* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Properties of Light Lab Background
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
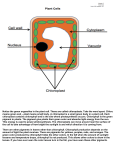
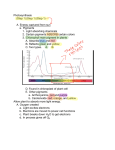
Properties of Light Lab Background The Electromagnetic Spectrum (Below) A very small part of this spectrum can be seen by the human eye i.e. between the wavelengths 380 and 750 nm. This part of the electromagnetic spectrum is called visible light. Almost all life depends ultimately on this part of A very small part of this spectrum can be seen by the human eye i.e. between the wavelengths 380 and 750 nm. the spectrum for its energy. Humans perceive the different wavelengths of visible light as different colors. Within the spectrum the longer the wavelength of the radiation, the slower the vibration of the photons and the less energy each photon contains. Thus photons of ultraviolet light, at the blue end of the visible spectrum, have shorter wavelengths and contain more energy than red light and infrared radiation. ** “rate of photosynthesis” line starts off above absorbance of chlorophyll line. Trace over the “rate of photosynthesis line GREEN. Sunlight contains 4% ultraviolet radiation, 52% infrared radiation and 44% visible light. Why is only visible light used by plants ? Light and photosynthesis. Chlorophyll does not absorb all the wavelengths of visible light equally. Chlorophyll a, the most important lightabsorbing pigment in plants, does not absorb light in the green part of the spectrum. Light in this range of wavelengths is reflected. This is the reason why chlorophyll is green and also why plants (which contain a lot of chlorophyll) are also green. Note in the graph above that the absorption of light by chlorophyll a is at a maximum at two points on the graph 430 and 662 nm. The rate of photosynthesis at the different wavelengths of visible light also show two peaks which roughly correspond to the absorption peaks of chlorophyll a. Plants do not depend only on chlorophyll a in their light harvesting machinery but also have other pigments (accessory pigments) which absorb light of different wavelengths What is an accessory pigment ? The most important pigment in the light harvesting machinery of a plant is chlorophyll, and more specifically chlorophyll a. However, plants do not rely on chlorophyll a alone, as their harvesting machinery contains other pigments as well. These pigments are often referred to as accessory pigments. What types of accessory pigments are there ? Chlorophyll b is very similar to chlorophyll a in structure and is blue green in color. Like chlorophyll a, it has absorption peaks in the red and blue ranges of the spectrum at wavelength 453 and 642 nm respectively. It occurs in all plants, green algae and some bacteria. Plants usually contain about half as much chlorophyll b as they do chlorophyll a. Carotenoids are a group of accessory pigments which occur in all photosynthetic organisms. They contain about forty carbon atoms, often without oxygen atoms and are fat soluble. They are chemically unrelated to chlorophyll and consist of rings connected by long chains of carbon atoms. They absorb light maximally at wavelengths between 460 and 550 nm and are therefore yellow, red or orange in colour as they reflect the wavelengths in this part of the spectrum. Carotenoids are found in all photosynthetic organisms. Other pigments There are other pigments which are also associated with the light harvesting machinery of plants. These include xanthophylls e.g. zeaxanthin (a yellow pigment) which absorbs red light, phycoerythrin (a red pigment) and phycocyanin (a blue pigment). (Many of these pigments are strong antioxidants ! Very good for you!!!! Ex. Blue berries, grapes, tomatoes, carrots, corn, etc… What role do the accessory pigments play in photosynthesis ? The accessory pigments play an important role in photosynthesis as they increase the range of wavelengths which the photosynthetic machinery of a plant can absorb. They thus tap sources of light energy which would otherwise be unused by the plant, if the plant relied only on chlorophyll a as a light harvesting pigment.