* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Photovoltaic and dye-sensitized solar cells
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
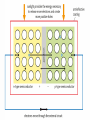
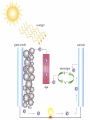
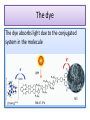
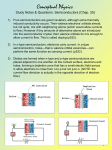
Energy topic 8 Photovoltaic and dye-sensitized solar cells Semiconductors Semiconductors • A solid substance that has a conductivity between that of an insulator and that of most metals, either due to the addition of an impurity or because of temperature effects. Devices made of semiconductors, notably silicon, are essential components of most electronic circuits. Semiconductors versus metals Low Temperature -Metals conduct electricity due to delocalised electrons -Semiconductors don’t really work at low temperatures High Temperatures -Metals still have same amount of delocalised electrons; however ions moving more so resistance increases which affects the overall conductivity -More electrons released from the material which increases its conductivity Silicon • Sp3 hybridised • No conductivity at absolute zero • As the temperature increases the electrons get freed and the conductivity increases • Its an intrinsic semiconductor as the energy comes from within • The number of positive holes equals the number of free electrons Doping N type’s electrical conductivity is due to negative carriers. (still uncharged) P type’s electrical conductivity is due to positive carriers (still uncharged) Silicon Diodes pn-junction Diodes • Here p-type and n-type semiconductors are joined together. • The principal characteristic of a pn-junction diode is that it allows current to flow easily in one direction but hardly at all in the other direction. We call these situations forward bias and reverse bias, respectively. • This means that it can convert alternating current into direct current Youtube video • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ar7xDMR 4P_U Questions Answers Photovoltic cell • Light causes electrons to gain energy • Electron leaves and an ion is left behind • Normally when the electron looses the energy (as heat) it will rejoin and form a neutral atom • This does not happen in a photovoltaic cell Photovoltic cell • Due to the electric field caused by the p-n junction current is produced • The electron will pass around the whole circuit before rejoining the atom Summary • Make a list of the advantages and disadvantages of photovoltaic cells Dye-sensitized solar cells A dye-sensitized solar cell (DSSC, DSC, DYSC or Grätzel cell) is a low-cost solar cell belonging to the group of thin film solar cells. It is based on a semiconductor formed between a photosensitized anode and an electrolyte, a photoelectrochemical system. Anode – porous layer of titanium dioxide Cathode – Transition metal wire The dye The dye absorbs light due to the conjugated system in the molecule Questions Solution Summary • What are the advantages and disadvantages of dye-sensitized solar cells