* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Path of the Sun
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
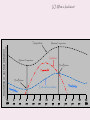
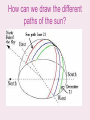
LO: How can we display the different patterns that the sun takes throughout the year? • Do Now: What is the intensity of insolation throughout the following dates: (High, Low, or Medium) – – – – January____________ December__________ March_____________ June______________ Relationship of Surface Temperatures to Insolation - Surface temperatures vary throughout each year and throughout each day. - These variations depend on a balance between energy gained from insolation and lost by Earth’s surface radiation. - More energy gained than radiated = temperatures rise. - More energy radiated than gained = temperatures decrease. Times of Yearly Maximum and Minimum Temperatures - The maximum intensity of insolation occurs on June 21st but the maximum temperatures occur in late July early August. - Between June 21st and the end of July the Earth is still gaining more energy than it is losing. - The minimum intensity of insolation occurs on December 21st but the minimum temperatures occur in late January early February. - Between December 21st and the end of January the Earth is still losing more energy than it is gaining. Times of Daily Maximum and Minimum Temperatures - The maximum intensity of insolation is at solar noon but the maximum temperatures occur between 2p.m. and 4p.m. - The Earth is still gaining more energy than it is losing from 12p.m. to 4p.m. LO: What is Insolation? 100 90 70 80 60 70 50 60 50 50 40 40 30 30 20 20 10 10 10 0 LO: What is Insolation? Insolation or surface radiation Temperature Maximum Temperature Insolation Minimum Temperature Heat Balance Heat Balance Earth surface radiation 12 Mid 2 am 4 am 6 am 8 am 10 am 12 pm 2 pm 4 pm 6 pm 8 pm 10 pm 12 Mid Seasons Direct causes of Seasons - Seasonal changes in weather conditions result from the cyclic variation in angle, intensity and duration of insolation throughout the year. - The seasons follow the shift in the 90° insolation between 23½°N and 23½°S. - This causes seasons to be opposite of each other in the northern and southern hemispheres. Astronomical causes of seasons Tilt of Earth’s axis -The Earth’s axis is tilted 23½° which causes the 90° insolation to shift between 23½°N and 23½°S. - If the tilt of Earth’s axis was more, the 90° insolation would reach farther north and south resulting in warmer summer and cooler winters. - If the tilt of Earth’s axis was less, the 90° insolation would not reach as far north or south resulting in cooler summers and warmer winters. Parallelism of Earth’s Axis - Regardless of Earth’s position in its orbit Earth’s axis always point in the same direction. - The north pole always point to the North Star (Polaris). Revolution of Earth Around the Sun - As the Earth revolves around the sun the tilt of the axis changes with respect to the sun. - June 21st Northern hemisphere tilted toward the sun. - December 21st Southern Hemisphere tilted toward the sun - March 21st + September 23rd Neither hemisphere tilted toward the sun. LO: What is Insolation? 50°N 0° 10°N 0° 50°S 23½° N 10°S 23½°N 0° 90° 90° 90° 23½° N 0° 23½°S 0° 23½° S 23½° 23½° S 23½°N 90° 0° 23½°S How can we draw the different paths of the sun? Summary • Complete the 4 Regents Questions on your sheet! LO: Heat Budget Lab Do Now: Copy the following definitions: 1)Analogy: comparison between two things. 2)Arbitrary: an unspecified value. 3)Deficit: having less than necessary. 4)Surplus: having more than necessary. 5)Radiative Balance: The relationship between the amount of energy reaching an object (or a portion of it) and the amount leaving it. A good example of this is our Earth receiving energy from the sun, and giving off energy into the near future.