* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Big Bang
James Webb Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Space Interferometry Mission wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Shape of the universe wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Fine-tuned Universe wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Ultimate fate of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe wikipedia , lookup
Expansion of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Dark matter wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic microwave background wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Flatness problem wikipedia , lookup
Observable universe wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
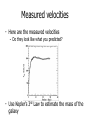
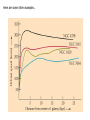
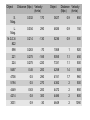
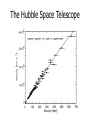
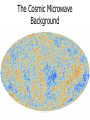
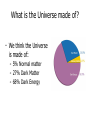
What is the Universe Made of? Scales in The Universe • If the Earth were the size of a golf ball, how far away would the Sun be? • How far away would Neptune be? • How far away would the nearest star be? Kepler’s Laws 1. All planets orbit in ellipses with the Sun at one focus 2. The orbit draws out equal areas in equal times. 3. The square of the period is proportional to the cube of the radius These apply to all orbiting bodies, not just planets... Circular Orbits • Centripetal acceleration • Gravitational force • Newton’s 2nd Law 2 v a r GMm F 2 r F ma Moon Radius of Orbit Period of Orbit (km: all nearly circular) (days) Io 4.22 x 105 1.77 Europa 6.71 x 105 3.55 Ganymede 1.07 x 106 7.15 Callisto 1.88 x 106 16.69 GM v r 2 Finding Dark Matter • Use Kepler’s 3rd Law to predict the velocities of stars around the centre of a galaxy: – – – – Mass of Galaxy = 28 billion solar masses 30 1 solar mass = 2x10 kg -11 3 -2 -1 G = 6.67x10 m s kg 16 1 light year = 10 m Measured velocities • Here are the measured velocities – Do they look like what you predicted? • Use Kepler’s 3rd Law to estimate the mass of the galaxy What is Dark Matter? • It’s matter that’s not visible, but can only be detected by its gravitational effects – Best theory is that it is an exotic particle – If it is what we think it is, we might be close to finding it! Here are some other examples… Expansion of the Universe • In 1929 Edwin Hubble found link between distances to galaxies and their radial velocities • Plot Hubble's data Object Distance (Mpc) Velocity (km/s) Object Distance Velocity (Mpc) (km/s) Hubble's Data 0.032 170 3627 0.9 650 L. Mag. 0.034 290 4826 0.9 150 N.G.C.6 822 0.214 -130 5236 0.9 500 598 0.263 -70 1068 1 920 221 0.275 -185 5055 1.1 450 224 0.275 -220 7331 1.1 500 5457 0.45 200 4258 1.4 500 4736 0.5 290 4151 1.7 960 5194 0.5 270 4382 2 500 4449 0.63 200 4472 2 850 4214 0.8 300 4486 2 800 3031 0.9 -30 4649 2 1090 S. Mag. The Hubble Space Telescope The Hubble Space Telescope The Cosmic Microwave Background The contents of the Universe • We currently think the Universe is composed of three constituents: – Normal matter (“atoms”) – Dark Matter – Dark Energy • To find out how much of each, we need to look at the evidence Heavens’ Kitchen • Choose your ingredients – Total Matter, Normal Matter, Dark Energy • How does the Cosmic Microwave Background Compare? • When did Galaxies form? • How to the galaxies compare? What is the Universe made of? • We think the Universe is made of: – 5% Normal matter – 27% Dark Matter – 68% Dark Energy The Planck Satellite • • • • • • 4x4x4m 2 tonnes on launch 2m mirror Cooled to 0.1K 2 instruments 300-10000 microns All sky (visible) DSS www.chromoscope.net All-sky (microwave) Planck