and a costing template allowing you to estimate the local costs and savings involved. Audit support and baseline assessment tool – for monitoring local practice and helping to identify which areas of practice may need more support, decide on clinical audit topics and prioritise implementation activities. Delirium admission assessment: template – a template assessment document for use when assessing people on admission for delirium. NICE clinical guideline 103: Delirium prevention care plan template 10 Delirium awareness workshop session plan and slide set. A structured workshop which can be used locally to raise awareness about delirium and delirium prevention Related NICE guidance Acutely ill patients in hospital. NICE clinical guideline 50 (2007). Dementia. NICE clinical guideline 42 (2006). Parkinson’s disease NICE clinical guideline 35 (2006). Nutrition support in adults. NICE clinical guideline 32 (2006) Violence. NICE clinical guideline 25 (2005). Contains more information about deescalation techniques Infection control. NICE clinical guideline 2 (2003) Acknowledgments Thank you to the: members of the National Clinical Guideline Centre members of the Guideline Development Group attendees of the planning meeting members of the External Reference Group who reviewed this tool Glossary Multidisciplinary team: a team of healthcare professionals with the different clinical skills needed to offer complete care to people with complex problems such as delirium. Long-term care: residential care in a home that may include skilled nursing care and help with everyday activities. This encompasses nursing homes and residential homes. NICE clinical guideline 103: Delirium prevention care plan template 11