* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Relays
Telecommunications engineering wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electrician wikipedia , lookup
Electrical engineering wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Utility pole wikipedia , lookup
Ignition system wikipedia , lookup
Resonant inductive coupling wikipedia , lookup
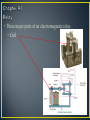
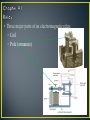
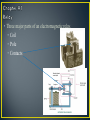
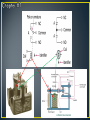
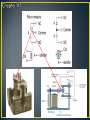
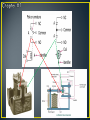
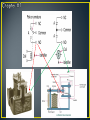
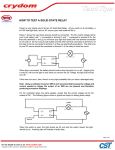
• Control method for machinery that creates a sequential operation of events. • The RELAY is the major component for this control method. • The main purpose of a PLC was to replace the relay. • The relay is a mechanic device that wears out • Changing the relay control structure required shutting down the line (equipment) and rewiring • PLC relays are bits inside the computer that can be turned off and on millions of times, changes to the program can be made in minutes without physical rewiring • An electromagnetic device. • A device that requires the flow of current to produce a magnetic field. • Magnetic field will cause mechanical movement. • Need a potential difference to produce current. • Need current to produce a magnetic field. • Need a magnetic field to produce mechanical movement. • Three major parts of an electromagnetic relay. • Coil • Three major parts of an electromagnetic relay. • Coil • Pole (armature) • Three major parts of an electromagnetic relay. • Coil • Pole • Contacts • Coil • Fine wire wrapped around a steel or iron core. • Current flows through wire to produce a magnetic field. • Coils will have a voltage rating. Typical ratings: 120VAC, 24VDC, 12 VDC and 6 VDC. • Coil • Sample data sheet of a relay coil. • Potter/Brumfield Relay • Pole • Part of relay that moves. • Electrical terminal connection to POLE is called a common. • Other names for a POLE: • Armature and clapper. • Contacts • Part of relay that makes an electrical connection out to a load. • Contacts are controlled by the coil. Contacts will only change state when the coil is energized. • A contact can be: • NC ~ Normally closed • Contacts are closed when no current through coil. • Contacts are open when current flows through coil. • NO ~ Normally open • Contacts are open when no current through coil. • Contacts are closed when current flows through coil. • Relay manufacturers use a common code to simplify the identification of relays. • This code uses a form letter: • Form A: One contact that is normally opened NO. • Form B: One contact that is normally closed NC. • Form C: Has one pole that will provide one NO and one NC set of contacts. • Contacts • The electrical terminal connection of a relay contact is called a throw. • Contacts • The electrical terminal connection of a relay contact is called a throw. • Relay contacts will have a voltage and current rating. • Drawing symbols Electronic Symbols Control Symbols • Drawing symbols Relays on electrical prints are always drawn in an un-energized state. Electronic Symbols Control Symbols • Relay Nomenclature • Single Pole, Single Throw ~ SPST • One armature that has only one electrical terminal. • Relay Nomenclature • Single Pole, Single Throw ~ SPST • One pole that has only one electrical terminal. • Example: • Relay Nomenclature • Double Pole, Single Throw ~ DPST • Two poles that each have only one electrical terminal. • Relay Nomenclature • Double Pole, Single Throw ~ DPST • Two armatures that each have only one electrical terminal. • Example: • Relay Nomenclature • SPST • DPST • SPDT • DPDT • Relay Nomenclature • Break • Number of places the a pole opens or closes an electrical circuit. • Single Break: • Double Break: • Double break reduces arcing as the contacts are separated allowing the relay to operate with high voltages • Relay Nomenclature • Pole – Throw - Break *Application for relay controls. *When relay A is energized: *Contact A1 will close and place voltage across solenoid valve. *Application for relay controls. *When relay A is energized: *Contact A1 will close and place voltage across solenoid valve. Control Drawing Electrical Drawing Control Drawing Task: ◦ Switch S1 will enable control relay CR ◦ CR will activate solenoid SOL 1 and motor control relays MCR 1 and MCR 2. ◦ If water level falls below level probe LP then only run pump #1 and shut off pump #2. ◦ Create a control schematic.