* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Science 9 Environmental Chemistry Chemicals in the Environment
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
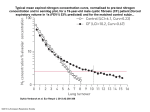
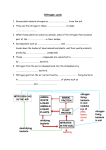
Science 9 Environmental Chemistry Chemicals in the Environment The environment is made up of chemicals that can support or harm living things: ◦ Essential Chemicals: Water Air Human activities can also cause chemical changes in the environment Recall that are cannot be broken down Chemicals are necessary for life but can also be harmful to the environment which To constantly the energy in an ecosystem, chemicals must be through living organisms and their environment. Nitrogen, and are the most important elements recycled through organisms and their environment The Nitrogen Cycle: Free nitrogen is converted ( ) to form nitrogen compounds which are then available to plants Lightning, and supply nitrogen to plants which are then eaten by animals. Bacteria live in with . Steps Recap: Farmers and Nitrogen The Carbon Cycle In the carbon cycle, things and back to the environment Steps: The Water Cycle: passes from the environment into living Pollution: Any Can be caused by in the environment that is harmful to living things or processes. Fertilizers: Natural or Numbers mean potassium (sulfur) Example: 5-10-15 chemicals used in soils for plants to grow of , What do these numbers really mean? Over-application can lead to environmental problems (crop damage, etc.) Pesticides: Pest = organism which harms people, crops or structures Herbicides Insecticides Fungicides Improper use of environment DDT: can be harmful to living things & the , Solid Wastes: Landfill and incinerators are used to deal with the wastes humans produce. Wastewater: Sewage moves to a treatment plant (or septic tank) it is treated and the is released. Effluent: Street drains go directly to rivers/lakes therefore any oils, go into the , detergents . Wastewater Treatment: Wastewater left untreated becomes a breeding ground for harmful bacteria The treatment process involves three stages: , biological and chemical 1) Physical: 2) Biological: sewage material is by the action of 3) Chemical: are added to remove and Fossil Fuels: Coal, oil and natural gas are called are formed from Hydrocarbons are very important in our lives Examples of Hydrocarbons: Burning fossil fuels is part of the cycle because they . and part of the C-O Electrical Energy Most of our electricity comes from generators Dirty Fuels: Fossil fuels can have many other compounds mixed in with them including sulfur, mercury and . Sour gas is that has a high content so the must be Sweet gas has no Recap: So What’s the Big Deal? Your Task: Read pages 180-190 and take relevant notes Do Check and Reflect page 190 ◦ Questions: 1-9, 11 It is very important that you put some thought into question 11 as this will be the focus of our next class Questions: 1. Lightning that occurs during thunder storms is beneficial because it replaces nutrients in soil. This is part of the a. Nitrogen cycle b. Carbon cycle c. Water cycle d. Energy cycle 2. Carbon dioxide is put back into air during the process of a. Transpiration b. Photosynthesis c. Respiration d. Precipitation 3. Draw a simple diagram of the nitrogen cycle. 4. Farmers occasionally plant alfalfa and sweet clover legume crops to build up the nutrients in their soil. Explain how alfalfa plants build up the nutrients in the soil. 5. A bag of fertilizer has the label 16-20-5 On the chart below, indicate what elements each number represents and say what that element does- its nutrient value- to ensure a healthy plant Label Number 16 Element Nutrient Value 20 5 6. DDT, a pesticide used to control the mosquito population in the mid 1900’s was banned 30 years later. Explain why it is no longer used as an insecticide. 7. What are the steps in sewage treatment? Indicate what happens in each of the three steps of the process and how the term “effluent” fits into the process.