* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download History 155 American Business History Lecture 6
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
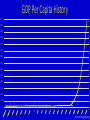
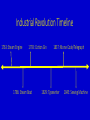
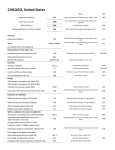
History 155 American Business History Lecture 6 Overview of the Industrial Revolution Shelley Morrisette Review of Prior Lectures and Readings: Whaling Industry Wealth of Nations The Business of Slavery American Mercantilism Free Trade Industrial Revolution Images Objectives for the Lecture: Why was the Industrial Revolution a Revolution? It may appear as an evolution, but it impacts the population in an immediate and revolutionary manner! GDP Per Capita History 7000 6800 6500 6000 5500 5000 4500 4000 3800 3500 3000 2500 2000 1650 1500 1000 500 0 679 92 92 93 103 103 112 112 113 113 116 116 109 109 138 141 160 190 Source: Brad DeLong GDP/Per Capita by year Year GDP/Per Capita Year GDP/Per Capita -1000000 92 1200 109 -300000 92 1400 109 -25000 93 1500 138 -10000 103 1600 141 -5000 103 1700 160 -2000 112 1800 190 -1000 112 1900 679 0 113 1950 1650 200 113 1975 3800 800 116 2000 6800 1000 116 Source: Brad DeLong GDP Per/Capita 2014 1. 2. 3. Qatar Luxembourg Singapore $143,427 $92,049 $82,762 6. Norway $66,937 10. United States $54,597 89. China $12,010 125. India $5,327 198. Central African Republic $600 Source: WHO How long does it take to earn an hour of light? Today: ½ second of work (new bulb) 1950: 8 seconds of work (incandescent) 1880: 15 minutes of work (kerosene lamp) 1800: 6 hours of work (candle) Source: Matt Ridley What was the Industrial Revolution? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3Efq-aNBkvc When did it occur? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JhF_zVrZ3RQ Industrial Revolution Timeline 1763: Steam Engine 1793: Cotton Gin 1786: Steam Boat 1837: Morse Code/Telegraph 1829: Typewriter 1845: Sewing Machine What were the outcomes of the I.R.? Answers Huge migration of cities Factory system launched Mass production of goods Industrial capitalism Increased standard of living Expansion of democracy Power of ordinary people rises Increased leisure time Science and research stimulated Foreign markets for goods Why is it important? Answers Changed the world – forever! Industrialization destroyed workers’ independence Huge investments required to operate large businesses – modern capitalism Overproduction Monopoly power Unemployment Mass produced goods were cheaper Increased standard of living What was good about the I.R.? Answers Country and people became wealthier Child mortality decreased Literacy increased Life expectancy increased Overall health and wellbeing increased Workers received more political power Growing middle class What was bad about the I.R.? Answers Until regulation and laws were enacted, businesses created many externalities that included: Pollution Child – labor Work death/accidents Monopoly profits Political influence/corruption Workers lost independence When did it end? Answers There is no date certain. Many historians use different dates for different countries: England (1760 – 1880) USA (1800 – 1908) Many other countries are industrializing now! China India Vietnam What does it all mean? Answers Industrialization is good and bad. With regulation the bad can be managed. For industrialization to occur a power source is necessary Energy and GDP are perfectly correlated Energy must be – cheap, plentiful, reliable, dense, and scalable All countries of the world want to industrialize because it means more “stuff” for their citizens People want stuff – smartphones, jeans, cars, etc. Next time Impact of Industrial Revolution Communication/Transportation/Production/War Economics Politics Society/Culture/Quality of Life Backlash of Industrial Revolution Romanticism Marxism/Socialism Luddites Questions?