* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Question: How does a radiographic image get on a film?
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
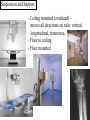
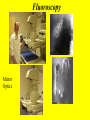
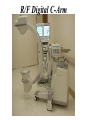
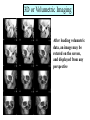
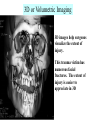
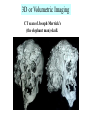
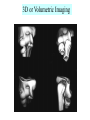
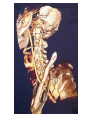
Introduction to RDSC 235 Chapter 5, pp 88-91 (To “Power for…”) Two types of equipment to generate x-rays Diagnostic – To find disease Therapeutic (Radiation Therapy) – To treat disease Two types of diagnostic equipment Radiographic – Still images: single or serial Fluoroscopic – In motion Patient’s head on your left Tables Table tops: - Radiolucent – x-rays pass through readily - Made of bakelite or carbon graphite fibers - Flat or curved (curved for fluoro) - Adjustable (height) - Compression band (accessory) Tables - Fixed or tilting – Tilting 90-15. Tilting on fluoro units - Footboard – removable - Hand grips/shoulder supports - Tops are floating (rad) or motorized (fluoro) Tables - Bucky tray - Automatic Exposure Control (AEC) Collimator: Positioning light & shutters for beam restriction Suspension and Support - Ceiling mounted (overhead) – moves all directions on rails: vertical longtitudinal, transverse, - Floor to ceiling - Floor mounted Upright film holders - Upright bucky (cassette holder). Used in radiograph rooms instead of tilting tables - Detent – Lock for aligning the tube and film (detector) Parts of a Fluoroscope Vidicon or Plumbicon Camera (or CCD if digital) Reflecting or beam splitting Mirror Spot Film Camera Image Intensifier (II) Spot Film Device X-ray tube under table Fluoroscopy Mirror Optics Fluoroscopy (Radiographic Fluoroscopic or R/F) Mobile radiography (Portables) ER OR ICU Neonatal ICU Any room, any floor Nursing homes Prisons C-arms (Portable R/F) R/F Digital C-Arm Mammography Cardiovascular Interventional Technology (CVI) Cardiovascular Interventional A C-arm Fluoroscope Video camera Image intensifier Cine camera Patient table X-ray tube CCD II Computed Tomography (CT) X-ray tube and detectors (all digital) 3D or Volumetric Imaging After loading volumetric data, an image may be rotated on the screen, and displayed from any perspective 3D or Volumetric Imaging 3D images help surgeons visualize the extent of injury. This trauma victim has numerous facial fractures. The extent of injury is easier to appreciate in 3D 3D or Volumetric Imaging CT scan of Joseph Merrick’s (the elephant man) skull. 3D or Volumetric Imaging Extras