* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download v - UD Physics
Spectrum analyzer wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Spectral density wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Transmission line loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Chirp spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical filter wikipedia , lookup
Ringing artifacts wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Audio crossover wikipedia , lookup
Resonant inductive coupling wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Distributed element filter wikipedia , lookup
Analogue filter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
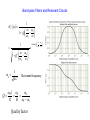
Topic 3: Op-Amp: Golden Rules of OP Amp 1. iin=0, no current flow into op amp. 2. V+=V• Typically one end of op amp is connected to ground, therefore, V+=V-= 0V, virtual ground. Often V+ is connected to ground to avoid stability problem. 3. Various circuits: amplifier, sum and abstract, differentiator, integrator, etc. Example • What does the following circuit do? That is, find an expression for the gain and give the circuit a suitable name. Example II (a) (7pts)The circuit is an integrate circuit. Derive vout(t). RS=10 kΩ, CF=0.008 µF. (b) (5pts)If the input signal vin=sin(2000πt) V, calculate vout(t) and the peak amplitude. (c) (3pts)If the input signal vin=10 mV, calculate vout(t) and vout(t=100ms) (d) (3pts)Op-amp is saturated when the output voltage reach the power supply voltage, ±15V in this case. At what time does the integration of the DC input cause the op-amp to saturated fully? (e) (7pts) If the input signal is now vin=0.01+ sin(2000πt) V, describe what happens to the output waveform till the op-amp is fully saturated. a. vout 1 vin dt 12500 vin dt RS C F b. vout 2 cos 2000t (V) c. vout (t ) 125t (V) vout (100ms) 12.5 (V) d. t 0.12( Sec) 120 ms e. vout (t ) 125t 2 cos 2000t Example 4 Design an op-amp circuit to convert the triangular waveform v1 in the following Figure into the square wave vo shown. Use 0.1 mF capacitor. (Hints: First quantitatively determine the mathematical expression of vo in terms of v1 ). v1(t) v0 RF CS dv1 dt 0.5 RF 0.1 106 RF 25k 0.2 1 103 Topic 4: Filters • Low-pass filters (LP) HV j V0 j V0 j Vi j ZC Vi j ZC Z R 1 jC HV j 1 R jC 1 1 e j0 j tan 1 RC 2 1 1 jRC 1 RC e 1 1 RC 2 1 1 RC 2 e j tan e 1 RC j tan 1 / 0 ; 0 1 RC Active Filter Vout ZF VS ZS It is phasor time again Vout ZF 1 VS ZS Active Low Pass Filter A( j ) Vout Z F VS ZS Z F RF || 1 RF jCF 1 jRF CF A( j ) RF / RS 1 jRF CF RF/RS=10, 1/RFCF=1 • Amplification: RF/RS • low pass factor 1/(1+jRFCF) • Cut off frequency: RFCF=1 Band-pass Filters and Resonant Circuits HV j 1 Q 2 0 0 1 LC 0 L R 1 jQ 0 0 1 0 Q 1 0 B 2 e arctan Q 0 0 Resonant frequency 0 2 1 Quality factor RLC Resonant when 0 L 1 C jL 1 jC Z L ZC I j V ( j ) Z R Z L ZC At resonance: • current is max. • Zeq =R • current and voltage are in phase. • the higher Q, the narrower the resonant peak. V 1 R j L C V V I 2 R 1 2 R L C Applications: tuning circuit Example a. Write the transfer function for this filter. (Both Vin and Vout are referenced to ground). H V vout R vin R 1 jC 1 1 j RC b). Design a high-pass RC filter with a characteristic frequency of 80 Hz using a capacitor of 2.0 mF. c). What is the new characteristic frequency when the filter is loaded with 50 ohm? 50 980 Req 47.6 1 1 50 980 RC 1 1 f 1.67kHz 6 R 980 2 47 . 6 2 10 2 80 2 106 How do you solve the problem: Use small R or use active filter A( j ) Vout Z F VS ZS RF RS 1 jCS RF 1 1 RS 1 jRS CS Example 2 The circuit shown in an active filter. Determine: The voltage transfer function. The pass-band gain. v v1 v+ RF Ri v v v 0 Ri Z c RF v0 v RF 1 v Ri jC v0 RF 1 1 v Ri 1 1 jRiC G 1 RF 68 1 14.6 Ri 5 Exam 3 The input signal can be written as Vi=10mV(sin10t+sin10,000t). Design a circuit so that the output signal is V0=-100mVsin10t. In another words, the high frequency signal has to be much smaller (<1%) than the low frequency part. A( j ) Vout RF / RS VS 1 jRF CF Low frequency RF 100 10 RS 10 1RF C F 1, let' s say : RS 1k; RF 10k high frequency RF / RS 1 1 j2 RF CF 10 1 1 2 RF CF 2 1 100 2 RF CF 100 CF Check low freq. 100 1mF 10 104 4 1RF CF 10 104 106 0.1 1 Topic 5: Electromachine • Motion Electricity (generator): Magnetic Induction, Faraday’s law • Electricity Motion (motor): force on a current, torque • Three phase power: structure, advantages.