* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Box of Convention
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
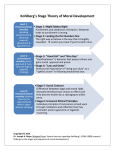
Beyond Inclusion, Beyond Empowerment The Box of Convention Every society sets expectations of appropriate behavior for adults, and socializes children learn to fit into those expectations. A certain range of skills is expected of adults in our culture. We are all trained to fit into them, and most of us manage to do this fairly well. The necessary skills include cognitive, moral, interpersonal, and self-management skills. We learn, for example, to follow directions (requiring cognitive and self-management skills), to obey traffic rules (cognitive, self-management, and ethical skills), and to participate in the give-and-take of mealtime conversational (cognitive and interpersonal skills as well as self-management). Following the work of Lawrence Kohlberg and Ken Wilber, we refer to this socially expected set of skills as Conventional, and the social expectations for these skills as the box of convention. Children are expected to be pre-conventional, but adults who use mainly pre-conventional skills are frequently in trouble with other people, the law, or the structures of daily life. (For example, an adult who has not mastered dominant social conventions about showing up on time will have problems with employers, and possibly friends as well.) Once we have adapted to this set of skills, no further development is expected or encouraged by society. In fact, if we show signs of developing beyond the conventional skill sets, we may encounter resistance and face losing relationships or our job. The box of convention pulls us up into it, but when we try to develop beyond its limitations, we encounter a kind of ceiling that limits our growth. The conventional skill set does not recognize post-conventional growth; from within the conventional expectations, both pre-conventional and post-conventional look “wrong.” An important dimension of our development is our moral awareness, and theorists such as Lawrence Kohlberg and Carol Gilligan have explored the process of developing moral awareness. At a Pre-Conventional level of moral awareness, our concern is with “me and mine,” and we may care about other people only insofar as they can impinge on our own desires. Preconventional means self-centric. As a person with Conventional moral awareness, we are likely to extend our care and awareness to people who we see as like us – members of our own family, nation, or other group – making us socio-centric. When we develop post-conventional moral awareness, our circle of care and concern expands to include “everyone,” all people, perhaps all beings everywhere, and we become world-centric in our moral awareness. Anti-oppression and liberation work call us to cultivate a post-conventional moral awareness – liberation work cannot grow from conventional morality. Developing anti-oppression skills beyond the double line – in both our Agent and Target memberships – means going beyond the box of convention. The fundamental stages of moral development identified by Kohlberg: Pre-conventional 1. Obedience and Punishment: How can I avoid punishment? Self-Centric Conventional 2. Individualism, instrumentalism, and exchange: What’s in it for me? 3. Good boy/nice girl: social norms 4. Law and Order Socio-Centric 4 1/2 Nonconformist conformity: I’m a rebel… Post-conventional 5. Social contract World-Centric 6. Principled conscience: universal ethical principles 7. Agape: heroism and sanctity, self-sacrifice This material is from a manuscript draft of Beyond Inclusion, Beyond Empowerment, with some help from Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kohlberg%27s_stages_of_moral_development Accessed October 27, 2009