* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geometry 10.5 student copy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
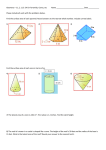
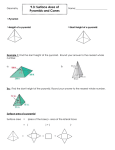
10-5 Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones 10-5 Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones Objectives Learn and apply the formula for the surface area of a pyramid. Learn and apply the formula for the surface area of a cone. Vocabulary vertex of a pyramid right cone regular pyramid oblique cone slant height of a regular pyramid slant height of a right cone altitude of a pyramid altitude of a cone vertex of a cone Holt Geometry The vertex of a pyramid is the point opposite to the base of the pyramid. The base of a regular pyramid is a regular polygon, and the lateral faces are congruent isosceles triangles. The slant height of a regular pyramid is the distance from the vertex to the midpoint of an edge of the base. The altitude of a pyramid is the perpendicular segment from the vertex to the plane of the base. Holt Geometry 10-5 Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones 10-5 Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones Practice: Finding Lateral Area and Surface Area of Pyramids 1. Find the lateral area and surface area of the regular pyramid. Round to the nearest tenth, if necessary. Step 1 Find the lateral area. Step 2 Find the surface area. Holt Geometry Holt Geometry 10-5 Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones 10-5 Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones Practice: Finding Lateral Area and Surface Area of Pyramids 2. Find the lateral area and surface area of a regular pyramid. Step 1 Find the lateral area. The vertex of a cone is the point opposite the base. Step 2 Find the surface area. The axis of a cone is the segment with endpoints at the vertex and the center of the base. The axis of a right cone is perpendicular to the base. The axis of an oblique cone is not perpendicular to the base. Holt Geometry Holt Geometry 10-5 Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones 10-5 Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones Practice: Finding Lateral Area and Surface Area of Right Cones 3. Find the lateral area and surface area of the cone. The slant height of a right cone is the distance from the vertex of a right cone to a point on the edge of the base. The altitude of a right cone is a perpendicular segment from the vertex of the cone to the plane of the base. Holt Geometry Holt Geometry 10-5 Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones 10-5 Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones Practice 4. Find the lateral area and surface area of the right cone. Holt Geometry Practice: Exploring Effects of Changing Dimensions 5. The base edge length and slant height of the regular hexagonal pyramid are both divided by 5. Describe the effect on the surface area. Holt Geometry 10-5 Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones 10-5 Surface Area of Pyramids and Cones Practice Practice Find the surface area of the composite figure. Find the surface area of the composite figure. 6. 7. Holt Geometry Holt Geometry