* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download KEY - Cobb Learning
History of virology wikipedia , lookup
Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
Trimeric autotransporter adhesin wikipedia , lookup
Quorum sensing wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Microorganism wikipedia , lookup
Typhoid fever wikipedia , lookup
Phospholipid-derived fatty acids wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Disinfectant wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial cell structure wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Marine microorganism wikipedia , lookup
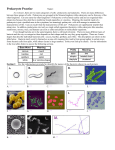
Bacteria: Round, Rod or Spiral? Dichotomous Key Introduction: Thousands of different types of bacteria are known and have been observed, and there are possibly many more that have not yet been observed. How can a scientist tell these organisms apart when they are so small? One way is the bacteria's characteristic shape or pattern of joining together in groups. Objective: TLW identify bacteria names by using a dichotomous key and by observing the shape and pattern of the bacteria. Procedure: Using the key, name the eleven organisms drawn below KEY 1. a. the general shape of the bacterium is round…………………….………………..go to # 2 b. the general shape of the bacterium is rod-like (long & straight)……………..…go to # 5 c. the general shape of the bacterium is spiral……………..Treponema pallidum (syphylis) 2. a. grouped in pairs………………………………………………..………………….go to # 3 b. grouped in chains…………………………..………………………………….....go to # 4 c. grouped in clumps………………………………………..Staphylococcus aureus (Boils) 3. a. without a heavy cover……………………..…Diplococcus menigitidis (Spinal meningitis) b. with a heavy cover………………………..…..… Diplococcus pneumoniae (Pneumonia) 4. a. large in size………………………………..…….…...Streptococcus pyogenes (Tonsillitis) b. small in size………………………..…… Streptococcus lactis (Used to make buttermilk) 5. a. rods are in chains…………………………………….……. Bacillus anthracis (Anthrax) b. rods are in pairs…………………………….... Bacillus lactis (Used to make sauerkraut) c. rods are single………………………………………………….….……………..go to # 6 6. a. rods have hairs (cilia)…………………………….….… Bacillus typhosa (Typhoid fever) b. rods have a bulge (spore) in middle…………… Bacillus botulinum (Botulism poisoning) c. rods have a bulge (spore) at end……………….…….……….... Bacillus tetani (Tetanus) 1. ________________________ 7. ________________________ 2. ________________________ 8. ________________________ 3. ________________________ 9. ________________________ 4. ________________________ 10. ________________________ 5. ________________________ 11. ________________________ 6. ________________________