* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 7.3
Propaganda in the Soviet Union wikipedia , lookup
Operation Torch wikipedia , lookup
Pursuit of Nazi collaborators wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of the Winter War wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
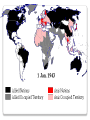
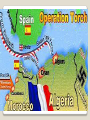
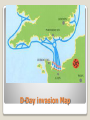
7.3 Explain how controversies among the Big Three Allied leaders over war strategies led to post-war conflict between the United States and the USSR, including delays in the opening of the second front in Europe, the participation of the Soviet Union in the war in the Pacific, and the dropping of atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki. Hitler and the Nazis hated Communism (Fascism hated communism) ***Yet Hitler didn’t want the Soviets fighting in 1939 ***Stalin wasn’t ready for entering war either ***Signed a Non-Aggression Pact (neither side would attack each other) Allied leaders, Churchill, Roosevelt, Stalin and DeGaulle met throughout the war to plan strategy and make post-war plans Major Points of the War ***Hitler attacked the Soviet Union in June of 1941. (violated Non-Aggression Pact) Stalin wanted the United States and the allies to go into France to open a second front. However, Churchill and Roosevelt did not feel their armies were ready for an invasion of France. Instead they attacked the Germans in North Africa because Axis control of the area prevented the Allies from using the Suez Canal. The Allies successfully launched ***Operation Torch in November of 1942. (Military operation to defeat Axis Powers in North Africa) Operation “Torch” Goal of Operation torch…takeover Northern Africa Then…. Attack Italy to invade Europe from the south Invasion of the Soviet Union and the Battle of Stalingrad June 1941 Hitler decided the time had come to attack Russia, violating the NonAggression Pact he signed with Stalin. The Germans quickly advanced into Russia raping, pillaging, executing, and burning large numbers of homes and people. (the favor was re-paid) ***Operation Barbarossa- name of Nazi operation to invade USSR The Germans spearheads got within 30 miles of Moscow when they were stopped by the Russian Army and a brutal winter. Nazi tanks invading the Soviet Union Russian Priest and Nazi Officer They were also stopped from capturing Stalingrad. The Russians held on to the city after fierce fighting and winter came to their aid. Then the Soviets attacked and surrounded a large German Army. Eventually, the Germans had to surrender and lost 100,000 men captured. ***This was the turning point of the war for the Russians (battle of Stalingrad). They were on the offensive from this point onward. Planning for D-Day- The Tehran Conference ***The Big Three- Stalin, Roosevelt, Churchill met at the Tehran Conference in December of 1943. Stalin was desperate for an invasion of France to open a second front. ***WOULD ONLY ACCEPT THE UNCONDITIONAL SURRENDER OF HITLER & the NAZIS ***Dwight D. Eisenhower was named commander of all allied forces in Europe for… ***Operation Overlord- military operation to invade northern Europe to defeat the Nazis. ***The allies assembled over 3 million men and on June 6th, 1944 the D-Day invasion got under way. After establishing a foothold at Normandy, France, the allied armies started to march across France. On August 25th, 1944 Paris was liberated. D-Day invasion Map D-Day Memorial in Bedford, VA The Big Three The Battle of the Bulge: The Germans fought fiercely as the allies pushed into their homeland. ***They mounted one last ditch German offensive and tried to divide the allied armies. The Germans never pierced the lines, but they did create a huge bulge in the lines. ***This battle signified the beginning of the end for the Germans ***Now Allies are marching from the South (Italy), West (France), and East (Russia) towards Berlin Battle of the Bulge American soldiers advancing on Germany War in the Pacific ***The Japanese attacked the U.S. held island at Midway and were heavily favored to win. However, and unexpected US victory stopped the Japanese advance in the Pacific and out them on the defensive. From this point on the U.S. began a process of ***Island Hopping- attacking one island at a time and securing it to get closer to Japan ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Guadalcanal The Philippines Iwo Jima Okinawa Winning the War in the Pacific Okinawa was at the southern end of the Japanese homelands. The next step would be to invade Japan itself. The battles of the island hopping campaign demonstrated the tenacity of the Japanese soldier. It was estimated that 1,000,000 U.S. causalities would be sustained. There was another option opened up by the ***Manhattan Project that developed and tested this first Atomic Bomb in New Mexico ***The new President Harry Truman ordered the two bombs be dropped and on August 6th, 1945 Hiroshima was bombed. On August 9th Nagasaki was bombed. ***Japan surrendered on August 14th, 1945 (V-J Day) and World War II was over. Manhattan Project Lab Tested in the New Mexico desert Hiroshima bombing Enola Gay (plane that dropped A-bomb on Hiroshima Japan officially surrendering to end WWII Japanese surrender aboard USS Missouri