* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download High Speed Electronics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
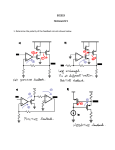
Class D amplifier: The current-switched class D amplifier with transformers Switch the constant current IDC rather than a constant voltage Like class B but!! CB1 => RFC so the centre tap carries a constant current IDC L0C0 => short harmonic currents Each primary winding carries half-sine collector voltages The class D amplifier with reactive load The reactance load causes phase shift between iO, vR Freewheel diode D1 & D2 All parasitic capacitance Cs at the switching node A is periodically charged and discharged, causing additional power loss that cannot be avoided Q2 is forced to source a current instead of sinking it Place external diodes (at horizontal FET’s) Output current divided by Charge left on CS is dissipated Class F amplifier with LC circuits Or biharmonic, poly-harmonic, class CD, class C with increased efficiency, single-ended class D, mutli-resonator Operates at very high frequencies Add one or more harmonic frequencies Current source during 180° For a given VOM the min. peak amplitude (= maximal flattening) when VCM3 = VOM / 9