* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SexSeln - life.illinois.edu
Sex and sexuality in speculative fiction wikipedia , lookup
Human female sexuality wikipedia , lookup
Sex in advertising wikipedia , lookup
Lesbian sexual practices wikipedia , lookup
Slut-shaming wikipedia , lookup
History of human sexuality wikipedia , lookup
Rochdale child sex abuse ring wikipedia , lookup
Female promiscuity wikipedia , lookup
Human male sexuality wikipedia , lookup
Sexual ethics wikipedia , lookup
Sexual attraction wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Body odour and sexual attraction wikipedia , lookup
Human mating strategies wikipedia , lookup
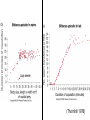
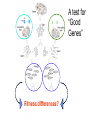
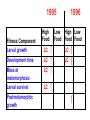
Extra credit question Sexual selection theory predicts that ___________ pipefish should compete with each other for access to mates, and that ___________ will be the choosy sex. Darwin’s Problem If selection favors alleles that increase survival and reproduction, how does one explain conspicuous traits such as bright colors, horns, and displays of many species that seemingly lower survival of the bearers? Darwin’s Solution: Sexual Selection Selection that arises from differences in mating success (# of mates that bear progeny over a defined time interval). Natural Selection Ecological selection Sexual selection Sexual Selection Arises because one sex is a limiting resource for the other sex Q: How can one sex be a limiting resource for the other? Q: Which sex will be a limiting resource? Q: Can both sexes be a limiting resource? Butterflies Pipe fish Giant Water Bug Midwife Toad Types of Sexual Selection Intrasexual Contests between members of one sex for access to members of the other sex Intra-sexual selection Types of Sexual Selection Intersexual Selection via mate choice: Individuals of one sex preferentially mate with individuals of the other sex based on particular phenotypes (size, color pattern, behavior, etc.) Intersexual Selection Sexually selected behavior http://tolweb.org/tree/eukaryotes/animals/arthropoda/arachnida/araneae/salticidae/++salticidae/movies/spiderdances.html Artificial head feather in zebra finches Why do these preferences exist? 1. Direct Benefits 2. Indirect Benefits 3. Sensory Bias Direct benefits: hanging flies and scorpion flies (Thornhill 1976) Direct benefits cannot explain mate choice when one sex provides nothing except gametes • Indirect Benefits Models • Good genes: females prefer traits that indicate genetic quality; high-quality mates pass on ‘good genes’ to their offspring. Runaway: females prefer arbitrary traits; preference for arbitrary traits leads to ‘runaway’ process. • Indirect Benefits: Good Genes Females prefer traits that indicate genetic quality; high-quality mates pass on ‘good genes’ to their offspring. Females choose based on some trait that indicates high fitness. Assumption: both trait and fitness must be heritable, (h2 > 0). A test for “Good Genes” Fitness differences? 1995 Fitness Component Larval growth High Food 1996 Low High Low Food Food Food LC LC Development time LC LC Mass at metamorphosis Larval survival LC Postmetamorphic growth LC Fitness Component Larval growth LC Development time LC Mass at metamorphosis Larval survival LC LC Indirect Benefits: Runaway Females Males Genotypes P1 (no preference) P2 (preference) T2 (no trait) T2 (trait) P2 females tend to mate with T2 males. P1 females mate randomly. Offspring of P2 females inherit both T2 & P2, ==> “genetic correlation” between preference & trait. T2 males have higher mating success than T1, so T2 increases in frequency. P2 increases in freq b/c it is co-inherited with T2. Elaboration (runaway) of trait & preference until mating advantage of trait outweighed by survival cost. Sensory bias Preference for a trait may be a by-product of the sensory system that has adapted to be sensitive to certain kinds of signals for reasons that are unrelated to mating. Guppies Swordtails Zebra finch Genus Xiphophorus Male swordtail Male platy Natural Selection Ecological selection Sexual selection Tradeoffs between natural and sexual selection