* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Year 9 Extended
Foundations of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Bra–ket notation wikipedia , lookup
History of logarithms wikipedia , lookup
Big O notation wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
History of the function concept wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental theorem of algebra wikipedia , lookup
Principia Mathematica wikipedia , lookup
List of important publications in mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
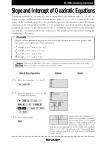
Mathematics DPT Year 7 Unit Content Number 1 Decimal system, place value, ordering and rounding Number2 Decimal numbers, rounding Shape, Space and Measures 1 Units, Perimeter and Area Number 3 Six operations, BIDMAS, directed numbers, co-ordinates Algebra 1 Algebraic expressions and formulae Handling Data Collecting, Organising, Displaying and Analysing Data Shape, Space and Measures 2 Angles, Shapes and Construction Year 8 Unit Content Number 1 Integers, fractions, decimals, powers and roots Number 2 Decimals, Indices and Standard Form Algebra 1 Expressions and formulae Handling Data 1 Probability Shape, Space and Measures 1 Angles, shapes and constructions Number 3 Percentages, Ratio and Proportion Shape, Space and Measures 2 Symmetry and Transformations Algebra 2 Equations and inequalities Shape, Space and Measures 3 Perimeter, area and volume Year 9 Extended Unit Content Number 1 Basic number work, rounding and accuracy Algebra 1 Algebraic manipulation 1 Shape, Space and Measures 1 Algebra 2 Angles, shapes and constructions Circle Theorems Linear equations, inequalities and formulae Shape, Space and Measures 2 Number 2 Pythagoras and Trigonometry (right angled triangles) Handling Data 1 Probability Algebra 3 Algebraic manipulation 2 Handling Data 2 One variable statistics Shape, Space and Measures 3 Perimeter, Area and Volume Sets of numbers and set theory Year 9 Core (James´s group) Unit Content Number 1 Basic number work, rounding and accuracy Algebra 1 Algebraic manipulation 1 Shape, Space and Measures 1 Angles and shapes Handling Data 1 Probability Number 2 Sets of numbers and set theory Algebra 2 Linear equations, inequalities and formulae Shape, Space and Measures 2 Pythagoras and Trigonometry (right angled triangles) Algebra 3 Straight line graphs Year 11 Studies Unit Content Number 1 Sets Approximation Standard form Currency conversions Algebra 1 Arithmetic series Geometric series Sets and Logic Set theory Logic theory Probability Probability Coordinates in two dimensions Equation of a straight line Coordinate geometry Simultaneous equations Linear functions Functions Domain and range Plot functions Quadratic functions Quadratic equations Quadratic functions One variable statistics Types of data Organising data Displaying data Cumulative frequency Measures of central tendency Year 11 Standard Unit Content Revision Revision: algebra. Sets of numbers. Real numbers. Surds. Equation of a straight line. Functions 1 Functions, function notation, images. Domain, range, roots, max and min values. Equations and graphs of a variety of functions Use of GDC. Composite functions. Inverse function. Transformations of functions: translations, stretches, reflections in the axes. Functions 2: Transformations 1 The graph of y f ( x) as the reflection in the line y =x of the graph of y = f (x) . Composite transformations. Use of GDC and Geogebra. Different forms of the quadratic function: f ( x) ax 2 bx c , f ( x) a( x h)2 k , f ( x) a( x )( x ) Functions 3: Quadratic functions Graphs of quadratic functions. Vertex, axes intercepts, axis of symmetry. Quadratic equations. The quadratic formula. The discriminant b 4ac and the nature of the roots. Application of quadratic functions. Other polynomial functions. 2 Functions 4: Exponential and logarithmic functions Laws of exponents; exponential equations. Exponential functions and their graphs. Horizontal asymptote. Definition of logarithms. Laws of logarithms. Logarithmic functions and their graphs. Logarithmic equations. Vertical asymptote. Relationships between these functions. a x e x ln a ; log a a x x, a loga x x, x 0 The number e. Natural logarithms. Change of base. Applications: Growth and decay problems. Unit Content 1 x ,x0 x The reciprocal function : its graph and self-inverse nature. Functions 5: Rational functions x ax b cx d and its The rational function graph. Vertical and horizontal asymptotes. Informal idea of limits. Limit notation. Polynomial and rational functions f ( x) lim( Calculus 1 f ( x h) f ( x ) ) h h 0 Definition of derivative as Derivative interpreted as a gradient function and as a rate of change. Tangent and normal lines. The second derivative. Higher derivatives. Maximum and minimum points. Points of inflexion. f , f , f . Optimization. Graphical behaviour of Applications to kinematics. Function analysis Differentiation rules The circle: radian measure of angles. Length of an arc; area of a sector. The unit circle. Definition of sine and cosine in the unit circle. Definition of sin x 2 2 tangent as cos x . The Pythagorean identity sin cos 1 . 0, Trigonometry 1 Exact values of the trigonometric ratios multiples. , , , 6 4 3 2 and their Simple trigonometric equations with an without calculator i.e sin x 0.6 ; cos x 2 2 in the interval 0, 2 . Trigonometric functions: their domains and ranges; amplitude, their periodic nature. Their graphs. Transformations of trigonometric functions. Unit Content Statistics 1: Bivariate data Linear correlation of bivariate data. Pearson’s product–moment correlation coefficient, r. Scatter diagrams; lines of best fit. Equation of the regression line of y on x. Use of the equation for prediction purposes. Interpolation, extrapolation. Mathematical and contextual interpretation. Year 11 Higher Unit Content Algebra Revision Expansion of brackets. Simultaneous equations. Radical equations and extraneus solutions. Algebra of linear and quadratic expressions The real number line and corresponding interval notation. Linear inequalities, including their graphical representation. Number systems, rational and irrational numbers. Surds as one subset of irrational numbers. The definition of the absolute value of a number. Equations with absolute value. Absolute value inequalities. Quadratic equation. Quadratic formula and the discriminant. Completing the square. Quadratic function. Sketching the graph of a quadratic function. Quadratic inequalities. Simultaneous equations involving linear and quadratic equations. Definition of polynomial functions. Synthetic division. The remainder and the factor theorems. Polynomial inequations. Sketching polynomials and graphical significance of roots: unique single factors, repeated squared factors, repeated cubed factors. Algebra of polynomials Binomial theorem The binomial theorem. Pascal´s triangle to find the coefficients. The general term. Combinatorial numbers. Sequences and Series Arithmetic and geometric sequences. Sum of finite and infinite geometric series. Compound interest and superannuation. Exponential and logarithmic functions Revision of indices. Exponents and logarithms. Logarithmic function and its inverse. Laws of exponents. Laws of logarithms. Change of base. Concept of domain, range, image value. Identification of horizontal, vertical and oblique asymptotes. Composite functions and inverse functions. Domain restriction. The graph of a function. The quadratic function in its three forms, in standard form, vertex form and x-intercepts form. Solution of f(x)=g(x) graphically and analytically. Solution of f(x)=0 to a given accuracy. The circle as an example of a many to many relation. Equation of the circle and mid-point. Functions and Relations Transformations of graphs Transformations of standard functions, absolute value function, reciprocal, polynomial, etc. Horizontal and vertical translation. Dilation parallel to the x- and y- axis. Reflections in coordinate axes and the graph of the inverse function as the reflection in the line y=x. The reciprocal of a function. Mathematical Induction Proof by mathematical induction. Forming conjectures to be proved by mathematical induction. Circular trigonometric functions The circle: radian measure of angles, length of an arc, and area of a sector. Definition of (cos x, sin x) in terms of the unit circle. The six circular functions: sin x, cos x, tan x, csc x, sec x, cot x; their domains, ranges, periodic nature graphs. The Algebra of Complex Numbers Introduction to complex numbers and notation. The real imaginary part of a complex number in the form z=a + bi. Operations of complex numbers. Geometrical representation of complex numbers: the modulus of z and the Polar form of complex numbers z = (cosα + isinα). De Moivre's theorem, proof by mathematical induction. Polynomials over the complex field. nth roots of unity. Vectors as displacements in the plane and in three dimensions. components of a vector. Column representation. Vectors The sum of vectors, the zero vectors, the inverse vector. Multiplication by a scalar. Magnitude of a vector. Position vector Unit vectors i, j, k.