* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IBD Cases - Amazon S3
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
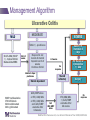
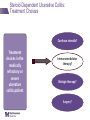
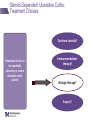
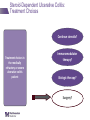
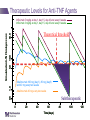
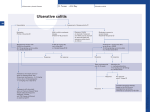
IBD Cases Stephen B. Hanauer, MD Professor of Medicine Feinberg School of Medicine Medical Director, Digestive Health Center 24 year old female States that she is “fatigued” 2-4 bloody, loose stools with urgency and cramping daily for 3 weeks No weight loss 24 year old female Past Medical History Unremarkable Family History No family history of IBD Social History No recent foreign travel, non-smoker Review of Systems Unremarkable Medications None Allergies None 24 year old female Vital Signs Abdomen Laboratory Findings BP: 110/60, P=80, afebrile Wt = 65 kg (no change from baseline) BS-present, soft nontender, no guarding or rebound tenderness and normal perianal examination Hematologic: • WBC = 8.9/mm3 • Hgb = 11.2 g/dL • Plt = 433/µL Renal and liver function: Normal Stool studies: • Enteric pathogens - Negative • Ova & parasites x 3 - Negative • C difficile toxin (A & B) - Negative 24 year old female DX: Moderate active left sided ulcerative colitis What options are available for treatment of this patient ? Management Algorithm Ulcerative Colitis MODERATE MILD SEVERE 5ASA +/- prednisone Oral 5-ASA/ SASP +/- topical 5-ASA Budesonide MMX Fail 2-4 weeks Respond to 1-2 rounds of steroid tapered over 6-8 weeks Continue 5-ASA Admit + IV steroids 3-5 days 2-4 weeks No response Unable to taper prednisone Steroid refractory Steroid dependent SASP=sulfasalazine IFX=infliximab ADA=adalimumab GOL=golimumab AZA/6MP alone or IFX/ ADA/GOL or IFX/ ADA/GOL and AZA/6MP evaluate after 12 weeks Fail AZA/6MP alone IFX/ADA/GOL +/-AZA/6MP evaluate after 12 weeks IFX therapy or cyclosporine +/- AZA Surgery No response Modified from Panaccione R, et al. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008;28:674-88. 24 year old female Mesalamine 2.4 g/d No significant improvement at 2 wks Treatment Follow-up at 6 weeks Mesalamine dose escalated to 4.8 g/d Due to persistent symptoms at 4 wks Budesonide MMX 9mg one po qd added Symptoms slightly improved some days 24 year old female For 2 months Symptoms Chief Complaint On mesalamine and Budesonide MMX (for 4 weeks) Transiently better but now continues to worsen 4 to 6 stools per day with occasional bleeding What should be done at this point ? What are her options? 1. Continue current therapy for 4 more weeks 2. Stop Budesonide MMX and treat with prednisone 3. Add 6MP or Azathioprine after checking TPMT 4. Switch Budesonide MMX to Budesonide EC 24 year old female Treated with prednisone 40 mg/day for 1 week duration Stool frequency decreased to one formed BM a day with no fecal urgency Began to taper prednisone at 5mg/day every week At a dose of 20 mg a day of prednisone disease she had recurrence of diarrhea (6 BM/day) with minimal bleeding, fecal urgency and tenesmus Steroid-Dependent Ulcerative Colitis: Treatment Choices Continue steroids? Treatment choices in the steroiddependent ulcerative colitis patient Immunomodulator therapy? Biologic therapy? Surgery? Steroid-Dependent Ulcerative Colitis: Treatment Choices Continue steroids? Treatment choices in the medically refractory or severe ulcerative colitis patient Immunomodulator therapy? Biologic therapy? Surgery? Steroid-Dependent Ulcerative Colitis: Treatment Choices Continue steroids? Treatment choices in the medically refractory or severe ulcerative colitis patient Immunomodulator therapy? Biologic therapy? Surgery? Steroid-Dependent Ulcerative Colitis: Treatment Choices Continue steroids? Treatment choices in the medically refractory or severe ulcerative colitis patient Immunomodulator therapy? Biologic therapy? Surgery? Who should NOT be offered continued medical therapy? • Emergent indications for surgery ‒ Fulminant disease activity unresponsive to maximal medical therapy ‒ Toxic megacolon ‒ Colonic perforation ‒ Massive hemorrhage • Elective indications for surgery ‒ ‒ ‒ ‒ ‒ Disease activity refractory to medical therapy Mucosal dysplasia Diagnosis of carcinoma Colonic stricture Growth retardation in children Ford D; American Society of Colon & Rectal Surgeons. Ulcerative colitis. Available at http://www.fascrs.org/physicians/education/core_subjects/2005/ulcerative_colitis/ Cyma RR, et al. Arch Surg. 2005;140:300-310. Colectomy for UC • Delay in surgery more important predictor of poor outcome than hospital volume • OR for death 2.12 (1.1-3.9) if colectomy after 6 days of hospitalization • OR increases to 2.89 (1.4-5.9) if colectomy after 11 days • Emergently admitted patients 5 times more likely to die compared to electively Kaplan G. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:680-687. Risk-Benefit Ratio of Surgery in UC Benefit • Probably reduces rate of mortality in the sickest patients • Considered “cure” for UC • Subtotal colectomy during acute phase – IPAA – Permanent ileostomy Risk • Post-surgical complications – Infection – Small bowel obstruction – Sepsis – Leak – Pouch dysfunction – Irritable pouch • Pouchitis/Cuffitis • Crohn’s disease • Reduced female fertility • Risk male erectile dysfunction Case 2 40-Yr-Old Man With Long-Standing Ileocolonic Crohn’s Disease s/p 2 ileocecal resections Recurrent disease in small and large bowel despite steroids and azathioprine 2.5 mg/kg with therapeutic 6-TGN levels Case 2 Treatment History Treated with single infusion of infliximab • Excellent response lasting ~6 mo Second infliximab infusion • Complicated by an acute infusion reaction • Response lasted ~8 wk Third infliximab infusion • Pretreated with prednisone, diphenhydramine, and acetaminophen • Flushing and headache • Response lasted ~4 wk Fourth infliximab infusion • Pretreated as above and increased dose to 10 mg/kg • Headache and flushing • Benefits lasted only 12 wk Case 2 What is the mechanism for his loss of response? Comments on Biologics •Despite “humanness” they are all immunogenic Immunogenicity is reduced by Immune suppressants….. •Anticipate dose adjustment with all •There will be diminishing returns with 2nd and/or 3rd agent Duration of Disease Refractory Disease Immunogenicity Therapeutic Levels for Anti-TNF Agents 5.0 10.0 50.0 Theoretical threshold 1.0 Adalimumab 160 mg (day 1), 80 mg (day8) and 40 mg every two weeks Adalimumab 40 mg every two weeks 0.5 Simulated anti-TNF biologic conc Infliximab 5 mg/kg at day 1, day 15, day 43 and every 8 weeks Infliximab 3 mg/kg at day 1, day 15, day 43 and every 8 weeks Subtherapeutic 0 20 40 60 Time (days) 80 100 120 Implications of Low Drug (trough) Levels •Disease Recurs No longer maintenance but re-treatment •Development of anti-drug antibodies Eventual loss of response Factors that Influence the Pharmacokinetics of Biologics Impact on Pharmacokinetics Presence of Anti-Drug Antibodies (ADAs) Decreases drug concentration Increases clearance Worse clinical outcomes Ordas I et. al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 10:1079-1087. 24 Factors that Influence the Pharmacokinetics of Biologics Impact on Pharmacokinetics Concomitant use of immunosuppressives Reduces ADA formation Increases drug concentration Decreases drug clearance Better clinical outcomes Ordas I et. al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 10:1079-1087. 25 Factors that Influence the Pharmacokinetics of Biologics Impact on Pharmacokinetics Low serum albumin concentration Increases drug clearance Worse clinical outcome High baseline CRP concentration Increase drug clearance High baseline TNF concentration May decrease drug concentration by increasing clearance Ordas I et. al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 10:1079-1087. 26 Factors that Influence the Pharmacokinetics of Biologics Impact on Pharmacokinetics High body size May increase drug clearance Sex Males have higher clearance Ordas I et. al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 10:1079-1087. 27 Case 2 Continued • How should loss of response in this patient be assessed? • What are your current options to treat him? Algorithm for loss of response to Anti-TNF Is there active disease? Yes No Measure Drug Level and AntiDrug Antibodies Therapeutic Levels IBD refractory to anti-TNF Alternative Class (e.g. vedolizumab) Undetectable Drug & undetectable ADA Suboptimal Dosing Increase Drug dose or frequency Undetectable Drug & Detectable ADA Loss of response due to ADA Switch within same Drug Class IBS SBBO Bile-acid diarrhea Strictures Case 2 continued • Patient was prescribed adalimumab • 160 mg at wk 0; 80 mg at wk 2; and then 40 mg EOW • He initially responded with resolution of diarrhea and abdominal pain • He then developed recurrent abdominal pain and loose stools Case 2 Continued • How should loss of response in this patient be assessed? • What are your current options to treat him? Case 2 Summary • Several mechanisms can lead to loss of response to a biologic For patients who respond to anti-TNF therapy and then lose response or become intolerant, switching within the anti-TNF class is a reasonable option • Absolute likelihood of response to second anti-TNF agent is lower than response in naïve patients Loss of response requires • Evaluation for active inflammation (eg, CRP, imaging, endoscopy) • Exclusion of inflammatory and non-inflammatory complications