* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download pediatrics
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
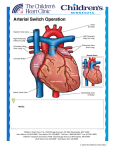
PEDIATRICS UNIT 2 History of Child Care •Colonial America •Industrialized America •Dr. Abraham Jacobi –Father of Pediatrics Pediatric Nursing - Purpose •Prevent disease or injury •Optimal health and development •Treat health problems The pediatric nurse •Keen observation skills •Conveys respect and honesty •Communication •Enjoys working with children •Teaches parents and children •Role model Special Needs Children •Congenital anomalies •Malignancies •Abnormalities •35% of hospitalized children Family Centered Care •24 hour visitation •Parental access to health information •Parents involved in decisions Growth and Development •Know normal to recognize abnormal •Illness, lack of stimulation affect G&D Anticipatory Guidance •To decrease anxiety, teach parents and children what to expect Physical Assessment •Use different skills for each age group •Growth assessment: •Ht or Length •WT.- Balance scale first •Head Circ.- up to 36 mo. Vital Signs •Resp.- always do first •1 full minute •< 6 yrs – abd breathers •Neonate – nasal breathers •Heart rate: •Apical rate up to 5 years •One full minute •Temperature: •Tympanic – most common for infant or small child •Rect., ax., oral •B.P.: •Sites: pg. 960 •Correct cuff size- covers 2/3 of upper arm Head to Toe Assessment •Head: •Circ. •Fontanel's •Eyes, nose, mouth •Lungs •Chest •Back •Abd. •Extremities •Genitalia •Renal Function •Bowel Function Factors Influencing G&D •Nutrition: •Most important influence on growing bones and muscles •0-6 mo. - Breast or bottle •6-12 mo.- breast/bottle, food •> 12 mo. – cows milk •In hospital serve high quality food when child is hungry •Metabolism: •Faster than adults •Heal faster •Rest and sleep: •Sleep less when older •Infant – 2 naps/day •Toddler/preschool – 1 nap/day •Communication: •Determined by stage of development The Hospitalized Child •Pre admission education varies by age •Anticipatory guidance – explain what to expect •Be honest to establish trust •Allow parents to stay •Developmental support: •Expect regression, • anger and •rejection Surgery •Age appropriate pre op teaching •Allow to verbalize fears Parent Participation •Review info from physician •Parents may not understand due to anxiety •Listen Pain Management •Anything that is painful to an adult is painful to a child •Observe for changes in behavior • PEDIATRIC PROCEDURES Bathing •Before a feeding •Prevent chilling •Only water on face Feeding • infants are nose breathers •burping •Solids: •Introduce at 4-6 mo. •Weaning: •Bedtime bottle removed last Safety Devices •Restraints: •Used as a last resort •Remove Q2 hours ot exercise body part Urine Collection •Urine collection bag •Cath specimen •Voided specimen Venipuncture •Position securely Lumbar Puncture •Side lying Oxygen Therapy •Hood •Mist tent •Nasal canula •Mask Suctioning •No more than 5 seconds I&O •Weigh all diapers Medication Administration •6 rights •Calculate safe dose •P.O. is preferred route •Review Safety Considerations •Use a syringe to measure exact dose •Aim toward side of mouth •Children are more susceptible to toxic effects of drugs than adults Injections •Vastus lateralis is preferred site until walking •Ventral Gulteal on children who are walking Ear gtts. •< 3 y/o pinna down and back •> 3 y/o pinna up and back Nasal gtts. •Head hyper extended over edge of bed Rectal •See box 30-11 •Less reliable •Suppository w/ jelly •Enema procedure same as adult Safety •Prevent accidents •See Table 30-12 for developmental safety hazards & prevention Child With A Physical Disorder •Children are not miniature adults •Care may differ from care for adults with the same disorder • Caring for the Pediatric Patient with a Cardiovascular Disorder Congenital Heart Disease •Present at birth •Majority are treated with surgery •10% of term neonates Etiology •Environmental •Genetic •Foramen Ovale and Ductus arteriosis close at birth 4 Types of CHD •Increased pulm. blood flow •Decreased pulm. blood flow •Obstruction to systemic flow •Mixed blood flow Clinical Manifestations •Cyanosis •Pallor •Cardiomegly •Murmurs •Additional heart sounds •Digital clubbing •Apical and radial pulse differences 1. Increased Pulmonary Blood Flow Defects • PDA Patent Ductus Arteriosis •ASD Atrial Septal Defect •VSD Ventricular Septal Defect PDA •Patent Ductus Arteriosis •Blood shunts from aorta to pulmonary artery •“Machine like” murmur ASD •Atrial Septal Defect •Opening in atrial septum •Murmur VSD •Ventricular Septal Defect •Murmur •50% close spontaneously •Remainder require open heart surgery •Dacron patch or close w/ sutures Decreased Pulm. Blood Flow Defects 1) Pulmonary Stenosis 2) Pulmonary Atresia 3) Tetrology of Fallot (most common) Tetralogy of Fallot consists of the following 4 defects: •Pulmonary artery stenosis •Ventruculoseptal defect •R. ventricular hypertrophy •Overriding aorta Signs & Symptoms •Profound cyanosis •Tet spells •Clubbing of nailbeds •Murmur •dyspnea •Squatting •Poor growth •syncope Surgical Treatment •Blalock-Taussig Shunt (temporary) •Closure of VSD •Pulmonic Valvotomy •Repair of overriding aorta Mixed Flow Defect •TGV – transposition of great vessels •S/S: severe cyanosis •Treatment surgical repair a) Palliative b) Complete OBSTRUCTIVE FLOW DEFECTS •Pulmonary Stenosis •Aortic Stenosis •Coartication of the Aorta •Treatment: surgical repair Coarctation of the Aorta •Narrowing of the aorta at the site of the ducturs arteriosus •Results in increased pressure to heard and arms and •Decreased pressure to lower extremities •BP in arms will be higher than in legs (upper extremity hypertension) Surgery •Remove the narrowed portion of the aorta and an end to end anastomosis or graft replacement if narrowing is extensive.