* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download population
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
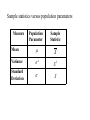
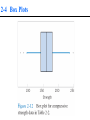
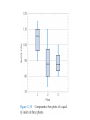
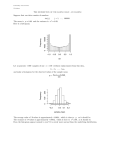
Statistics Descriptive Statistics Collecting, summarizing, and describing data Collect data ex. Survey Present data ex. Tables and graphs Characterize data ex. Sample mean Inferential Statistics Drawing conclusions and/or making decisions concerning a population based only on sample data Estimation ex. Estimate the population mean weight using the sample mean weight Hypothesis testing ex. Test the claim that the population mean weight is 120 pounds POPULATION A population consists of all the items or individuals about which you want to draw a conclusion. SAMPLE A sample is the portion of a population selected for analysis. PARAMETER A parameter is a numerical measure that describes a characteristic of a population. STATISTIC A statistic is a numerical measure that describes a characteristic of a sample. Sample statistics versus population parameters Measure Population Parameter Sample Statistic Mean X Variance 2 S2 Standard Deviation S 2-1 Data Summary and Display Sample Mean Population Mean For a finite population with N measurements, the mean is The sample mean is a reasonable estimate of the population mean. Sample Variance and Sample Standard Deviation Population Variance When the population is finite and consists of N values, we may define the population variance as The sample variance is a reasonable estimate of the population variance. The sample variance is The sample standard deviation is Percentile (= Quantile) • • For any whole number P (between 1 and 99), the Pth percentile of a distribution is a value such that P% of the data fall at or below it. The percent falling at or above the Pth percentile will be (100 – P)%. Quartiles • • • • Percentiles that divide the data into fourths Q1 = 25th percentile Q2 = the ” median ”= 50th percentile Q3 = 75th percentile 25% 25% Q1 25% Q2 25% Q3 Five-Number Summary of Data The five numbers that describe the spread of data are: Minimum First Quartile (Q1) Median (Q2) Third Quartile (Q3) Maximum Range = Maximum-Minimum Inter-quartile range IQR Q3 Q1 2-2 Stem-and-Leaf Diagram Steps for Constructing a Stem-and-Leaf Diagram 2-2 Stem-and-Leaf Diagram 2-2 Stem-and-Leaf Diagram Note: 1Minitab orders the leaves from smallest to largest on each stem 2The left column shows • a count of the observations at and above each stem in the upper half • a count of the observations at and below each stem in the lower half • at the middle stem (16), the number of observations at this stem. 2-3 Histograms A histogram is a more compact summary of data than a stem-and-leaf diagram. To construct a histogram for continuous data, we must divide the range of the data into intervals, which are usually called class intervals, cells, or bins. If possible, the bins should be of equal width to enhance the visual information in the histogram. Constructing a histogram • • • • Make a frequency table Place class boundaries on the horizontal axis Place frequencies or relative frequencies on the vertical axis For each class draw a bar whose width extends between corresponding class boundaries. The height of each bar is the appropriate frequency or relative frequency. 2-3 Histograms 2-3 Histograms 2-4 Box Plots • The box plot is a graphical display of the fivenumber summary of data. • Box plot describes several important features of a data set, such as center, spread, departure from symmetry, and outliers. • Outlier: an observation that lie unusually far from the bulk of the data 2-4 Box Plots 2-5 Time Series Plots • A time series or time sequence is a data set in which the observations are recorded in the order in which they occur. • A time series plot is a graph in which the vertical axis denotes the observed value of the variable (say x) and the horizontal axis denotes the time (which could be minutes, days, years, etc.). • When measurements are plotted as a time series, we often see •trends, •cycles, or •other broad features of the data 2-5 Time Series Plots Graphical Errors: Compressing the Vertical Axis Bad Presentation Quarterly Sales $ $ 200 50 100 25 0 0 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Good Presentation Quarterly Sales Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Graphical Errors: No Relative Basis Bad Presentation Freq. A’s received by students. 300 Good Presentations % 30% A’s received by students. 20% 200 100 0 10% 0% FR SO JR SR FR SO JR SR FR = Freshmen, SO = Sophomore, JR = Junior, SR = Senior