* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Math 10th grade LEARNING OBJECT To solve problems involving
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
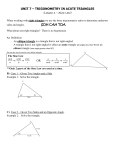
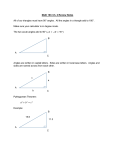
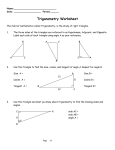
Math 10th grade LEARNING UNIT A world of relationships using triangles! S/K LEARNING OBJECT To solve problems involving the use of oblique triangles SKILL 1: Recognize the elements that make up the scalene triangle. SKILL 2: Relate the known data with the variable to be found, using the law of sine and / or law of cosine. Language Socio cultural context of the LO Curricular axis Standard competencies Learning object Basic Learning Rights Background knowledge Vocabulary box SKILL 3: Apply the laws of sine and cosine in problem solving situations. English School, classroom Spatial thinking and geometric systems Solve and formulate problems using criteria of congruence and similarity in triangles, never forgetting to support answers. To solve problems involving the use of oblique triangles Understand and use the law of sines and cosines to solve math problems and other disciplines involving non-right triangles Measuring and comparing angles, functions and trigonometric ratios, Pythagorean Theorem. Hobby: Recreational activity. Leisure Square root: Mathematical process to find the number multiplied by itself. Journey: Long path travelled GPS: Global Positioning System Aircraft: Aerial means of transportation. Airplane Kites: Rhombus-shaped flying device. English Review Topic Counterweight: Weight used to create an opposite force. Prepositions – Place (Position and Direction) NAME: GRADE: Introduction Photography is a very common hobby that allows people to remember lived experiences. Phillipe is on the top of a mountain taking pictures. He can see two towns: San Antonio and La Fuente (as seen below). Mountain image Town image The distance from San Antonio to La Fuente is 10 Km. Is it possible to find the altitude of Felipe’s position on the mountain? Can we find the distance from San Antonio to Felipe’s position? Can we find the mountain’s angle of inclination on San Antonio’s side? Objectives To find the sides and angles of an oblique triangle using the laws of sine and cosine. To identify the elements of an oblique triangle. To recognize the four cases of oblique triangles. To solve oblique triangles where three measurements are given by means of the laws of sine or cosine. To analyze problems using the laws of sine and cosine. To explain results of calculations based on arguments. ACTIVITY 1 Skill 1: Recognize the elements that make up the scalene triangle. OBLIQUE TRIANGLES Remember that! To develop the following topic we will use the following notation: A is the angle formed by sides b and c, B is the angle formed by sides a and c, and C is the angle formed by sides b and a. The oblique triangles have no right angles (90°), like right triangles do; they can be solved using the laws of sines or cosines, as appropriate. An oblique triangle is composed of three internal angles A, B, C and three sides a, b, c as illustrated in Figure 3. Figure. Example of an oblique triangle Learning Activity Circle all the oblique triangles. SINE LAW 𝒂 𝒃 𝒄 = = 𝒔𝒆𝒏 𝑨 𝒔𝒆𝒏 𝑩 𝒔𝒆𝒏 𝑪 ACTIVITY 2 FOUR CASES OF OBLIQUE TRIANGLES Remember that a triangle has three sides (L) and three angles (A). To solve problems involving oblique triangles we must know three measurements, therefore we will take into account the following considerations. Figures. SINE AND COSINE LAW Skill 2: Relate the known data with the variable to be found, using the law of sine and / or law of cosine. SINE LAW 𝒂 𝒃 𝒄 = = 𝒔𝒆𝒏 𝑨 𝒔𝒆𝒏 𝑩 𝒔𝒆𝒏 𝑪 Example: Solve for the following oblique triangle C b 45 cm a 84° 35° A c B Solution: Calculate b 45 𝑏 = 𝑠𝑒𝑛 84 𝑠𝑒𝑛 35 𝑏= 45∗𝑠𝑒𝑛84 𝑠𝑒𝑛 35 Replace the values of A, a, B in the sine law equation Solve for b and calculate the value 𝑏 = 78.02 cm Calculate C 𝐴+𝐵+𝐶 =0 35° + 84° + 𝐶 = 180° 35° + 84° + 𝐶 = 180° Based on this relation… Replace the values of A and B Solve for C and calculate the value 𝐶 = 180° − 35° − 84° 𝐶 = 61° Calculate c 45 𝑐 𝑠𝑒𝑛 35 𝑏= = 𝑠𝑒𝑛 61 45∗𝑠𝑒𝑛61 𝑠𝑒𝑛 35 Solve for c Solve for c and calculate the value 𝑏 = 68.6 cm Did you know that...? If you have the calculator in radians, the result is different than when the calculator is in degrees. Keep the calculator in degrees when performing the calculations proposed in the activities. COSINE LAW 𝑎2 = 𝑏 2 + 𝑐 2 − 2𝑏𝑐 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝐴 𝑏 2 = 𝑎2 + 𝑐 2 − 2𝑎𝑐 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝐵 𝑐 2 = 𝑎2 + 𝑏 2 − 2𝑎𝑏 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝐶 Example: Solve for the following oblique triangle Solution: Calculate a Replace the values of A, b, c in the cosine law equation 𝑎2 = 72 + 132 − 2 ∗ 7 ∗ 13 𝑐𝑜𝑠 30° Calculate the approximate value of a2 2 𝑎 ≈ 60 Solve the square root 𝑎 = √60 ≈ 7.7 Calculate the smallest angle, in this case: B 7.7 7 = 𝑠𝑒𝑛 𝐵 𝑠𝑒𝑛 30 𝑠𝑒𝑛 𝐵 = 7∗𝑠𝑒𝑛30 7.7 = 0.45 𝐵 = 𝑠𝑒𝑛−1 (0.45) ≈ 27 Solve for SenB and calculate Solve for B and calculate sen-1 0.5 Calculate angle C by adding the angles 𝐴 + 𝐵 + 𝐶 = 180° 𝐶 = 180 − 27 − 30 𝐶 = 123 Replace the values of A and B, solve for c Calculate the value Learning Activity: 1. The following is an oblique triangle Using the sine law, find the approximate value. B is __________ 𝑎 is __________ c is ___________ 2. Match the triangle to the missing values 𝐵 = 40°, 𝑎 = 13.5, 𝑐 = 15.3 𝐵 = 35°, 𝑎 = 25, 𝑐 = 13.8 𝐵 = 71°, 𝑎 = 13, 𝑐 = 20 ACTIVITY 3 APPLICATIONS Skill 3: Apply the laws of sine and cosine in problem solving situations. APPLICATIONS OF SINE LAW Remember that… We use the sine law when we know one side and two angles (Case 1 SAA), and when we know two sides and an angle (but not the angle formed by the two sides (Case 2 SSA). Use the cosine law for Case 3 (SAS) and Case 4 SSS. Example: A car driving east observes the highest part of an antenna, with an orientation of 65° E. When the car has traveled 2300 m, the orientation of the upper part of the antenna is 48° east, as seen in the figure. The car continued its journey. What is the height of the antenna? Solution: Step 1. Use the sum of the interior angles of a triangle to find C 180 = 𝐴 + 𝐵 + 𝐶 𝐶 = 180° − 135 − 25 𝐶 = 20 Step 2. Using the sine law, calculate a (the position of the car from the top of the antenna). 𝑎 𝑐 = 𝑆𝑒𝑛 𝐴 𝑆𝑒𝑛 𝐶 𝑎= 𝑐 𝑠𝑒𝑛 𝐶 2300 ∗ 𝑠𝑒𝑛20 = 𝑠𝑒𝑛 𝐴 𝑠𝑒𝑛25 𝑎 ≈ 2842 Step 3. To find h, use the right triangle, therefore use the ratio: 𝑠𝑒𝑛 𝐻 = 𝑜𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 𝑠𝑖𝑑𝑒 ℎ𝑦𝑝𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑢𝑠𝑒𝑎 , where h is the opposite side and a the hypotenuse 𝐻 = 180° − 135° = 45° 𝑠𝑒𝑛 45° = ℎ 2842 ℎ = 2842 ∗ 𝑠𝑒𝑛 45 ℎ = 2010 𝑚 Conclusion The height of the antenna is 2010 m Did you know that...? Although aircraft have sophisticated equipment that provides them with information about their orientation (such as GPS) and can determine the position of the aircraft on the ground, planes deviate from their course due to factors such as weather and winds; however trigonometry helps aircraft not to lose their course. APPLICATIONS OF COSINE LAW The distance from Bogota to Barranquilla is 982.5 km. Due to weather conditions a plane deviates from its path. If it has travelled a distance of 850 Km and has 180 Km left to reach Barranquilla. What is the angle at which the pilot must turn to reach his destination? The following figure shows a diagram of the situation. Figure Solution Figure. The plane is located at point C, use the cosine rule the find the angle at which it must turn. 𝑐 2 = 𝑎2 + 𝑏 2 − 2𝑎𝑏 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝐶 Replace the values in the formula 982.52 = 1802 + 8502 − 2 ∗ 180 ∗ 850 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝐶 Solve for cos C 982.52 − 1802 − 8502 cos 𝐶 = 2 ∗ 180 ∗ 850 Calculate cos 𝐶 = 0.813 𝐶 = 𝑐𝑜𝑠 −1 0.813 = 35°36" We conclude that the pilot must turn with an angle of 35°36”when located at point C Learning Activity 1. From the example above use the law of cosine to calculate the angle (A) at which the plane deviates and the angle at which it reaches its destination (B). 2. A boy flies two kites at the same time. He has 380 feet of rope for one kite and 420 feet for the other. The boy estimates the angle between the two ropes is 30°. Calculate a. The distance between the two kites. b. The magnitude of the angles formed by the ropes and the distance between the kites. Exercise retrieved from Stewart, J., Redli, L., Watson., Precálculo Matemáticas para el cálculo, (5ta. Edición), México, CENGAGE Learning. SUMMARY Oblique triangles Suggested steps to find the answer Case I. SAA o ASA Calculate the remaining One side and angle using the sum of two angles the angles in a triangle. 𝐴 + 𝐵 + 𝐶 = 180° are given Calculate the remaining angles using the sine law. Case II. SSA Ambiguous case Two sides and one angle (other than Calculate the angle using the angle formed by the sine law. the sides) are Calculate the remaining given. angle using the sum of the interior angles. Calculate the remaining side using the sine law. Case III. SAS Calculate both sides Two sides and the using the sine law. angle formed by Calculate the smallest of them are given. both angles using the sine law. Calculate the remaining angle using the sum of the interior angles. Case IV. SSS Use the cosine law to All sides are given. calculate the biggest angle. Calculate any of the remaining angles using the cosine law. Calculate the last remaining angle using the sum of the interior angles. HOMEWORK 1. In groups of three, propose a situation where of the laws of sine and cosine are applied. 2. Draw the situation and set values so that there is a real answer. 3. Present the situation and your results to your classmates. EVALUATION I. WRITE TRUE (T) OR FALSE (F) WHERE IT CORRESPONDS. 1. Oblique triangles are known to have three acute angles. A. True B. False 2. We have an oblique triangle where the measurement of two angles (A, B) and a side (c) are given as illustrated in the figure To find the measurement of side b we must use the cosine law. A. True B. False 3. The following is an oblique triangle Suppose that the measurements of sides a and b are given, also the measurement of angle B, therefore to calculate the measurement of side b we use the laws of cosines. A. True B. False II. Fill in the blanks If we have all sides of an oblique triangle, we use the _________ law to calculate the angles. If we have two angles and any side of the triangle, we use the ________ law to find the missing information. III. In the next figure we see a crane with a counterweight. USING THE PREVIOUS INFORMATION, ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS: 6. To calculate the distance between the two ends of the crane (a) it is best to A. Use the sine law B. Use the cosine law C. Use the sine law and then cosine law D. Use neither of the laws 7. The steps to solve the problem (finding side a and angles B and C) are: A. Sine law, cosine law, sum of interior angles. B. Cosine law, sine law, sum of interior angles. C. Sine law, sum of interior angles, cosine law. D. Cosine law, sum of interior angles, sine law. 8. The approximate measurement of side a and angle B is: A. 66 cm y 37° B. 37 cm y 66° C. 20 cm y 132° D. 132 cm y 20° Bibliography Ayres, F., (1990), Trigonometría plana y esférica, Bogotá, McGraw – Hill Latinoamericana, S.A. Lial, M., Hornsby, J., Schneider, D., Dugopolski, M., Trigonometría, (8va. Edición), México, Pearson Educación. (2006), Stewart, J., Redli, L., Watson., Precálculo Matemáticas para el cálculo, (5ta. Edición), México, CENGAGE Learning. Realini, C.S. (21/05//2012). Teorema del seno y coseno. Plan Ceibal – Creative Commons: Reconocimiento – No comercial –Compartir bajo la misma licencia. http://www.ceibal.edu.uy/userfiles/P0001/ObjetoAprendizaje/HTML/Teor ema%20del%20seno%20y%20el%20coseno_Silvana%20Realini.elp/fich a.html. [Retrieved on: 02/04/2016]. RÍOS, Julio, "Problema con Ley de Senos" [video en línea], en: YouTube http://www.youtube.com/], Colombia, 17 de marzo de 2011. Disponible en Internet: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yizdJXO2yME&feature=related [Retrieved on: 02/04/2016]. Glossary Angle: Is formed by turning a ray around itself. Ambiguous case: Corresponds to the Case II (SSA), it can be one, two or no triangles. Degree: The most common unit to measure angles. It is written as 1° 1 and it represents 360 of the rotation. Radian: Unit used to measure angles. An angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle intercepts an arc as long as the radius of the circle and has a measure of 1 radian. Vocabulary Box Hobby: Recreational activity. Leisure Square root: Mathematical process to find the number multiplied by itself. Journey: Long path travelled GPS: Global Positioning System Aircraft: Aerial means of transportation. Airplane Kites: Rhombus-shaped flying device. Counterweight: Weight used to create an opposite force. English Review Prepositions – Place (Position and Direction)