* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Writing Linear Equations – 10 days Lesson Topics Objective
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
Recurrence relation wikipedia , lookup
History of algebra wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
System of linear equations wikipedia , lookup
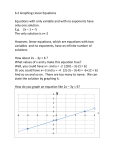
Writing Linear Equations – 10 days Lesson Topics Objective Slope Calculate slope given a graph. Calculate slope given two points. Example Problems Find the slope of the line. Common Core Standards 2008 State Standards MA09-S03-C04-01 Determine the slope and intercepts of the graph of a linear function, interpreting slope as a constant rate of change Find the slope of the line through the given points. 4, 5 and 5,10 Writing Linear Equations from a Graph Given the graph, write the linear equation. Write the equation of the line. MA09-S03-C03-03 Writing Linear Equations given two Points Write a linear equation from two points. Write an equation of the line that passes through each pair of points. (3,1) and (2,4) MA09-S03-C03-03 Write an equation given a table of values, two points on the line, the slope and a point on the line, or the graph of the line. Write an equation given a table of values, two points on the line, the slope and a point on the line, or the graph of the line. Writing Linear Equations given the slope and a point. Write linear equation given a slope and a point. Write an equation of the line that passes through (2,1) with a slope of 3 Rate of Change Calculate and interpret the average rate of change of a function over a specified interval. The average rate of change of a function y = f(x) over an interval [a,b] is . Basic Ex. 1 Use the following table to find the average rate of change of g over the intervals [-2, -1] and [0,2]: x -2 -1 0 2 g(x) 2 -1 -4 -10 Core Ex. 2 (Table to the right) The table below shows the elapsed time when two different cars pass a 10, 20, 30, 40 and 50 meter mark on a test track. o For car 1, what is the average velocity (change in distance divided by change in time) between the 0 and 10 meter mark? Between the 0 and 50 meter mark? Between the 20 and 30 meter mark? Analyze the data to describe the motion of car 1. o How does the velocity of car 1 compare to that of car 2? MA09-S03-C03-03 Write an equation given a table of values, two points on the line, the slope and a point on the line, or the graph of the line. HS.F-IF.6. Calculate and interpret the average rate of change of a function (presented symbolically or as a table) over a specified interval. Estimate the rate of change from a graph. Car 1 Car 2 d t t 10 4.472 1.742 20 6.325 2.899 30 7.746 3.831 40 8.944 4.633 50 10 5.348 MA09-S03-C04-02 Solve problems involving rate of change. Write Linear Equations in two or More Variables using Real-World Problems. Create equations in two or more variables to represent relationships between quantities. The cost of basic cable is $35 plus $8 per movie channel. Steve installs cable with "m" movie channels. What is the total cost “C” of his cable? HS.A-CED.2. Create equations in two or more variables to represent relationships between quantities; graph equations on coordinate axes with labels and scales. MA09-S03-C03-03 Write an equation given a table of values, two points on the line, the slope and a point on the line, or the graph of the line. MA09-S03-C02-04 Use equations, graphs, tables, descriptions, or sets of ordered pairs to express a relationship between two variables. These standards should be evident throughout the unit (may not be in each lesson). HS.A-REI.1: Explain each step in solving a simple equation as following from the equality of numbers asserted at the previous step, starting from the assumption that the original equation has a solution. Construct a viable argument to justify a solution method. HS.A-SSE.1: Interpret expressions that represent a quality in terms of its context. a. Interpret parts of an expression, such as terms, factors and coefficients. HS.A-SSE.1. Interpret expressions that represent a quantity in terms of its context.