* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
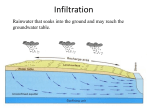
Download variation of steady state infiltration rate with land use type
Crop rotation wikipedia , lookup
Soil erosion wikipedia , lookup
Terra preta wikipedia , lookup
Soil respiration wikipedia , lookup
Soil salinity control wikipedia , lookup
Surface runoff wikipedia , lookup
Soil food web wikipedia , lookup
Canadian system of soil classification wikipedia , lookup
No-till farming wikipedia , lookup
Soil microbiology wikipedia , lookup
Soil compaction (agriculture) wikipedia , lookup
th 4 July, 2013 Book of Abstracts of the Peradeniya University Research Sessions, Sri Lanka - 2012 Vol. 17 E.ENG.10 VARIATION OF STEADY STATE INFILTRATION RATE WITH LAND USE TYPE K. Sulakxan, S. Lavaniyan, C. A. Samsen, H. K. Nandalal Department of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University of Peradeniya The infiltration characteristics of soils under three different land use practices were studied in the premises of the University of Peradeniya, Sri Lanka. The land use practices considered were: turf area, forest area and shrub area. The study aimed at examining the effect of various land use types on infiltration and determining the degree of relationship between infiltration rates and selected soil properties under different land use types. The soil properties selected were initial moisture content, and results of sieve analysis test and Proctor compaction test. These results were used to determine the level of compaction and soil type. The experiment was arranged randomly in selected land use areas and was replicated thrice. The infiltration rates of the soils were measured using a double-ring infiltrometer. The soil samples from these areas were analysed for selected soil properties. It was found that the soil type of all these places was sandy clay loam. The results showed that forest area had the highest average infiltration rate of 31-48 cm/hr while the turf area experienced the least infiltration rate of 14-27 cm/hr; the infiltration rate in shrub area was 30-35 cm/hr. A negative correlation was found between the level of compaction and infiltration rate. Initial moisture content had less influence on steady infiltration rate and it only changed the time to reach the steady infiltration rate. 62