* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MBA MKT MAN - CH15
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Predictive engineering analytics wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
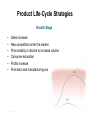
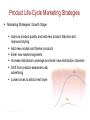
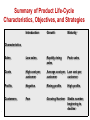
New Market Offering CH15 Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 1- slide 1 New-Product Development Reasons for new product failure Overestimation of market size Poor design Incorrect positioning Wrong timing Priced too high Ineffective promotion Management influence High development costs Competition Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 1- slide 2 New-Product Development Process Major Stages in New-Product Development Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 1- slide 3 New-Product Development Process Idea Generation Idea generation is the systematic search for new-product ideas Sources of new-product ideas • Internal • External Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 1- slide 4 New-Product Development Process Concept Development and Testing Product idea is an idea for a possible product that the company can see itself offering to the market Product concept is a detailed version of the idea stated in meaningful consumer terms Product image is the way consumers perceive an actual or potential product Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 1- slide 5 New-Product Development Process Marketing Strategy Development • Marketing strategy development refers to the initial marketing strategy for introducing the product to the market • Marketing strategy statement includes: – Description of the target market – Value proposition – Sales and profit goals Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 1- slide 6 New-Product Development Process Marketing Strategy Development Business analysis involves a review of the sales, costs, and profit projections to find out whether they satisfy the company’s objectives Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 1- slide 7 New-Product Development Process Marketing Strategy Development Product development involves the creation and testing of one or more physical versions by the R&D or engineering departments • Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Requires an increase in investment Chapter 1- slide 8 New-Product Development Process Marketing Strategy Development Test marketing is the stage at which the product and marketing program are introduced into more realistic marketing settings Provides the marketer with experience in testing the product and entire marketing program before full introduction Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 1- slide 9 New-Product Development Process Types of Test Markets Standard test markets Controlled test markets Simulated test markets Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 1- slide 10 New-Product Development Process Marketing Strategy Development When firms test market • New product with large investment • Uncertainty about product or marketing program Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall When firms may not test market • Simple line extension • Copy of competitor product • Low costs • Management confidence Chapter 1- slide 11 New-Product Development Process Marketing Strategy Development Commercialization is the introduction of the new product • • • When to launch Where to launch Planned market rollout Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 1- slide 12 Managing New-Product Development Successful new-product development should be: • Customer centered • Team centered • Systematic Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 1- slide 13 Managing New-Product Development New-Product Development Strategies Customer-centered new product development focuses on finding new ways to solve customer problems and create more customer satisfying experiences • Begins and ends with solving customer problems Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 1- slide 14 Managing New-Product Development New-Product Development Strategies Team-based new-product development is a development approach where company departments work closely together in crossfunctional teams, overlapping in the productdevelopment process to save time and increase effectiveness Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 1- slide 15 Managing New-Product Development New-Product Development Strategies Systematic new-product development is an innovative development approach that collects, reviews, evaluates, and manages new-product ideas • • Creates an innovationoriented culture Yields a large number of newproduct ideas Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 1- slide 16 Product Life-Cycle Strategies • Product development – Sales are zero and investment costs mount • Introduction – Slow sales growth and profits are nonexistent • Growth – Rapid market acceptance and increasing profits. • Maturity – Slowdown in sales growth and profits level off or decline • Decline – Sales fall off and profits drop Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 1- slide 17 Product Life-Cycle Strategies Introduction Stage • Slow sales growth • Little or no profit • High distribution and promotion expense Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 1- slide 18 Product Life-Cycle Strategies Growth Stage • • • • • • Sales increase New competitors enter the market Price stability or decline to increase volume Consumer education Profits increase Promotion and manufacturing costs gain economies of scale Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 1- slide 19 Product Life-Cycle Marketing Strategies Marketing Strategies: Growth Stage Improve product quality and add new product features and improved styling Add new models and flanker products Enter new market segments Increase distribution coverage and enter new distribution channels Shift from product-awareness advertising to product-preference advertising Lower prices to attract next layer of price-sensitive buyers Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 1- slide 20 Product Life-Cycle Strategies Maturity Stage Slowdown in sales, Many suppliers, Substitute products Overcapacity leads to competition Increased promotion and R&D to support sales and profits Marketing Strategies: Maturity Stage Market Modification Expand number of brand users by: 1. Converting nonusers 2. Entering new market segments 3. Winning competitors’ customers Convince current users to increase usage by: 1. Using the product on more occasions 2. Using more of the product on each occasion 3. Using the product in new ways Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 1- slide 21 Product Life-Cycle Strategies Decline Stage Maintain the product, Harvest the product or Drop the product Marketing Strategies: Decline Stage 1. Increase firm’s investment (to dominate the market and strengthen its competitive position) 2. Maintain the firm’s investment level until the uncertainties about the industry are resolved. 3. Decrease the firm’s investment level selectively by dropping unprofitable customer groups, while simultaneously strengthening the firm’s investment in lucrative niches 4. Harvesting (“milking”) the firm’s investment to recover cash quickly 5. Divesting the business quickly by disposing of its assets as advantageously as possible. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Chapter 1- slide 22 Summary of Product Life-Cycle Characteristics, Objectives, and Strategies Introduction Growth Maturity Sales Low sales Rapidly rising sales Peak sales Costs High cost per customer Average cost per customer Low cost per customer Profits Negative Rising profits High profits Customers Few Growing Number Characteristics Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Stable number beginning to decline Chapter 11-23 1- slide 23