* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 4 Test Review
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
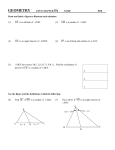
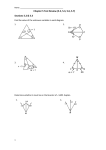
Name_________________________________________________ Date ____________ Period _____ Geo w/ Trig Unit 4 – Properties of Triangles – Test Review (Sections 4.1, 4.6, 4.2, 5.3, 5.5, 5.1, 5.2) Multiple Choice: Circle the correct answer. 1. If AD is an altitude of ABC, which 2. Which of the following do NOT represent the side lengths of a of the following must be true? triangle? (Draw a diagram to help!) A. AD DC 3. A(n) ___________ is a segment that contains a vertex of a triangle and the midpoint of the opposite side. A. 7, 11, 5 A. altitude B. BD DC B. 8, 9, 9 B. angle bisector C. ADC is a right angle C. 7, 8, 2 C. median D. BAD CAD D. 12, 6, 6 D. perpendicular bisector Matching: Use the diagram to match the segment with the correct vocabulary word. ______ 4. Perpendicular bisector A. AD ______ 5. Angle bisector B. CH ______ 6. Median C. EB ______ 7. Altitude D. FG For #8-9, be sure to mark the diagram! 8. If AD is an altitude of ABC, find the perimeter of ABC. 12x – 9 A 9. If GF is a median of GIT, find IT. G C (15x + 45)° 10x – 9 I 15 x+3 F 2x – 6 T D 9 B Now, list the angles of ABC in order from least to greatest. 10. Circle the sets of numbers that can represent the side lengths of a triangle. There are more than one! 13 ft, 43 ft, 37 ft 8 in, 23 in, 9in 2 cm, 2 cm, 1 cm 1 ft, 24 in, 18 in 6 m, 8 m, 14 m 5 km, 5 km, 5 km 11. What is the range of possible lengths for the third side? 12. In ΔRQP, QP = 15 ft, RP = 25 ft, and RQ = 13 ft. Order the angles from smallest to largest. 4.5 12 13. Given that three side lengths of a triangle are 13, 2x – 4, and 7, find all possible values of x. 14. Using ∆ABC, order the sides from largest to smallest. A 75 C 36 B 15. Triangle ABC has vertices at A(2, 8), B(8, 6), and C(4, 2). Plot the points and then draw in the specified segment. Be sure to label your diagram with ALL information! a) Draw the perpendicular bisector of AB. b) Draw the median from B. c) Draw the line containing the altitude from A. 16. a) Find the measure of each angle and write them ON the diagram. Then write them on the lines provided. mD = _________ mBCA ________ mDCA ________ mB ________ mDAC ________ mBAC ________ b) Use the labeled diagram to classify each triangle by its angles and sides. ΔABC: _________________ ,_____________________ ΔACD: _________________ ,_____________________ ΔBAD: _________________ ,_____________________ 17. Use the given diagram to find the side lengths or angles measures. a) Given: ΔFGH is an equilateral triangle. b) FG = ________ m1 _______˚ m2 _______˚ GH = ________ m3 _______˚ FH = ________ m4 _______˚ 18. Complete each statement below with sometimes, always, or never true. (Hint: Sketch diagrams OR replace the last word of the sentence with its definition and read the statement again.) a) Equiangular triangles are _________________ right triangles. b) Equilateral triangles are _________________ isosceles. c) Right triangles are _______________ acute. d) Acute triangles are ________________ isosceles. 19. Find the value of x and/or y. Then classify the triangle by its angles and sides, if possible. Be sure to mark your diagram! Show all work, including an algebraic equation. a) b) y˚ 50˚ c) d) e) f) (9y)˚ (2x + 5)˚ (3x – 15)˚ 20. Draw an example of each type of triangle below, if possible. Be sure to mark the diagram. If not possible, explain why not. a) Right scalene b) Right isosceles c) Obtuse isosceles d) Obtuse equilateral