* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geothermal Presentation
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
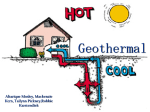
GEOTHERMAL ENERGY Veronica Boyer - Geology 100 Web - Spring 2012 GEOTHERMAL ENERGY Geothermal Greek roots: geo (earth) and therme (heat). Meaning “Earth's heat”. Is thermal energy generated and stored in the earth. Thermal energy is the energy that determines the temperature of matter. Originates from from the original formation of the planet 20% and from radioactive decay of minerals. 80%. Geothermal gradient is the difference in temperature between the core of the planet and its surface, drives a continuous conduction of thermal energy in the form of heat from the core to the surface. Inner Earth´s heat - Result of radiactive decompose of elements in rocks, which continuously regenerates this heat, for this reason, geothermal energy is a renewable energy resource. Geothermal Energy has huge potential because is 50,000 times bigger from all energy that can be gained from oil and coal accross the world. Geothermal resources are located from shallow surface to couple of kms deep reservoirs of hot water springs, wells and geysers, which could be brought to surface and there exploited. Water or steam - Medium that is transfering heat from inner core to surface, since heat is always transferring from hotter to colder parts, this heat is the major mover of tectonic plates. Temperature rises 50-87°F every one mile deeper from the earth´s crust. The mantle composed of partly melted rocks has a temperature of 1200-2800°F and Earth´s core of 7200-12600°F. USES: - For millenniums for recreational-sanative bathing. - Now, for generating electricity and as the central heating of households and buildings. ELECTRICAL ENERGY PRODUCTION - Hot water and steam from earth is used for initiation of generators - 1911 in Larandello - First geothermal power station with power of 250Kw - Well developed geothermal systems are located in geologically active areas with continuous, concentrated heat flow to the suface. - Geothermal facilities must use of a closed loop system at all times or the re-injection of water back into the system for constant steam generation. DISADVANTAGES: - Not many places are suitable for exploiting. - Best areas are on the edges of tectonic plates located on the ring of fire. Ring of fire (area with high volcanic and tectonic activity) TYPES OF GEOTHERMAL POWER STATION - Dry Steam - Extremely hot steam, above 445°F runs generatos Ex. - Larandello´s first station & Geysers in California since 1960 - Flash Steam - Hot water from reservoirs under great preassure avobe 360°F Water transformed onto steam decreasing preassure Steam directed to start turbines. Water returns to reservoir. Most modern power stations use this principle. - Binary Cycle - Hot water used to heat a liquid with low boiling temperature Liquid is exhausted on temperature of the hot water Starts generator turbines, water returns to reservoir - Min water loss Newly stations will use this principle. - Fish breeding OTHER USES OF GEOTHERMAL - Heating Buildings - The largest system is located on Iceland. - Heat pumps - For circulation of geothermal liquid for heating, cooling, cooking and water heat. - Agriculture For increase of the crop at greenhouses - Balneology Hot springs bathing for healing and recreation ADVANTAGES - In this processes, there is no combustion of fossil fuels - No harmful emissions of gases to the atmosphere - Only water steam gets released - Water is returned to reservoirs - Could soften pressure on fossil fuels helping earth recover from dangerous greenhouse gases. EARTH ENERGY Type of Geothermal Energy “Heat pumps” - Used commercially - Extracted through heat pumps - Heat contained in shallow ground (Upper 10’ of the earth) is used to directly heat or cool houses since the temperature inside the ground tends to stay at the yearly average. - On winter ground is warmer than the air. On summer, ground is cooler than the air. - This system (Ground heat exchanger) acts as an air conditioner. - The shallow ground mantains a nearly constrant temperature between 50° - 60° F - Consists of a heat exchanger (loop of pipes) buried in the shallow ground near the building. A fluid (water or mixture of water-antifreeze) circulates through the pipes to absorb or relinquish heat within the ground. EARTH ENERGY Advantages: - Could be utilized anywhere - Could also be used to heat water - Reduces the reliance on other resources. - Significant environmental benefits and reduced energy costs - No active technology is more efficient than the “Geothermal heat pump” WHY WE DON’T USE THIS SYSTEMS MORE - Fields of sufficient quality to produce economic electricity are rare. - Many fields are located in protected wilderness areas that enviromentalists preserve. - There is a need to harvest geothermal power through non traditional means, such as deep crustal drilling or the acquisition of heat from magma to preserve those scarce fields. - There is a an enviromental concern - Some applications produce carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide emissions and dispose of toxic waste and dissolved solids. - There is a very large geothermal resource in the world, much of which can not yet be economically used. - Our current technology is not sufficient or economical enough to warrant its widespread use. - Funding for energy extraction that involves the penetration of magma is not available because we don’t kow how to prevent a high-temperature, high pressure blowout. - Heat pumps can help reduce bill by $1 per day, not economically viable. Payback period longer than 5 years. - Earth energy is not intense enough to produce power for the electrical distribution grid, it only reduces the drw from the grid. RENEWABLE ENERGY PRODUCTION BY STATE REFERENCES 1. http://energy.gov/science-innovation/energy-sources/renewable-energy/geothermal 2. http://geothermal.marin.org/index.html 3. http://www.geo-energy.org/ 4. http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/rea/tech/geothermal-energy 5. http://www.altenergy.org/renewables/geothermal.html 6. http://www.our-energy.com/geothermal_energy.html 7. http://energy.gov/maps/renewable-energy-production-state 8. http://greenlaurier.ca/wp-content/uploads/2010/10/GEOTHERMAL-system-in-house.jpg THANKS!