* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reconstruction
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Freedmen's Colony of Roanoke Island wikipedia , lookup
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Carpetbagger wikipedia , lookup
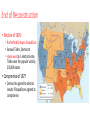
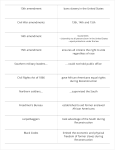
Reconstruction 1865-1876 The aftermath of the Civil War Lincoln’s View • US as “one indivisible nation” had prevailed • Plan to quickly restore state governments loyal to the Union • Lincoln’s plan was jeopardized by his assassination • John Wilkes Booth • Ford’s Theater • April 14, 1865 Why “Reconstruction?” South is in RUINS Why Reconstruction? • Roads, bridges, buildings, and machinery were destroyed. • Once-rich farm fields were barren or weed choked • Confederate money was worthless • Farmers and planters had no money or credit to buy seeds and tools so they could start growing crops again • The vast labor pool of slaves had dried up. Radical Republicans want: • To punish states that seceded (ANGRY with South) • To ensure equal voting rights for African Americans • They clash with Lincoln’s successor: Andrew Johnson Andrew Johnson • Impeached by Radical Republicans 1868 • Not removed from office • Senate voted to acquit President Andrew Johnson by a margin of 35 guilty to 19 not guilty - one vote short of the two-thirds needed to convict. Text Book Assignment: Complete Sentences (except definitions) • Define vocabulary listed in sidebar on pages: 402, 410, 419 • Check Point Questions: 403, 405, 406, 409, 412, 415, 416, 418, 421, 424, & 427 • Explain what the following people contributed to Reconstruction: • Ulysses S. Grant • Frederick Douglass • Robert E. Lee The Civil War Amendments • 13th Amendment: • Abolish slavery permanently in the US • 14th Amendment: • States prohibited from denying equal rights under the law to any American • Some Southern states immediately implement “Black Codes” • These limit rights for African Americans • 15th Amendment: • Voting rights were guaranteed regardless of “race, color, or previous degree of servitude.” Black Codes differed by state laws designed to regulate the lives of the former slaves: • Employment was required of all freedmen; violators faced vagrancy charges • Freedmen could not assemble without the presence of a white person • Freedmen were assumed to be agricultural workers and their duties and hours were tightly regulated • Freedmen were not to be taught to read or write • Public facilities were segregated • Violators of these laws were subject to being whipped or branded. End of Reconstruction • Election of 1876: • Rutherford B. Hayes, Republican • Samuel Tilden, Democrat • Hayes won by 1 electoral vote, Tilden won the popular vote by 250,000 votes. • Compromise of 1877 • Democrats agreed to election results if Republicans agreed to compromise. Compromise of 1877 opens the door to the “Jim Crow Era” and began a long period in the South where African Americans were denied full rights of American citizenship. • To withdraw federal soldiers from their remaining positions in the South • To enact federal legislation that would spur industrialization in the South • To appoint Democrats to patronage positions in the South • To appoint a Democrat to the president’s cabinet. Economic Impact of War and Reconstruction North and Midwest South • Strong, growing industrial economies • Devastated by war, infrastructure destroyed • Labor force gone because of end of slavery and casualties of war • Remained agriculturally based economy and poorest part of country • Will cause the US to emerge as a global economic power Transcontinental Railroad: • Increases Westward movement towards the Pacific • Completed soon after war ends Social Impact of War and Reconstruction • African Americans: • Emancipation Proclamation allows them to serve in Union Army • Civil War Amendments end slavery • Black Codes restrict rights in South • Women: • Managed homes and families with little resources • Faced poverty and hunger • Found new roles in agriculture, nursing, and war industries Social Impact of War and Reconstruction • Common Soldier: • Warfare = gruesome hand to hand combat • Diaries and letters home record this • Left psychological scars • Returned home to find homes gone • Left with permanent disabilities Robert E. Lee • Urged Southerners to reconcile and rejoin U.S. • President of Washington and Lee University • Emphasized the importance of education in nation’s future Frederick Douglass • Supported full equality for African Americans • Urged passage of 14th and 15th Amendments • Encouraged government actions to protect rights of freedmen • Served as ambassador to Haiti Ulysses S. Grant • Urged Radical Republicans not to be harsh with former Confederates • Elected president 1869-1877 • Advocated rights for freedmen • Opposed revenge on the South New Vocab: • Scalawags--southern whites who supported republican policy throughout reconstruction • Carpetbaggers--northern whites who moved to the south and served as republican leaders during reconstruction or took advantage of vulnerable economy • Sharecropping--system in which landowners rented a few acres of land to farmworkers in return for a portion of their crops Reconstruction Poster • Title • Dates • Johnson’s View • Radical Republican View • What reforms were actually passed? • Explain the three Civil War Amendments • Explain the Compromise of 1877 and End of Reconstruction • Include Douglass’, Lee’s, and Grant’s view • Pictures and color to accent important information