* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download UG/Photo
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
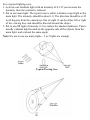
UG/Photo Hong Rujin 15, April High Quality Image Dialog View Visualization High Quality Image. Basic Procedure For High Quality Image Step 1 Select View Visualization High Quality Image Step 2 Select a Method to control the quality of the image Step 3 Import any materials that you might like for the image Step 4 Attach materials, textures, and finishes as needed to solids and surfaces in the view you are shading Step 5 Use the Assign Lights option to set light sources for the view, as needed. Step 6 Use Edit Visual Effects to set the foreground and background. Step 7 Use the Setup Shade option to set general shading parameters for the image. Step 8 Select the Start Shade option. Step 9 If desired, you can use the Save or Plot options to send the image to a system file or plotter. Activity: uge_shade_1.prt Importing and Exporting Features The Import filter allows you to selectively introduce new material, texture and light definitions to your Unigraphics part (done via system ASCII files). The Export filter allows you to write the same definitions to system ASCII files. Note: for Unigraphics you will find some predefined materials files: \ugs150\UGPHOTO\textures\*.lwi Attaching Materials and Textures Materials are defined as elements, alloys or compounds used in the construction of objects. They include such things as steel, copper and brass. Textures are defined as finishes, patterns or other characteristics that can be applied to a material. Textures for a finish include rough, brushed, eroded and cast. Setting up Light Sources for the View For a typical lighting case: 1. Activate one Ambient light with an intensity of 0.2. If you increase the intensity, then the contrast is reduced. 2. Put in one main light. The typical case is either a distant or spot light as the main light. The intensity should be about 1.0. The direction should be at 45 to 60 degrees from the camera/eye line of sight. It can be either left or right of the viewing line, and should be directed toward the object. 3. Put in one fill light of intensity 0.3 (to reduce the shadow darkness). This is usually a distant light located on the opposite side of the objects from the main light, and at about the same angle. Note:Try not to use too many lights - 2 to 3 lights are enough. Typical Viewing Case Using Setup For General Shading Parameters Advanced Setup Allow Transparent Shadows controls whether light passing through transparent and semi-transparent objects is accurately calculated. This option lets you have transparent shadows or colored shadows through transparent objects. Disable Raytracing This option turns off raytracing when generating an image. Raytracing is used to calculate reflections and refractions during image generation. Starting the Shade • Processing Geometry... Indicates that polygons are being generated for the Bodies in the model. • Processing Lights... Indicates shadows are being calculated. If the Setup option for Generate Shadows is not on, this step will be very quick. • Generating the Image... Indicates the process of generating the image data has begun. Process Shortcuts using the following key sequence: < Shift> <Ctrl> L Texture Spaces and Texture Mapping There are two basic types of textures that are supported in Unigraphics High Quality Shading: solid textures and wrapped textures. A solid texture is a three dimensional object. A solid texture gives the appearance that a shape has been carved out of a solid block of a particular material. A wrapped texture is a two dimensional object that is wrapped around a shape using a texture space. In general the most useful texture spaces are Auto Axis, Arbitrary Plane, Cylindrical and Spherical Auto Axis is used for any texture where orientation is not important, such as with the wrapped rough texture or a cast texture. Arbitrary Plane mapping is useful when the texture is intended for a planar or near planar surface and the orientation is important.For instance if you want vertical stripes on the side of a box, then use Arbitrary Plane as the texture space. Cylindrical and Spherical mapping are used for getting a better mapping on a curved surface, whether it is wrapping a logo around a can, or putting a world map on a sphere. Editing Materials, Lights and Textures Edit Visual Effects