* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review Questions
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
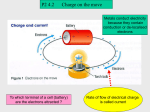
Student compiled review questions 1.) How many pathways does a series circuit have? A. 5 B. 2 C. 9 D. 1 2.) You can pick up static electricity by walking on a wool rug in leather-soled shoes. Explain why you are then negatively charged and what happens when you grab for a metal object such as a doorknob. You have been negatively charged by friction because you have picked up electrons from the rug. As you reach for a metal object, electrons will move from your body to the object because of their difference in electrical potential energy, and you will experience a mild shock. 3.) What’s Potential Difference? Potential difference is the work that must be done against electric forces to move a charge from one point to another. 4.) Potential difference is measured in volts? True or False? 5.) What is a superconductor? A conductor that provides zero resistance when it falls below a certain temperature 6.) Current is the flow of electricity True or False? 7.) Opposite charges repel True or False? 8.) If a circuit open its complete True or False? 9.) Switches open and close a circuit True or False? 10.) What causes resistance? What is it measured in? Internal friction. Measured in ohms. 11.) An open circuit is a pathway that in not connected, current cannot flow through? True or False? 12.) What do charged particles produce? a. protons b. electrons c. electric field d. magnetic field 13.) Electric field lines indicate a. direction only b. relative strength only c. both direction and relative strength d. neither direction nor strength 14.) Current is the rate at which charges move through a(n) a. conductor b. insulator c. voltage d. joule 15.) Batteries typically have a. two positive terminals b. two negative terminals c. one positive and one negative terminal d. no terminals 16.) What is charging by friction? Materials can be charged when two surfaces are in contact, and one surface transfers electrons to the other 17.) What is charging by contact? Objects without charge (neutral objects) can become charged if they are touched by a charged object 18.) Is the charge shown in the figure above positive or negative? Negative 19.) Why do electrical devices feel warm after they have been on for a period of time? Electrical devices feel warm because kinetic energy is transferred from moving electrons to surrounding materials, causing the atoms to vibrate 20.) What does a circuit breaker do? Automatically opens when the current gets too high 21.) Does the schematic diagram above represent a series or parallel circuit?